Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Complete ankylosis of the entire spinal column is a severe condition seen in spondyloarthritis. This study aims to investigate the possible risk factors associated with the bamboo spine in axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients treated with biological DMARDs.
Methods: TReasure; is a multicentre database, started in December 2017, in which clinical and demographic data of inflammatory arthritis patients using biological and synthetic DMARDs are recorded (1). This database contains 4911 SpA patients using bDMARD therapy. axSpA patients fulfilling the ASAS classification criteria (Sacroiliitis defined either according to the mNY- or ASAS positive MRI criteria) were analyzed. Patients with complete cervical and lumbar x-rays were divided into three groups. Group-1 consists of patients with a bamboo spine, Group-2 consists of patients with bridging (advanced radiographic involvement) bridging of two vertebrae in a row, Group-3 consists of patients with syndesmophytes in at least one vertebra, and Group-4 consists of patients with no syndesmophytes. The demographic and clinical features of these patients were recorded. One hundred and ten patients were selected as a matched control group based on the disease duration of patients with a bamboo spine.
Results: Out of the 4911 patients in the TReasure database, sacroiliac joint MRI and/or cervical and lumbar lateral radiographs were available for 1381 patients. AS (1071, 77.6%), psoriatic arthritis (102, 7.4%), non-radiographic (144, 10.4%), peripheral SpA (128, 9.3%), enteropathic arthritis (39, 2.8%) in 1381 patient. The bamboo spine was seen in 111 (8.0%), bridging of two vertebrae in a row in 125 (9.0%), syndesmophytes in at least one vertebra in 329 (23.8%), and 816 (59.2%) had no syndesmophytes.
The comparison between the patients with a bamboo spine to those with no syndesmophytes revealed that; male gender (85.6% vs 61.8%, p < 0.001), age (51 (45-61) vs 43 (36-50), p < 0.001), BMI (27.9 (25.9-31.2) vs 25.9 (22.9-29.3) , p < 0.001), smoking as package/year (12.2 (1-30) vs 3 (0-11), p < 0.001), delay in diagnosis of SpA (61 (19-134) vs 12 (5-47), p < 0.001), hip involvement (53.7% vs 17.8%, p < 0.001), family history of SpA (40.8% vs 24.8%, p = 0.014), and uveitis (25.6% vs 13.6%, p = 0.030) were associated with bamboo spine.
Bamboo spine was less common in patients with peripheral arthritis (9.6% vs 21.3%, p = 0.019) and psoriasis (4.5% vs 12.7% , p = 0.031).
Disease activity (BASDAI) and functional status (BASFI) of both patient groups were similar before bDMARD treatment.
In multivariate analysis, male gender OR 9.3 (95% CI 3.2-26.9), hip involvement OR 4.2 (1.8-9.5), family history for SpA OR 2.9 (1.3-6.6), delay in diagnosis 1.013 (1.005-1.021), age 1.11 (1.06 -1.116) as a risk factor.
Conclusion: Male gender, delay in diagnosis, family history of SpA, and hip involvement is the most important risk factors associated with a bamboo spine in axSpA patients, after a disease duration of more than 15 years. Interestingly, the presence of peripheral arthritis and psoriasis were protective.
References:
1) Kalyoncu U, Taşcılar EK, Ertenli Aİ et al. Methodology of a new inflammatory arthritis registry: TReasure. Turk J Med Sci. 2018 Aug 16;48(4):856-861.
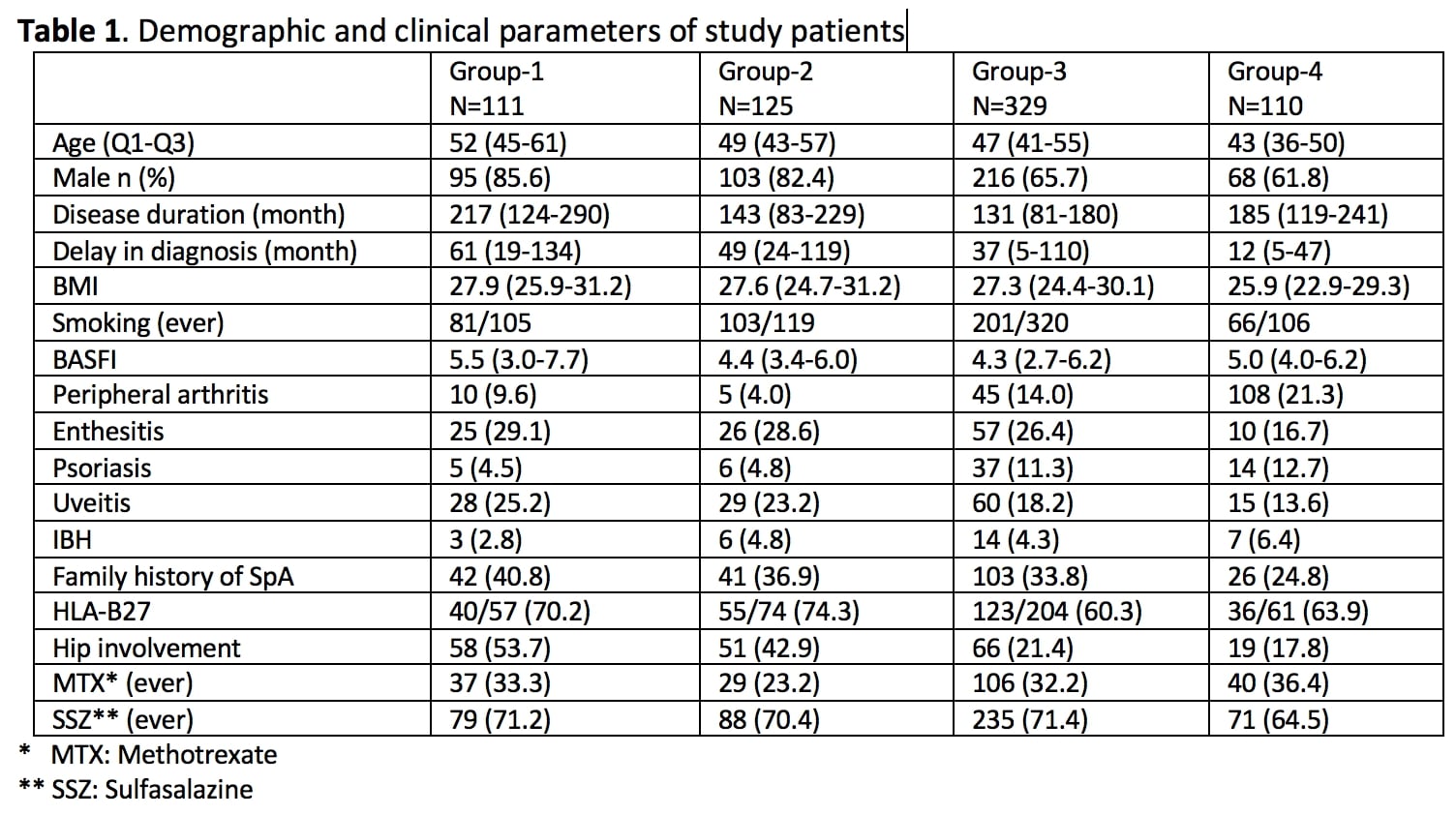 Table 1. Demographic and clinical parameters of study patients
Table 1. Demographic and clinical parameters of study patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Atagündüz P, Kiraz S, Akar S, Küçükşahin O, Erden A, Coşkun N, Yağız B, Bes C, Kılıç L, Karadağ �, Kaşifoğlu T, Emmungil H, Çınar M, Kimyon G, Yazısız V, Ates A, Ersozlu E, Gönüllü E, Mercan R, Ertenli �, Kalyoncu U. Are There Any Clues to Predict Bamboo Spine in Axial Spondyloarthritis? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-there-any-clues-to-predict-bamboo-spine-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-there-any-clues-to-predict-bamboo-spine-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/
