Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In psoriatic arthritis (PsA), there is a substantial life impact perceived by patients, although many treatments are now available at least in countries with access to more costly drugs (ref 1,2). Country of patient care, and in particular Gross Domestic Product (GDP) may be linked to PsA outcomes. The lack of large international registries has not up to now allowed any comparison of outcomes according to the country.
The objective was to explore potential differences in disease activity, disease impact and treatments across countries in PsA.
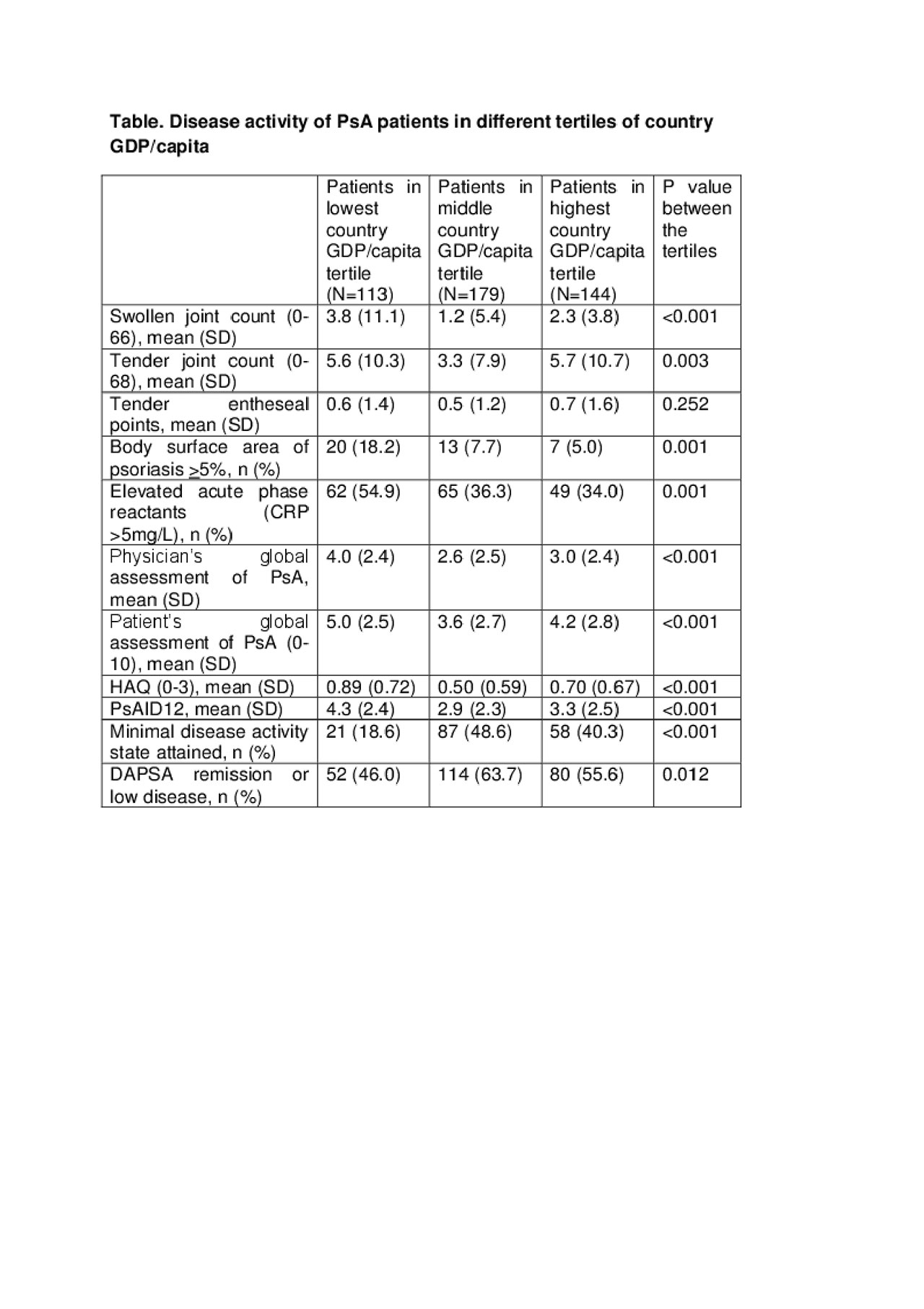
Methods: This was a cross-sectional analysis of an observational study (ReFlap, NCT03119805, ref3), which included adult patients with PsA with ≥ 2 years disease duration from 14 countries. Countries of inclusion were analysed separately, and classified into tertiles by GDP/capita (lowest tertile, Brazil, Turkey, Russia, Romania, Estonia; middle tertile: Spain, Italy, UK, France; highest tertile, Canada, Germany, Austria, USA and Singapore). Patient demographics, treatments prescribed (conventional synthetic DMARDs, biological DMARDs, glucocorticoids), disease impact (though patient global assessment, PGA, HAQ and the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease questionnaire, PSAID-12) and PsA disease activity (assessed through swollen and tender joint counts (of 66/68), CRP, entheseal points, psoriasis body surface area and the composite scores DAPSA and MDA) were analysed per coutrny and compared between the 3 tertiles of GDP/capita by non-parametric tests.
Results: Of the 466 patients, 436 had complete data available and were analysed: mean age 52.3 (SD 12.5) years, mean disease duration 10.1 (8.1) years, 218 (50.8%) male.
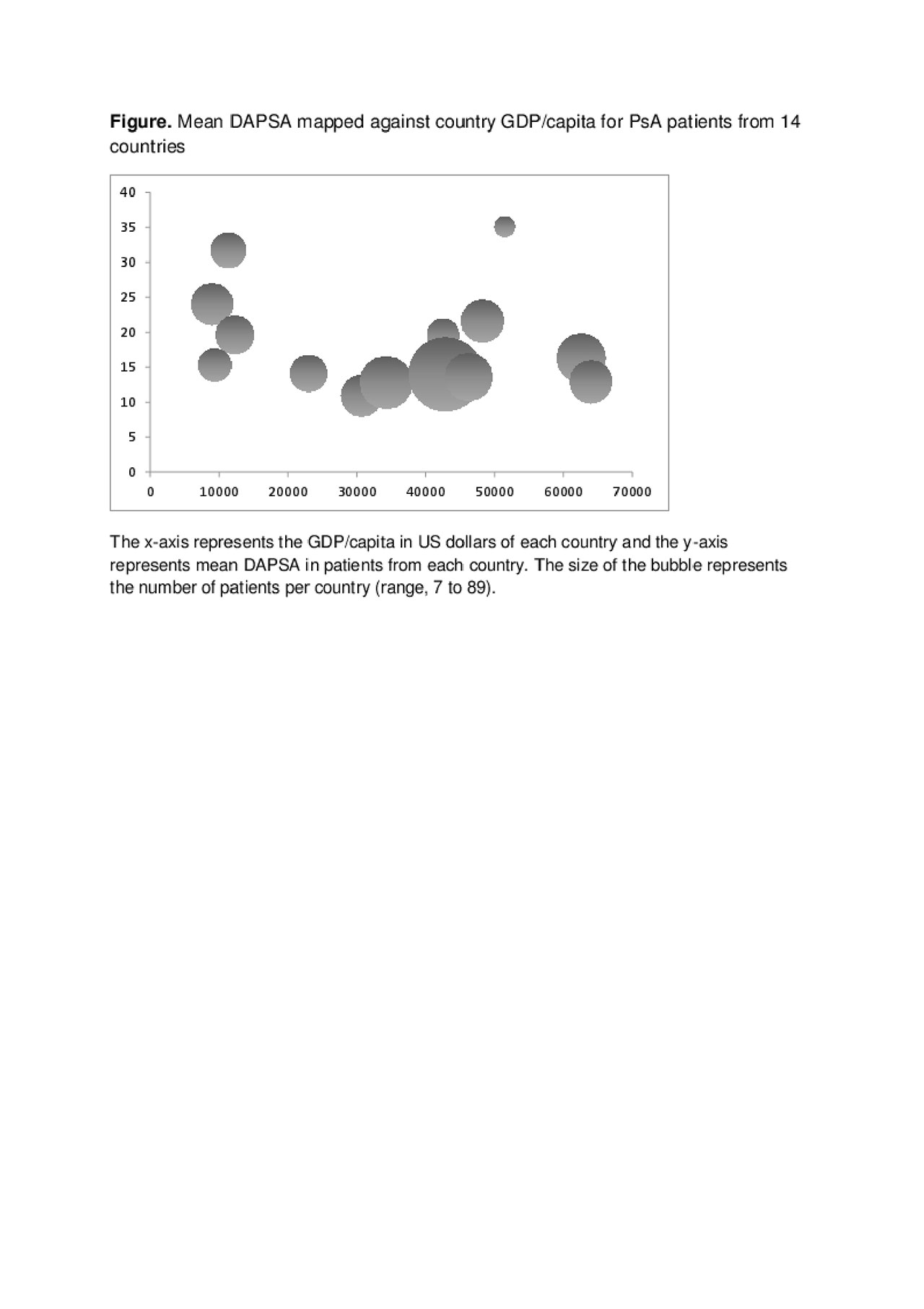
In countries with a lower GDP/capita, patients were slightly older, with a longer disease duration. There was a similar use of biologics (overall mean 60.5%) and of oral glucocorticoids (18.6%) but use of methotrexate was different (67.0% in the lowest GDP/capita tertile, versus 47.3% in the second and 53.4% in the highest tertile, p=0.007). Disease activity and impact were overall higher in the lowest GDP/capita countries (Table and Figure). The middle and highest GDP/capita tertiles had similar outcomes.
Conclusion: In this exploratory comparison of disease patterns and treatments choices in 14 countries, we relied on a relatively small and selected population from tertiary centers which is a limitation. We observed a similar use of biologics but more use of methotrexate in countries with a lower GDP/capita, though glucocorticoid use was similar. Both disease activity and disease impact appeared more important in the lower GDP/capita countries. This raises questions on the link between disease activity, disease impact, treatment choices and other (external) society and culture related elements such as lifestyle/diet or health care systems.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Cañete J, Orbai A, Leung Y, Palominos P, Scrivo R, Balanescu A, Dernis E, Talli S, Ruyssen-Witrand A, SOUBRIER M, Aydin S, Eder L, Gaydukova I, Coates L, Kalyoncu U, Richette P, Husni M, de Wit M, Smolen J, Lubrano E, Kiltz U. Are There Country Differences in Disease Activity and Life Impact of Psoriatic Arthritis? An Analysis of 436 Patients from 14 Countries [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-there-country-differences-in-disease-activity-and-life-impact-of-psoriatic-arthritis-an-analysis-of-436-patients-from-14-countries/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-there-country-differences-in-disease-activity-and-life-impact-of-psoriatic-arthritis-an-analysis-of-436-patients-from-14-countries/