Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2387–2424) Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
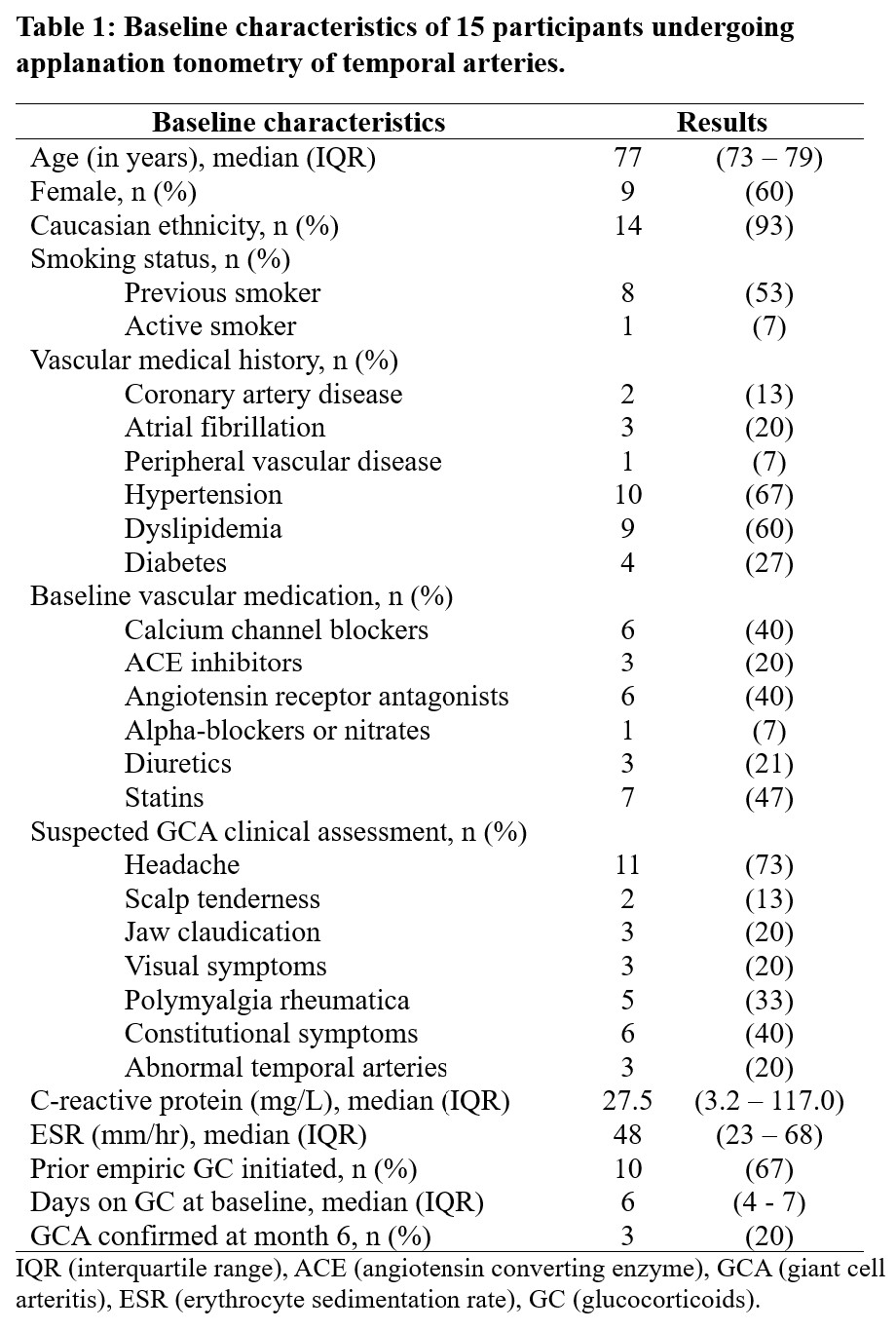
Background/Purpose: Applanation tonometry (ATn) is a non-invasive, point-of-care tool used to capture arterial pressure waveforms. It can measure arterial pulse wave velocity (PWV), a marker of arterial wall stiffness. Arterial inflammation increases vessel-wall stiffness and PWV, as previously demonstrated in patients with Takayasu arteritis. ATn on temporal arteries has not yet been studied, and it may help detect vasculitis in patients with active giant cell arteritis (GCA). The objective of this study is to investigate the feasibility of ATn on temporal arteries, assess the quality of the waveform/PWV obtained, and explore if PWV is increased in patients with GCA.
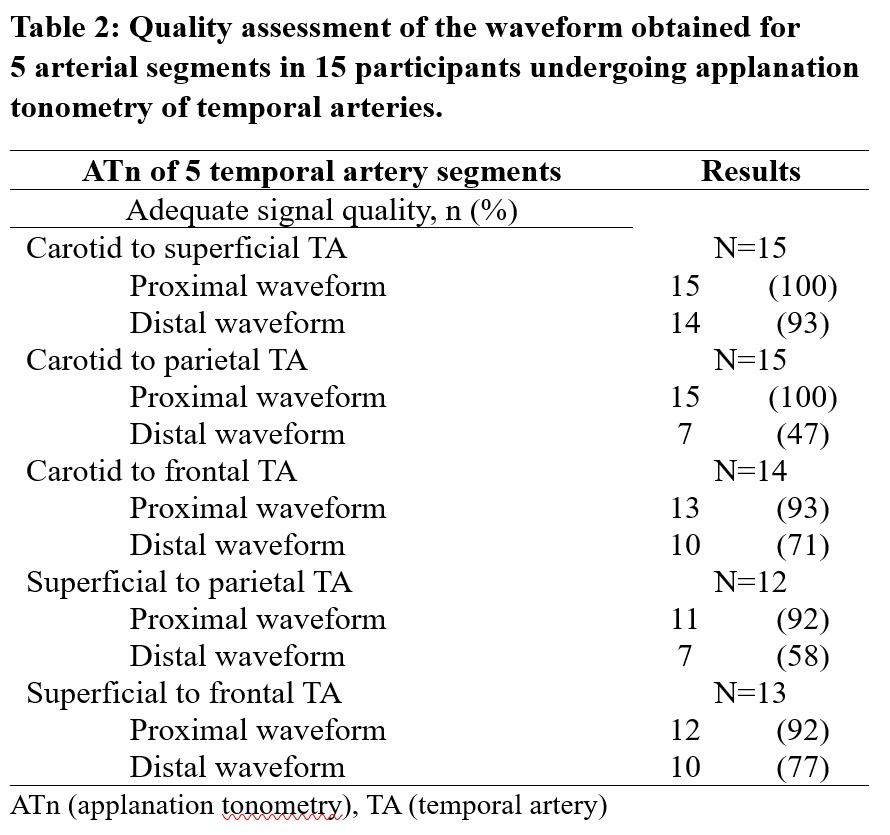
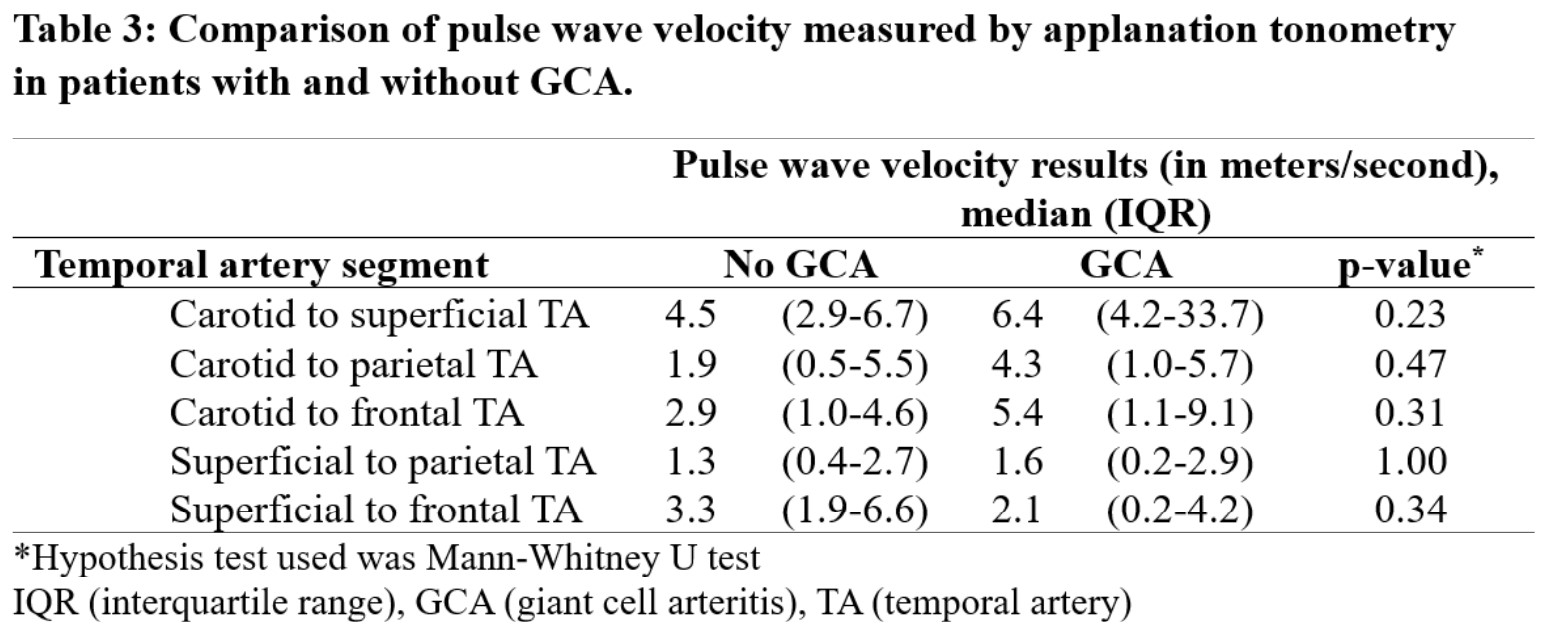
Methods: A cross-sectional study was performed in our quaternary vasculitis clinic from June to December 2022. Participants referred for suspected GCA, without prior temporal artery biopsy, were eligible. At baseline, participants had a clinical assessment, color doppler ultrasound (CDUS) and ATn of temporal arteries. ATn was performed by dedicated, blinded research personnel in a separate room. GCA specialists who completed the clinical assessment and CDUS were blinded to ATn results. Final diagnosis was established based on expert opinion at the 6-month follow-up. We used the Sphygmo Cor system to perform ATn. PWV were measured in five arterial segments on the right side: carotid to superficial temporal artery (C-S), carotid to parietal temporal artery (C-P), carotid to frontal temporal artery (C-F), superficial to parietal temporal artery (S-P), and superficial to frontal temporal artery (S-F). The quality of the waveform was confirmed visually. The coefficient of variation (CV = standard deviation/transit time) of the proximal and distal arterial points was assessed. A CV ≤ 6% denoted good capture quality as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. Descriptives statistics were performed for baseline characteristics and ATn quality assessment. Mann-Whitney U test was used to explore a potential difference in PWV in patients with and without GCA.
Results: Fifteen participants were enrolled, including 3 patients with a final diagnosis of GCA who satisfied the 2022 ACR/EULAR classification criteria (Table 1). A total of 69 arterial segments were assessed (PWV measures could not be obtained in 1 C-F, 3 S-P and 2 S-F segments). Quality assessment of the ATn waveform was satisfactory for the C-S, C-F, S-F arterial segments (Table 2). Parietal temporal arteries had a high proportion of low-quality waveforms, likely due to their small size relative to the probe. In patients with GCA, median PWV of the C-S, C-P, C-F and S-P segments were numerically but not statistically higher than in patients without GCA (Table 3).
Conclusion: ATn of temporal arteries is feasible, and PWV measures were of quality for 3 arterial segments (C-S, C-F, S-F). Median PWV was higher in patients with active GCA than in subjects without confirmed GCA; however, this study was underpowered to detect statistical difference. This proof-of-concept study allowed the identification of arterial segments that are now further evaluated in a larger trial of ATn in GCA (Clinicaltrials.gov id: NCT05703763).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Makhzoum J, Ducharme-Benard S, Hussein S, Meunier R, Ross C, Chamlian A, Ducharme J, Chamlian L, Dhahbi A, Pagnoux C, Goupil R. Applanation Tonometry of the Temporal Arteries in Participants with Suspected Giant Cell Arteritis: A Proof of Concept [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/applanation-tonometry-of-the-temporal-arteries-in-participants-with-suspected-giant-cell-arteritis-a-proof-of-concept/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/applanation-tonometry-of-the-temporal-arteries-in-participants-with-suspected-giant-cell-arteritis-a-proof-of-concept/