Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-phosphatidylserine prothrombin antibodies (aPS-PT) are reported to be highly associated with the LAC. Some have suggested a clinically useful role for aPS-PT as a potential surrogate marker for the LAC – especially in the clinical scenario of concurrent anticoagulation where the LAC can have decreased diagnostic performance. However, the studies revealing the aPS-PT and LAC relationship have primarily been carried out on well-established APS and SLE cohorts. Validation studies replicating this relationship in a real-world, all-comer study population are lacking. The purpose of this study was to determine the sensitivity and specificity of aPS-PT to the LAC and other APS serologies in an all-comer population undergoing evaluation for APS and other autoimmune syndromes.
Methods: A cross-section of patients from June 2017 to December 2018 undergoing evaluation for APS across all medical specialties were reviewed for APS testing inclusive of LAC, aPS-PT, anti-cardiolipin (aCL), and anti-β2 glycoprotein-1 (β2GP1). Presence of a LAC was determined by trained hematologists interpreting mixing and neutralization studies. Demographic details were abstracted from the medical record. Cases meeting the SLICC criteria for SLE and the revised Sapporo criteria for APS were enumerated. Sensitivities, specificities, negative-, and positive predictive values with 95% confidence intervals were calculated.
Results: A sample of 166 eligible patients was identified. Mean age was 49±17 years. Seventy-one percent were female, 89% Caucasian, 15% with SLE, and 21% with APS. At time of testing, 18% were on warfarin, 8% on direct factor Xa inhibitors and 1% on low-molecular weight heparin. The aPS-PT was found to be the most specific to the LAC as seen in table 1. Specificity of IgG aPS-PT was 100% (96-100%) and IgM aPS-PT was 97% (91-100%) to the LAC. This corresponds to a positive predictive value for IgG aPS-PT of 100% (89-100%) and IgM aPS-PT of 95% (84-99%). Specificities of aPS-PT to aCL and β2GP1 antibodies were slightly less in the 80% range. In contrast, the sensitivities of aPS-PT to the LAC were only in the 40-50% range.
Conclusion: In our study with an all-comer population undergoing evaluation for APS and other autoimmune syndromes, aPS-PT had high specificity and high positive predictive value to the presence of the LAC. The sensitivity and negative predictive performance of aPS-PT to LAC however was less robust. This study’s findings echo similar findings in past studies on APS and SLE cohorts. And, it corroborates the notion that a positive aPS-PT could be a clinically useful marker for the LAC in the general clinical setting.
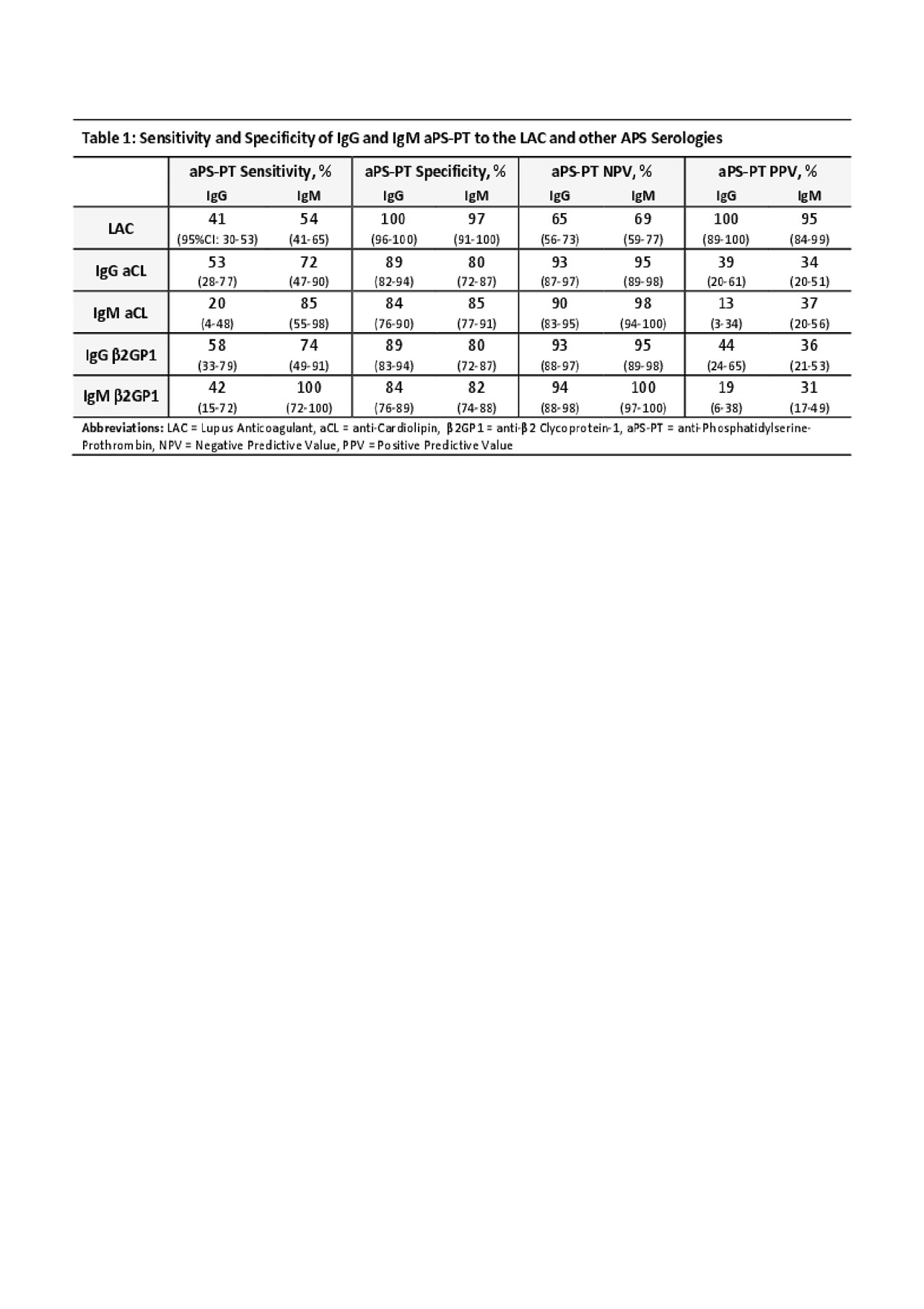
zACR_PSPT LAC association_PDF TABLE
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pham M, Orsolini G, Crowson C, Snyder M, Pruthi R, Moder K. Anti-Phosphatidylserine Prothrombin Antibodies as a Predictor of the LAC in an All-Comer Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-phosphatidylserine-prothrombin-antibodies-as-a-predictor-of-the-lac-in-an-all-comer-population/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-phosphatidylserine-prothrombin-antibodies-as-a-predictor-of-the-lac-in-an-all-comer-population/
