Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstracts
Results: 527 randomized pts received ≥1 dose of study drug; 47.4% were male and 52.6% female with a mean age of 49.4 yrs and mean PsA duration of 3.41 yrs. At BL, pts had active disease: mean SJC, 11.2; mean TJC, 20.1; mean HAQ-DI, 1.068. 65% of pts had enthesitis (median MASES: 3.0) and 50% of pts had dactylitis (median severity score: 2.0). 73.1% of pts were using NSAIDs at BL. All pts had a history of psoriasis (mean duration: 15.8 yrs).
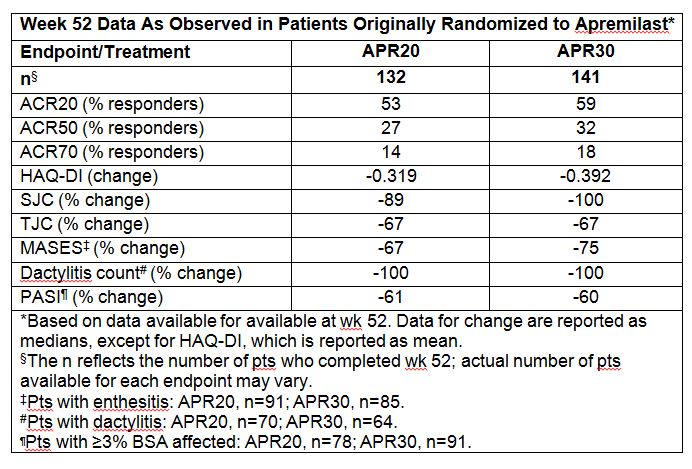
501 pts were included in the per-protocol population. At wk 16, a significantly greater proportion of pts treated with APR achieved modified ACR20 (primary endpoint): 29.2% (APR20) and 32.3% (APR30) vs 16.9% (P=0.0076 and P=0.0011 vs PBO). At wk 52, an ACR20 response was achieved by 53% (APR20) and 59% (APR30) of pts receiving APR from BL. <>Improvements in multiple endpoints were maintained or increased in pts originally randomized to APR and completing 52 wks (Table). <>APR was generally well tolerated. The incidence of any AE was comparable over the PBO-controlled period and through wk 52. AEs through wk 52 occurring in ≥5% of all APR-exposed pts were nausea, diarrhea, headache, and URTI. Most AEs were mild to moderate in severity. In the PBO-controlled period, SAE rates were 2.8% (PBO), 1.7% (APR20), and 0.6% (APR30). These findings were consistent at 52 wks based on EAIRs per 100 pt-yrs. No SAEs of diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting occurred up to 52 wks. The discontinuation rate related to these GI AEs was ≤2% over 52 wks. Discontinuation due to overall AEs in APR-exposed pts was 5.2% over 52 wks.
No new safety findings were identified through wk 52 compared to the previously characterized safety profile of APR. Four serious infections were reported through wk 52 with no imbalance across groups. No systemic opportunistic infections, including no cases of TB (new or reactivation), were reported with APR; TB screening was not required per protocol. <>Conclusion: APR demonstrated clinical benefit up to wk 52 in PsA patients naïve to DMARDs, including clinically meaningful improvements in signs and symptoms, physical function, and extra-articular features of PsA. APR had an acceptable safety profile and was generally well tolerated up to 52 wks with no new safety concerns identified with long-term exposure.
Disclosure:
A. F. Wells,
Celgene Corporation,
2;
C. J. Edwards,
Roche, Celgene Corporation, Pfizer and Samsung,
2,
Roche, Pfizer, Abbott and Glaxo-SmithKline,
8;
A. O. Adebajo,
Celgene Corporation,
2;
A. J. Kivitz,
Celgene Corporation,
2;
P. Bird,
Celgene Corporation,
2;
K. Shah,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
C. Hu,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
R. M. Stevens,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
J. A. Aelion,
Ardea, Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Centocor, Eli Lilly, Galapagos, Genentech, Glaxo Smith Kline, Human Genome Sciences, Janssen, Merck, Mesoblast, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, UCB Biosciences, Sanofi Aventis, Takeda,,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, UCB,
8.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apremilast-in-the-treatment-of-dmard-naive-psoriatic-arthritis-patients-results-of-a-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trial-palace-4/