Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) predisposes for increased arterial stiffness(1). In hypertension, arterial stiffness is a powerful modulator of left ventricular (LV) geometry(2). Whether this is true in patients with RA is unknown.
Methods:
Echocardiography, clinical and laboratory assessment were performed in 134 RA patients without prior myocardial infarction or cardiac surgery and 102 healthy controls. Arterial stiffness was determined by echocardiography as pulse pressure/stroke volume indexed to height2.04 (PPSVi). LV geometry was evaluated by relative wall thickness (RWT) and LV mass, and considered concentric if RWT≥0.43.
Results:
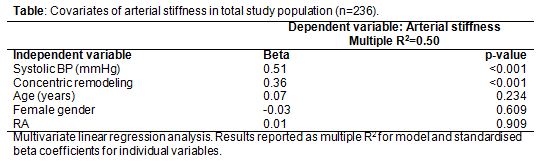
The RA patients were older, more often female, had higher blood pressure (BP) and PPSVi compared to controls (all p<0.05). In univariate analyses, higher PPSVi was associated with having RA, LV concentric remodeling, older age, and higher systolic BP (all p<0.001).In multivariate linear regression analysis, having RA was not directly associated with increased arterial stiffness, when adjusted for other variables (Table).
Conclusion:
In RA patients without established cardiovascular disease, increased arterial stiffness is mainly associated with higher systolic BP and concentric remodeling of the LV, pointing to the importance of BP control in RA patients.
References:
Disclosure:
H. Midtbø,
None;
E. Gerdts,
None;
I. C. Olsen,
None;
T. K. Kvien,
None;
E. Davidsen,
None;
A. G. Semb,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/arterial-stiffness-is-associated-with-abnormal-left-ventricular-geometry-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/