Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Anti-signal recognition particle (SRP) autoAb identifies a myositis subset with a necrotizing myopathy and poor prognosis. Currently, immunoprecipitation (IP) is used to identify anti-SRP. Our aim was to develop and validate a quantitative anti-SRP ELISA to streamline anti-SRP detection.
Methods: The anti-SRP ELISA utilized recombinant purified full length human SRP54 (Diarect AG product number 18401) coated on a high-binding ELISA plate (Costar, Corning, NY). Patient (pt) serum (dilution ≥1:100) was incubated with ELISA plates and a horseradish peroxidase conjugated secondary antibody that binds human IgG quantified anti-SRP binding. Units/ml of anti-SRP were determined using a standard serum sample. Values below the detection range (<4 U/ml) were considered (-) and assigned a value = 2. Values >128 U/ml were assigned a value = 128. Assay validation utilized lP as the gold standard. The following test characteristics were evaluated: sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), accuracy, ROC curve and sensitivity analysis, and area under the curve (AUC). Mann-Whitney tests compared anti-SRP levels and kappa statistics tested agreement between ELISA and IP. Controls included a) anti-SRP (+) and (-) myositis pts by IP, b) scleroderma (SSc) and lupus pts, and c) other SRP (-) necrotizing myopathy pts. Serial samples from 7 SRP (+) pts by IP were also tested.
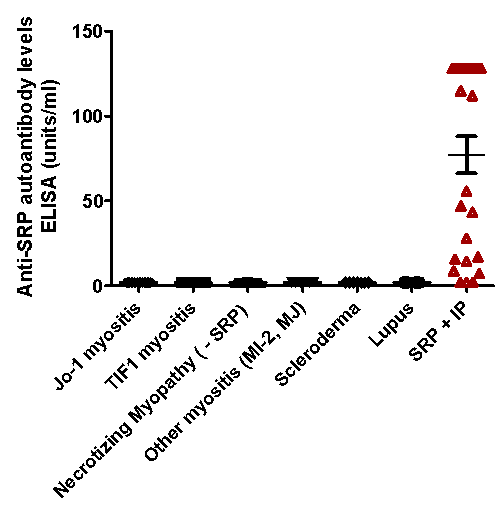
Results: We identified 26 SRP (+) myositis pts by IP. 77 SRP (-) myositis pts by IP were evaluated as controls (including 37 pts with necrotizing myopathy). Non-myositis control pts included SLE (n=4) and SSc (n=7). Anti-SRP positivity by ELISA correlated with IP results (p<0.001) with strong agreement between both methods (kappa 0.94). Median (IQR) anti-SRP levels in pts with (+) and (-) anti-SRP by IP was 113.3 (15.6-128) and 2 (2-2) units/ml, respectively (p<0.001). The sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy of the ELISA was 88%, 100%, 100%, 96% and 97%, respectively. The AUC of a ROC curve was 0.94. Serial samples showed that anti-SRP levels decreased consistent with clinical improvement in 3 pts, were unchanged at low levels in 2 pts with stable disease, and increased in 1 pt with a myositis flare. Inter-assay coefficient of variance (CV) was 23%.
Conclusion: We developed a quantitative ELISA for anti-SRP autoAbs, validating the assay in myositis and other rheumatic disease pts including a group of SRP (-) necrotizing myopathy pts. The ELISA is simple to perform, sensitive and highly specific. The availability of a validated, quantitative, easy to perform ELISA should improve anti-SRP autoAb detection in myositis pts facilitating early identification of pts with a refractory necrotizing myopathy necessitating aggressive therapy.
Figure 1: Anti-SRP antibody ELISA levels in different myositis subsets
Disclosure:
R. Aggarwal,
None;
C. V. Oddis,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
9;
D. Goudeau,
None;
C. Stephans,
None;
N. Fertig,
None;
Q. Zengbiao,
None;
D. Koontz,
None;
M. C. Levesque,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-signal-recognition-particle-autoantibody-elisa-development-and-validation-utility-in-patients-with-necrotizing-myopathy/