Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Miscellaneous Aspects of RA (0786–0812)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment of early RA with DMARDs is associated with particularly effective responses, resulting in sustained beneficial outcomes, including clinical and radiographic remission and optimal health related quality of life. The benefit of treatment with biological (b) and targeted synthetic (ts) DMARDs on work participation (WP), a top social role for RA patients, has been less frequently studied. Our aim was to review the evidence of treatment with b-/tsDMARDs in patients with early RA on WP outcomes.
Methods: Following PRISMA, a systematic literature review (SLR) was conducted in key electronic databases up to December 2020. The PICOT framework was: (P) RA with disease duration ≤3y; (I) b-/tsDMARDs; (C) any treatment/placebo (PBO); (O) employment status (ES), at-work productivity loss (presenteeism) and/or absence from paid work (sick leave – SL); (T) longitudinal studies (except cost-effectiveness) with any follow-up duration. Two reviewers independently identified eligible studies and extracted data using a self-composed extraction sheet. The Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for RCTs was used for the assessment of risk of bias. Odds ratios (OR) were computed for individual studies, and a pooled OR was obtained by random-effects meta-analysis. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed by I2.
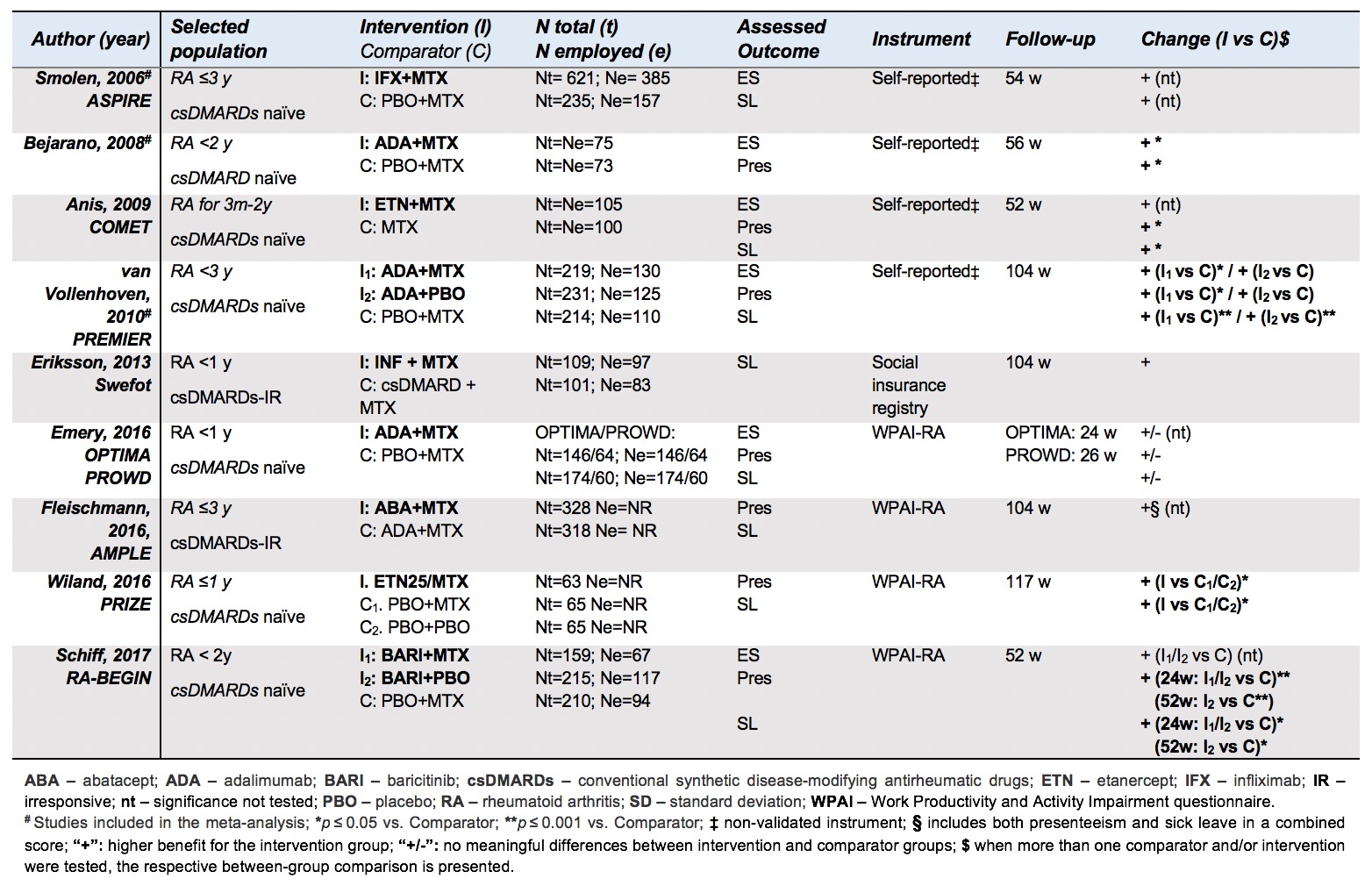
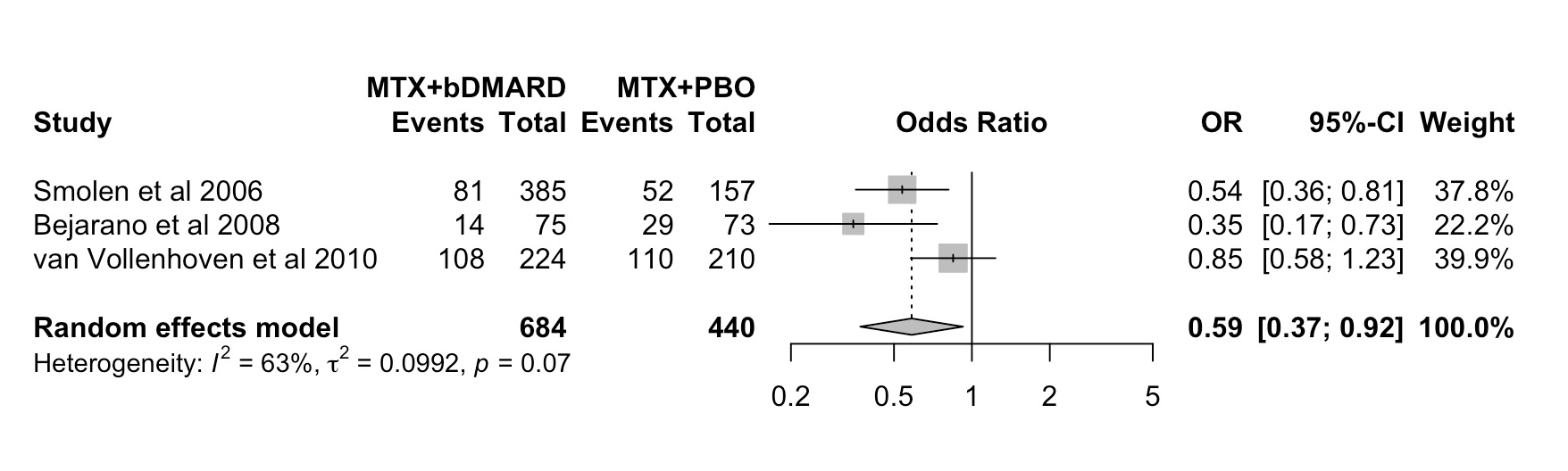
Results: From 5979 records (65 full-text articles screened), 9 studies were included in the SLR (6 RCTs in conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs-naïve patients; 2 RCTs in bDMARD-naïve patients with inadequate response to csDMARDs; 1 RCT of bDMARD tapering after initial combination with methotrexate (MTX)). Studies assessed WP outcomes with validated and non-validated instruments (Table 1). Interventions comprised 4 bDMARDs (abatacept, adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab) and 1 tsDMARD (baricitinib). Most studies had MTX monotherapy(±PBO) (n=7;78%) as active comparator; in 2 studies bDMARD(±PBO) was added to background MTX. For presenteeism and SL, most between-group comparisons showed improvement in favour of b-/tsDMARDs, but not all comparisons were statistically significant – Table 1. A meta-analysis for ES (weeks 56 to 104) included 3 studies (total of 1124 patients) with either adalimumab or infliximab as intervention (Figure 1). The pooled OR of the 3 studies showed a lower likelihood of employment loss in patients treated with MTX+bDMARDs (OR: 0.59; 95% CI:0.37 to 0.92) compared to MTX+PBO. High statistical heterogeneity was observed 63% [0.0%; 89.3%].
Conclusion: A protective effect against employment loss was observed in patients with early RA treated with MTX+bDMARDs compared to MTX monotherapy. Although trends towards beneficial effects of b-/tsDMARDs were seen on presenteeism and SL, the methodological heterogeneity hampers clear conclusions. The additional role of b-/tsDMARD in a real world T2T approach should be further studied in long term (preferably population controlled) studies. Efforts to homogenize the design, analysis and reporting of future studies with WP as an outcome by following recently developed points to consider are crucial1.
1Boonen A, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021 doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219523
MTX in monotherapy. bDMARD – biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; MTX – methotrexate; PBO – placebo.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marques M, Alunno A, Falzon L, Boonen A, Ramiro S. Are Biologic and Targeted Synthetic Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs Associated with Work Participation Improvement in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-associated-with-work-participation-improvement-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-biologic-and-targeted-synthetic-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-associated-with-work-participation-improvement-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis/