Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In SLE Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1) risk variants associate with cardiovascular and kidney damage. APOL1 is both a secreted and tissue intrinsic protein; the latter role mediates organ injury. Expression is driven by inflammatory stimuli which initially promotes survival through autophagy. At higher expression, APOL1 contributes to cell death partially by compromising mitochondria. The RV protein structure favors toxicity at lower thresholds. Macrophages express APOL1 and use metabolic plasticity to perform effector functions. We hypothesized that in activated macrophages, APOL1 expression impairs mitochondrial
Methods: Healthy controls were genotyped for APOL1 reference allele (G0) risk variants (RV) (n=15; G0/G0=8, RV/G0=4, RV/RV=3). Monocytes were isolated from PBMCs using a Miltenyi Biotec Pan Monocyte Isolation kit and differentiated into macrophages using GM-CSF. Cells were treated with SLE-relevant agonists ssRNA hY3 or IFNɣ; and APOL1 expression was observed by qPCR. As in-vivo correlates, APOL1 expression relative to IFN response gene, Siglec 1, in SLE patient monocytes (n=17); and expression in coronary artery tissue macrophages with (n=3) or without (n=3) atherosclerotic plaque were assessed through RNA seq data and immunohistochemistry respectively. To test mitochondrial respiration, cultured HC macrophages were left untreated or IFNɣ treated, and bioenergetics were measured by the Seahorse assay. Confirmatory fluorescent microscopy was done by staining cells with Mitoprobe (polarized mitochondria) and Mitotracker (all mitochondria) and the ratio of Mitoprobe to Mitotracker staining was quantified using ImageJ software.
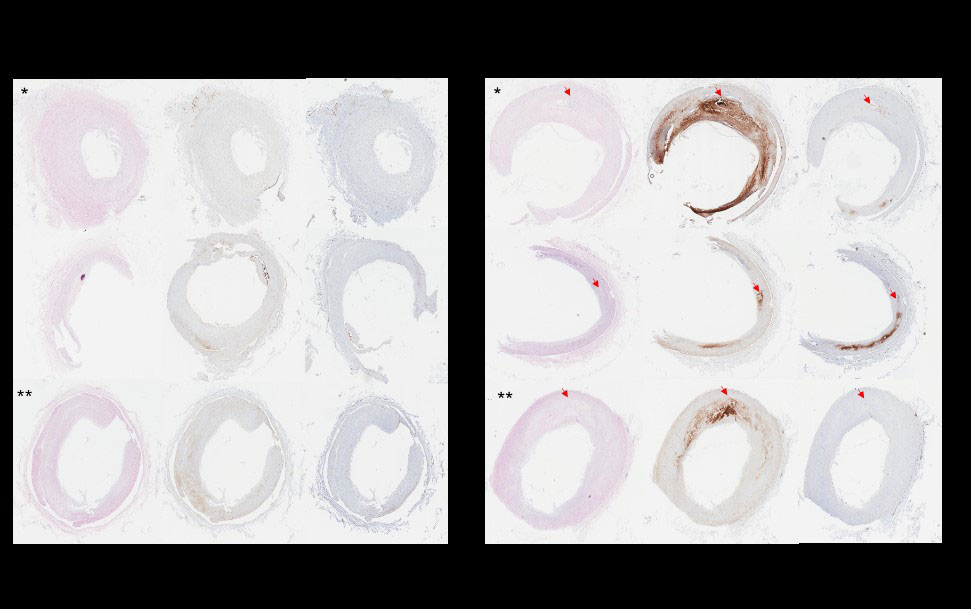
Results: Across the genotypes,hY3 and IFNɣ increased APOL1 mRNA expression 29.1±18.4 and 31.6±14.9 fold compared to untreated (p< 0.001 in each). In SLE monocytes, APOL1 significantly correlated with Siglec1 expression (R=0.64; P=0.005). APOL1 stained 4% of non-plaque containing and 18% of plaque-containing coronary arteries (p=0.05). APOL1 was apparent in multiple cell types including invading tissue macrophages (fig1). On the seahorse assay, there were genotype-dependent differences in Basal OCR (BO pmol/min), Spare Capacity (SC pmol/min), and total ATP production (ATP pmol/min) (G0/G0: BO: 99.4±11.3, SC:150.9±16.6, ATP: 88.1±9.5; RV/G0: BO: 46.1±4.5, SC: 52.1±8.8, ATP: 40.7±3.4; RV/RV: BO: 46±17.4, SC: 14.9±11.6, ATP: 36.7±9.5 each p< 0.001). Across genotype, these values fell with IFNɣ (G0/G0: BO: 73.9±6, SC: 129.4±17.3, ATP: 67.6±5.4; RV/G0: BO: 46±5.1, SC: 27.9±8.1, ATP: 39.5±3.9; RV/RV: BO: 42.1±8.6, SC: 9.5±8.3, ATP: 35.8±6.9) (fig2). Fluorescent microscopy confirmed findings with the mean respective MitoProbe/Mitotracker ratios in G0/G0, RV/G0, and RV/RV macrophages at rest 1.5±0.5, 0.86±0.3, and 0.89±0.3 and with IFNɣ 1.3±0.4, 0.74±0.3, and 0.6±0.2 (fig3).
Conclusion: Inflammation both in vitro and in vivo due to hY3, IFNɣ, and ischemia increase macrophage APOL1 expression across genotypes. In RV carrying macrophages, this results in diminished mitochondrial energy production—a potential underpin of variant-mediated toxicity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Blazer A, Chang M, Robins K, Buyon J, Clancy R. Apolipoprotein L1 Variant-Carrying Monocytes Exhibit Mitochondrial Respiration Defects [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apolipoprotein-l1-variant-carrying-monocytes-exhibit-mitochondrial-respiration-defects/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apolipoprotein-l1-variant-carrying-monocytes-exhibit-mitochondrial-respiration-defects/