Session Information
Date: Monday, November 6, 2017
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We have previously shown that rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) have higher disease activity measures, due primarily to patient reported measures including higher tender joint counts, pain, and worse patient global scores. However, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis reported increased serum expression of IL-1, IL-6, and IFN-γ in PTSD patients (Passos IC et. al., Lancet Psychiatry, 2015). The purpose of this study was to compare serum cytokine/chemokine expression in RA patients with and without PTSD.
Methods: Participants were enrollees in a multicenter, longitudinal observational cohort of US Veterans with RA categorized as having PTSD, other anxiety or depression, or neither based on administrative codes. Serum cytokines/chemokines were measured from banked serum at enrollment using a multiplex bead-based assay. Cytokines (CKs) were modeled using an overall cytokine (CK) score (log-transformed), the number of elevated cytokines (>2 SD above mean), and by individual CKs (log-transformed). CK score and number of elevated CKs were compared between groups using ANOVA and Χ2. The association of PTSD with CK parameters was assessed using multivariable least squares and negative binomial regression adjusted for age, sex, race, and smoking status. Analyses were additionally stratified by anti-CCP status.
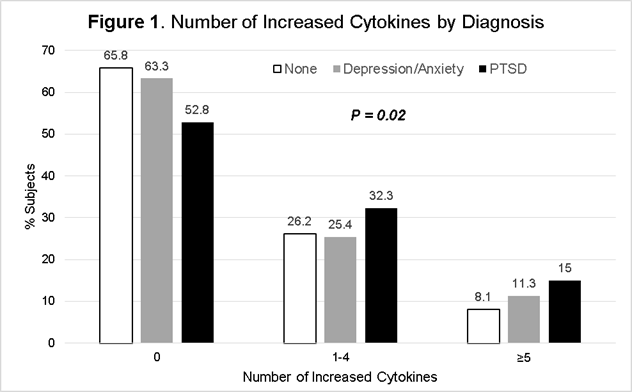
Results: Of 1,460 RA subjects with mean (SD) age of 64 (11) years, RA duration 11 (11) years, were 91% male, 76% anti-CCP positive, and 80% current or former smokers, 9% had PTSD, 24% had other depression/anxiety, and 67% had neither psychiatric condition. In unadjusted comparisons, those with PTSD had higher CK scores (P=0.02) and a greater number of elevated CKs (P=0.02, Figure 1). In multivariable least squares and negative binomial regression models, CK score and number of positive CKs were associated with PTSD, though this was limited to those who were anti-CCP positive (Table 1). Anxiety/depression subjects without PTSD had similar CK scores and number of elevated CKs as controls. PTSD was associated with heightened expression of several individual CKs (IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, MCP-1).
Conclusion: Anti-CCP positive RA patients with PTSD have a higher serum cytokine expression in comparison to those without PTSD. These findings support an objective measure of increased inflammation in RA patients with comorbid PTSD. Exploration of a potential mechanistic inflammatory link between RA and PTSD and contributions of specific cytokines will require future study.
|
Table 1. Associations of Serum Cytokines with PTSD in Rheumatoid Arthritis |
|||
|
|
No Depression, Anxiety or PTSD |
Depression or Anxiety |
PTSD |
|
Values, mean (SD) |
|
|
|
|
Cytokine score |
2.33 (0.89) |
2.39 (0.91) |
2.56 (0.93) |
|
Cytokine number positive |
1.08 (2.23) |
1.23 (2.42) |
1.64 (2.75) |
|
All subjects± |
|
|
|
|
Cytokine score |
Reference |
0.055 (-0.055, 0.165) |
0.193 (0.026, 0.361)* |
|
Cytokine number positive |
Reference |
0.145 (-0.051, 0.341) |
0.355 (0.197, 0.513)** |
|
Anti-CCP positive± |
|
|
|
|
Cytokine score |
Reference |
-0.027 (-0.170, 0.117) |
0.193 (-0.018, 0.405) |
|
Cytokine number positive |
Reference |
-0.036 (-0.272, 0.201) |
0.339 (0.162, 0.517)** |
|
Anti-CCP negative± |
|
|
|
|
Cytokine score |
Reference |
-0.048 (-0.266, 0.171) |
-0.074 (-0.410, 0.261) |
|
Cytokine number positive |
Reference |
0.184 (-0.403, 0.771) |
-0.233 (-0.588, 0.092) |
|
±Values represent b coefficients (95% confidence interval) *P < 0.05; ** P <0.01 Models adjusted for age, sex, race, and smoking status. |
|||
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
England BR, Sayles H, Thiele GM, Michaud K, Sokolove J, Cannon G, Reimold A, Kerr GS, Caplan L, Baker J, Mikuls TR. Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients with Comorbid Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Have Higher Serum Cytokine Expression [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-cyclic-citrullinated-peptide-antibody-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-comorbid-post-traumatic-stress-disorder-have-higher-serum-cytokine-expression/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-cyclic-citrullinated-peptide-antibody-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-with-comorbid-post-traumatic-stress-disorder-have-higher-serum-cytokine-expression/