Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There is an increasing demand from patients for medical cannabis in the German population [1]. Although medical cannabis might be used to treat pain and reduce inflammation in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRD) in addition to the immunomodulatory therapy data regarding the prevalent use of and the interest in the treatment with medical cannabis is scarce. We investigated the knowledge of patients with IRD about medical cannabis and to evaluate patients’ attitudes towards the use of medical cannabis in a clinical trial (CT). The analysis included whether attitudes towards medical cannabis depend e.g. on medication, treatment satisfaction, pain levels and health status.
Methods: A digital survey was conducted via an App from Asepha [2]. Our outpatients either filled out the questionnaire in the clinic using a clinic owned iPad (Version 9) or participated using a QR code handed out leading to the survey via their mobile device. Patients answered the questions anonymously. The survey included sociodemographic data, and current pain and immunosuppressive medication. Patients’ willingness to consume medical cannabis in a CT was inquired. Concerns (e.g. fear of side effects, dependence on medical cannabis) that might prevent patients’ from participating in a CT were assessed. Descriptive data and a penalized ordinal regression (POR) were performed using R. Ethical approval was obtained, DRKS registration number is DRKS00030875.
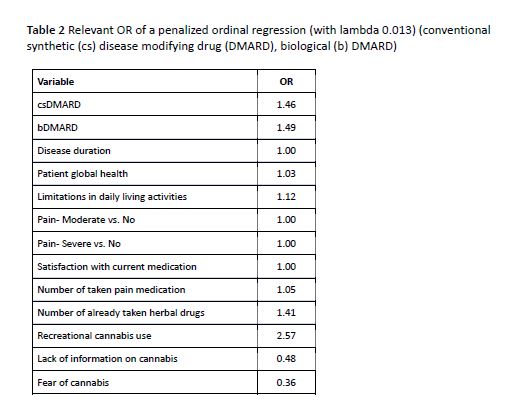
Results: Data were collected from 192 patients with IRD. Table 1 lists sociodemographic and clinical data. 70% were interested in the participation in a CT although of these 83% were satisfied with their current treatment. Mean number (± standard deviation) of taken pain medication was 0.8 (±0.9), mean number of taken herbal drugs was 0.6 (±1.0). Former recreational cannabis use increases the readiness to participate in a CT. Among those still undecided about taking medicinal cannabis in a CT, the main reason was the lack of sufficient information about cannabis (63%). Another relevant reason was fear of side effects (40%) and fear of cannabis (16%). The POR depicted that current cs- resp. bDMARD therapy, former recreational cannabis use, number of already taken herbal drugs, lack of information on cannabis, and fear of cannabis but not pain or satisfaction with the current medication significantly influence patients’ willingness to participate in a cannabis CT. Limitations in performing daily activities and patients global health status increase the willingness to participate in a cannabis CT, other OR are depicted in table2.
Conclusion: One third of IRD patients were interested in the participation in a CT with medical cannabis and additional 39% were potentially interested. Apart from current medication especially lack of information on cannabis and fear of cannabis were limiting factors. This demonstrates that patients’ education about medical cannabis is highly necessary to increase its acceptance and thus willingness to participate in a related CT. Cannabis trials are widely and significantly accepted by patients with a history of recreational use.
References [1] https://de.statista.com [2] https://www.asepha.com/
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Richter J, Beichert A, Filla T, Schneider M, Distler J, Frohne I. Are Patients with Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Ready for Studies with Medical Cannabis? – Results from a Digital Survey [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-ready-for-studies-with-medical-cannabis-results-from-a-digital-survey/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-patients-with-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-ready-for-studies-with-medical-cannabis-results-from-a-digital-survey/