Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Apremilast (APR), an oral phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, works intracellularly to modulate pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators. The PALACE 1, 2, and 3 trials compared the efficacy and safety of APR with placebo (PBO) in pts with active PsA despite prior DMARDs and/or biologics.
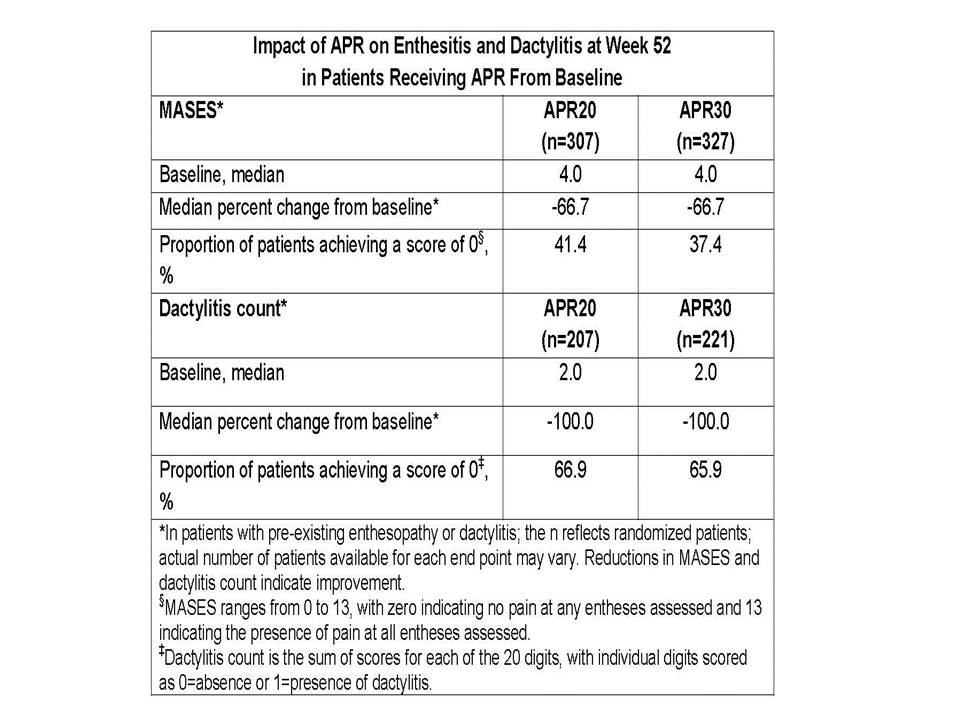
Methods: Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to PBO, APR 20 mg BID (APR20), or APR 30 mg BID (APR30) stratified by baseline DMARD use. At wk 16, pts with <20% reduction from baseline in swollen and tender joint counts qualified for protocol-defined early escape; those on PBO were re-randomized to APR20 or APR30 and those on APR remained on the initial APR dose. At wk 24, all remaining PBO pts were re-randomized to APR20 or APR30 through wk 52. Pts taking concurrent DMARDs were allowed to continue stable doses (MTX, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, or a combination). In order to increase the number of pts with pre-existing enthesopathy and/or dactylitis, data were pooled across PALACE 1, 2, and 3. Maastricht Ankylosing Spondylitis Enthesitis Score (MASES), ranging from 0-13, is the number of painful entheses out of 13 entheses. The dactylitis count, ranging from 0-20, is the number of digits on the hands and feet with dactylitis present; each digit is rated as 0 (no dactylitis) or 1 (dactylitis present).
Results: APR administration resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in ACR20 response (primary endpoint) in all 3 PALACE trials. In pts originally randomized to APR and with pre-existing enthesopathy (n=634) and/or dactylitis (n=428), APR was associated with improvements in the severity of enthesitis and dactylitis over the 52-wk period, as evidenced by reductions in MASES and dactylitis count. At wk 24, median changes in MASES were -21.1%, -40.0% (P=0.0789), and -50.0% (P=0.0167) in pts receiving PBO, APR20, and APR30, respectively. In those pts originally randomized to APR and completing 52 wks of study, median change in MASES was -66.7% with APR20 and APR30 (Table). A MASES score of 0, indicating no pain at any of the entheses assessed, was achieved by 41.4% of APR20 and 37.4% of APR30 pts. At wk 24, median changes in dactylitis count were -66.7%, -75.0% (P=0.2158), and -79.3% (P=0.0609) in pts receiving PBO, APR20, and APR30, respectively. At wk 52, both doses resulted in a median 100% decrease in dactylitis count. Dactylitis count decreased to 0 in 66.9% of APR20 and 65.9% of APR30 pts. Pts randomized to APR at wks 16 and 24 demonstrated results consistent with those originally randomized to APR. No new safety findings were identified and the incidence of pts experiencing any AE was comparable over the 0-24 and 0-52 wk periods.
Conclusion: Over 52 wks, APR continued to demonstrate efficacy in the treatment of PsA, including improvements in enthesitis and dactylitis. APR demonstrated an acceptable safety profile and was generally well tolerated for up to 52 wks.
Disclosure:
D. D. Gladman,
Janssen, Abbvie, Amgen, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, Lily, Celgene,
2,
Janssen, Abbvie, Amgen, Pfizer, UCB, Novartis, Lily, Celgene,
5;
P. J. Mease,
Celgene,
2,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
2,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
2,
Abbvie,
2,
Amgen,
2,
BiogenIdec,
2,
BMS,
2,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
2,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
2,
Eli Lilly and Company,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
UCB,
2,
Celgene,
5,
Merck Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Novartis Pharmaceutical Corporation,
5,
Abbvie,
5,
Amgen,
5,
BiogenIdec,
5,
BMS,
5,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
5,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
5,
Eli Lilly and Company,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
UCB,
5,
Abbvie,
8,
Amgne,
8,
BiogenIdec,
8,
BMS,
8,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
8,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
8,
Eli Lilly and Company,
8,
Pfizer Inc,
8,
UCB,
8;
A. Kavanaugh,
AbbVie Inc., Amgen, Astra-Zeneca, BMS, Celgene, Centocor-Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB,
2,
AbbVie Inc., Amgen, Astra-Zeneca, BMS, Celgene, Centocor-Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB,
5;
A. O. Adebajo,
None;
J. J. Gomez-Reino,
BMS, Pfizer, Roche, Schering-Plough, and UCB SA,
5,
BMS, Roche, Schering-Plough, and Wyeth,
8,
Roche and Schering-Plough,
2;
J. Wollenhaupt,
Abbott Laboratories, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer, and UCB,
5;
M. Cutolo,
BMS, Sanofi and Actelion,
2;
G. Schett,
Celgene,
2,
Abbott Laboratories, UCB, Roche,
5;
E. Lespessailles,
Novartis, Lilly, Servier, Amgen,
2,
Novartis, Lilly,
8;
K. Shah,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
C. Hu,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
R. M. Stevens,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
C. J. Edwards,
Pfizer,
2,
Pfizer, Samsung, Roche, Celgene,
5,
Roche, Pfizer, Abbott, Glaxo-SmithKline,
8;
C. A. Birbara,
Amgen, Lilly, Pfizer, Incyte, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb,
2.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apremilast-an-oral-phosphodiesterase-4-inhibitor-is-associated-with-long-term-52-week-improvements-in-enthesitis-and-dactylitis-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-results-from-three-phas/