Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Apremilast (APR) is a phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor that helps to regulate the immune response that causes inflammation and skin disease associated with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). PALACE 1, 2, and 3 compared the efficacy and safety of APR with placebo in patients with active PsA despite prior disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and/or biologics, including biologic failures. We assessed the impact of baseline weight and body mass index (BMI) on clinical response to APR over 24 weeks in a pooled analysis.
Methods: Patients were randomized (1:1:1) to receive placebo, APR 20 mg BID (APR20), or APR 30 mg BID (APR30) stratified by baseline DMARD use (yes/no). Patients whose swollen and tender joint counts had not improved by ≥20% at Week 16 were considered non-responders and were required to be re-randomized (1:1) to APR20 or APR30 if they were initially randomized to placebo, or continued on their initial apremilast dose. At Week 24, all remaining placebo patients were re-randomized to APR20 or APR30.
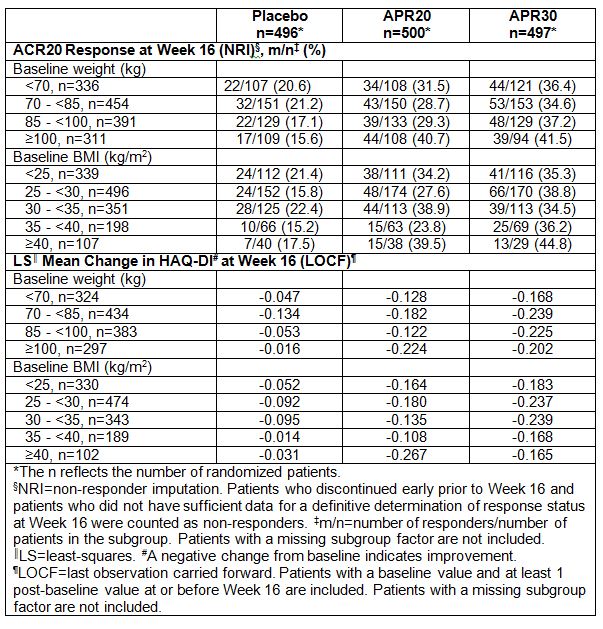
Results: 1,493 patients were randomized, received ≥1 dose of study medication (placebo: n=496; APR20: n=500; APR30: n=497), and were comparable across treatment groups for demographics, disease characteristics, and prior/concurrent therapy. At baseline, mean (SD) weight was 85.7 (20.6) kg and mean (SD) BMI was 29.9 (6.5) kg/m2. At Week 16, a significantly greater proportion of patients receiving APR20 or APR30 achieved a modified ACR20 response vs placebo (primary endpoint) in all 3 PALACE trials. APR30 was associated with significant improvements in Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score vs placebo at Week 16 (key secondary endpoint) across all 3 trials. At Week 16, similar ACR20 response rates and improvements in HAQ-DI scores were observed across all weight and BMI ranges (Table). A favorable treatment effect for both APR treatment groups vs placebo was observed, irrespective of baseline body weight or BMI. Overall, the treatment effect was dose-dependent, with greater effects generally observed in APR30 patients over APR20 patients. These treatment effects were generally maintained at Week 24.
Conclusion: APR demonstrated a favorable treatment effect in patients with active PsA. Comparable improvements in the signs and symptoms of PsA and physical function were observed across a broad range of baseline weight and BMI values. Results suggest that no dose adjustment is required to account for baseline body weight or BMI.
Disclosure:
G. A. Schett,
Abbott, Celgene Corporation, Roche, and UCB,
2,
Abbott, Celgene Corporation, Roche, and UCB,
5;
P. J. Mease,
Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Pfizer Inc, UCB, Celgene Corporation, Novartis, and Roche,
2,
Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Pfizer Inc, UCBCelgene Corporation, Novartis, and Roche ,
5,
Abbott, Amgen, Biogen Idec, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Genentech, Janssen, Eli Lilly, Pfizer Inc, and UCB,
8;
D. D. Gladman,
AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Novartis, and UCB,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Novartis, and UCB,
5;
A. Kavanaugh,
Abbott, Amgen, Astra-Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Centocor-Janssen, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and UCB,
2;
A. O. Adebajo,
None;
J. J. Gomez-Reino,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer Inc, Roche, Schering-Plough, and UCB SA,
9,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Schering-Plough, and Wyeth,
9,
Roche and Schering-Plough,
2;
J. Wollenhaupt,
Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer Inc, and UCB,
2,
Abbott, Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Pfizer Inc, and UCB,
5;
M. Cutolo,
Actelion, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Sanofi-Aventis,
2,
Actelion, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Sanofi-Aventis,
5;
E. Lespessailles,
Amgen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Servier,
2,
Amgen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Servier,
8;
C. Hu,
Celgene Corporation,
3,
Celgene Corporation,
1;
R. M. Stevens,
Celgene Corporation,
1,
Celgene Corporation,
3;
C. J. Edwards,
Celgene Corporation, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and Samsung,
2,
Celgene Corporation, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and Samsung,
5,
Abbott, Glaxo-SmithKline, Pfizer Inc, and Roche,
8;
C. A. Birbara,
Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Eli Lilly, Merck, and Pfizer Inc,
2.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apremilast-an-oral-phosphodiesterase-4-inhibitor-and-the-impact-of-baseline-weight-and-bmi-on-acr20-and-haq-di-response-pooled-results-from-3-phase-3-randomized-controlled-trials/