Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Although the pathogenesis and cause of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains uncertain, various disease-driving auto-antigens and auto-antibodies with different specificities have been used as diagnostic tools. Anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) has been implicated in disease process and due to its high specificity also been used as a diagnostic tool. There have been many studies in the literature using ACPA as an indicator of radiological (X-Ray) joint damage in both RA patients and animal studies, although few have quantified bone damage using Micro-CT. This is important since this approach is increasingly considered the gold standard for analyzing and quantifying micro-structural changes in bone morphology. Therefore the purpose of this study was to correlate joint damage as quantitated by micro-CT with ACPA using our novel citrullinated collagen induced arthritis (CCIA) model.
Methods: Thirty DBA/1 mice were randomly divided into three groups. Mouse collagen (C-II) was modified [citrullinated (Cit)] using peptidyl arginine deiminase (PAD) and injected weekly for 5 weeks. As controls, mice were injected with unmodified C-II (negative control) and with Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA) as positive control. Mice were sacrificed at week 5 and micro-CT was done to quantitatively analyze bone damage. A commercially available anti-CCP antibody kit was used to measure ACPA levels in serum. Data was expressed as mean ± SD’s. Pearson’s 2-tailed correlation was used to correlate ACPA with measures of bone damage.
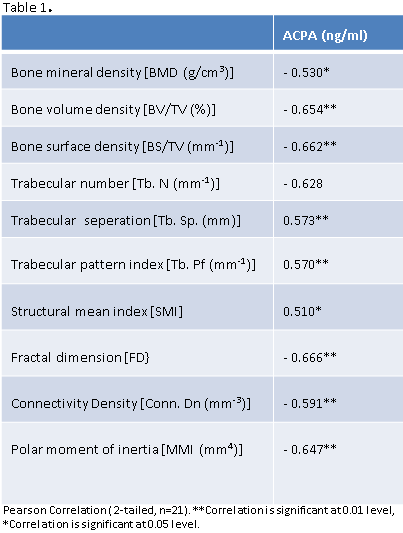
Results: Using ELISA, anti-CCP (ng/ml) was measured in serum and showed a significant increase in both Cit-C-II (29.03 ± 7.53, p = 0.03) and FCA-C-II (42.73 ± 4.56, p < 0.001) as compared to C-II (21.84 ± 5.20). Bone mineral density (BMD) showed significant loss in Cit-C-II (0.43 ± 0.04 g/cm3, p = 0.018) and FCA-C-II (0.35 ± 0.08 g/cm3, p = 0.001) as compared to C-II (0.49 ± 0.04 g/cm3) group. Data was found to be consistent for several other parameters of bone quality (not shown). Significant negative correlations were observed for BMD, BV/TV, BS/TV, trabecular number, fractal dimension, connectivity density and polar moment of inertia all indicating that as ACPA increases these decrease suggesting that higher ACPA concentration is inversely associated with bone quality [Table 1].
Conclusion: Due to the fact that no exogenous immunogenic factor such as non-self protein or any adjuvant is used in this novel model, CCIA closely mimics the auto-immunogenic origin of RA. Using this model, we observed significant inverse associations of circulating ACPA with measures of bone quality including density, volume, surface and mechanical properties of bone. In conclusion ACPA levels in serum can successfully predict bone morphological changes in RA. Further studies focused on identifying the mechanisms underpinning these relationships are ongoing.
Disclosure:
A. Dusad,
None;
M. J. Duryee,
None;
D. Wang,
None;
C. D. Hunter,
None;
B. C. Hamilton III,
None;
J. R. O’Dell,
None;
T. R. Mikuls,
None;
L. W. Klassen,
None;
G. M. Thiele,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-citrullinated-protein-antibodies-as-an-indicator-of-bone-damage-in-the-citrullinated-collagen-induced-arthritis-model/