Session Information
Date: Sunday, October 21, 2018
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a composite index to assess disease activity in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). According to the treat-to-target (T2T) recommendations for SpA, and the ASAS/EULAR management recommendations for axSpA, the C-reactive protein (CRP)-based ASDAS is the preferred instrument for the assessment of disease activity in the process of making decision on modification of axSpA treatment in clinical routine. Currently, measurement of CRP by routine lab methods takes hours to days what challenges the feasibility of T2T approaches in clinical-routine and studies. The objective of this study was to compare the performance of the ASDAS based on a quickCRP assay (ASDAS-quick-CRP) with the ASDAS-routine-CRP and with the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)-based ASDAS in the assessment of disease activity in patients with axSpA.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was performed in patients referred with a suspicion of axSpA as part of the OptiRef study. Briefly, referred patients underwent an assessment of SpA features by a rheumatologist. CRP was measured in the central lab (routine turbidimetric assay, lowest detection level: 0.3mg/l) and locally by ESR and a quantitative quick-CRP test (QuickRead go®, Orion Diagnostica Oy, lowest detection level: 5mg/l, test duration approx. 2 min.). If the quick-CRP was below the limit of detection, the value of 2mg/l was used. In patients with the final diagnosis of axSpA, ASDAS-routine-CRP, ASDAS-quick-CRP and ASDAS-ESR were calculated.
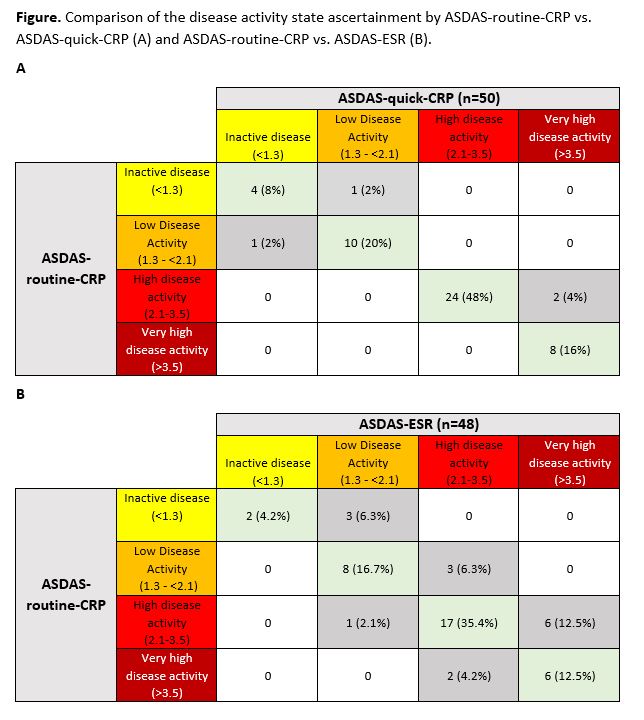
Results: A total of 137 patients had available routine and quick CRP levels; 50 patients of them were diagnosed with axSpA. Mean±SD routine / quick CRP serum levels were 3.6±7.0 mg/l and 5.0±7.2 mg/l, respectively, in the entire group, and 6.2±8.3 mg/l and 7.4±8.4 mg/l, respectively, in patients with axSpA. There was no significant difference (p=0.11) in the mean values of ASDAS-CRP (2.7±1.0) and ASDAS-quick-CRP (2.8±1.0), while the ASDAS-ESR (2.9±1.0) was significantly higher than ASDAS-routine-CRP (p=0.02). In 46 of the 50 cases of axSpA (92%) the status scores for disease activity showed no difference between ASDAS-routine-CRP and ASDAS-quick-CRP – figure. For ASDAS-ESR compared to ASDAS-routine-CRP, only 33/48 patients (68.8%) were assigned to the same DAC.
Conclusion: ASDAS-quick-CRP performed similarly well to ASDAS-routine-CRP with an agreement on the status score for disease activity of 92%, that was clearly better than the agreement of 68.8% between ASDAS-ESR and ASDAS-routine-CRP. With a duration of approximately 2 minutes the quick-CRP test is, therefore, feasible for immediate decision making as a part of clinical routine or clinical trials.
Acknowledgements: The OptiRef project was supported by an unrestricted research grant from Novartis. The “QuickRead go” was provided free of charge by Orion Diagnostica Oy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Proft F, Muche B, Spiller L, Rios Rodriguez V, Rademacher J, Weber AK, Lueders S, Protopopov M, Spiller I, Sieper J, Poddubnyy D. Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) Based on a Quick Quantitative CRP Assay Performs Similarly Well to ASDAS Based on Conventional CRP in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ankylosing-spondylitis-disease-activity-score-asdas-based-on-a-quick-quantitative-crp-assay-performs-similarly-well-to-asdas-based-on-conventional-crp-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ankylosing-spondylitis-disease-activity-score-asdas-based-on-a-quick-quantitative-crp-assay-performs-similarly-well-to-asdas-based-on-conventional-crp-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/