Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:00PM-3:30PM
Background/Purpose: Autoinflammatory Type I Interferonopathies (IFNopathies) include SAVI (STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy), CANDLE/PRASS (Chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatosis, with lipodystrophy and elevated temperature), and AGS (Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome). A high blood IFN-I signature/score correlates with disease activity and response to treatment2 and is used together with a ratio (IFN-I score/NFKB score) to characterize patients with yet genetically uncharacterized diseases3. JAK inhibitors (JAKi), which block the signaling of the IFN receptor, have been the mainstay of treatment,1 but suppression of the IFN-I score is only achieved in a subset of CANDLE/PRAAS patients. We treated patients with ongoing active disease and elevated IFN-I scores with the anti- type I IFN receptor (IFNAR) monoclonal antibody, anifrolumab to achieve better disease control and reduce side effects from high-dose JAKi treatment.
Methods: Pts (n=12), enrolled in NCT02974595, with type I IFNopathies (SAVI=3, CANDLE=6, Undifferentiated=3) and persistently elevated type I IFN score in the blood on optimized treatment with the JAKinhibitor, baricitinib, (n=11), were started on anifrolumab infusions every 4 wks (300 mg or 5.5 mg/kg) either as monotherapy (n=1) or in combination with the baseline JAKi treatment (n=11). The median length of treatment with anifrolumab (range 2-20, median 8 months). Table 1. All patients received zoster prophylaxis. Patient-reported outcomes (daily diaries and questionnaires, n=10) and clinical biomarkers, safety labs including BK viral titers were monitored (n=12).
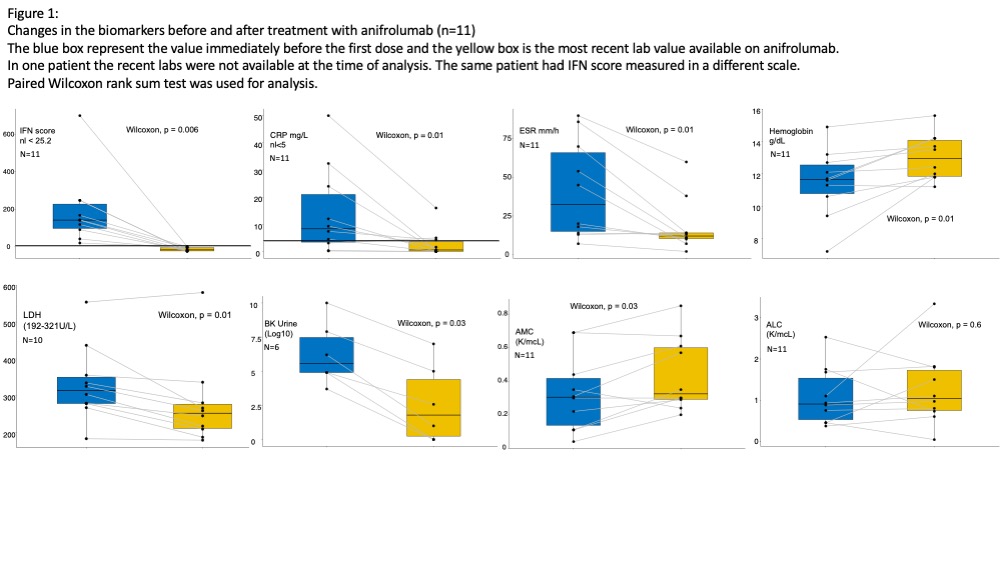
Results: Treatment with anifrolumab resulted in a median change in IFN-I score from 142 to -16 and normalized in all patients treated (n=12) (Figure1). Clinical flares did not occur. The baricitinib dose was tapered down by median of 3 mg/day (0.2 mg/kg/day) in 10/11 pts of the starting dose. Pts on systemic steroids (n=9) could taper down by median of 0.5 mg/kg (n=7) or discontinued steroids (n=2). Inflammatory markers, CRP, and ESR significantly improved on anifrolumab (2/3 SAVI patients continue to have high CRP). Anemia resolved in all patients. Urine BK viral load dropped in (n=6) who had baseline high BK viral titers. Two pts on the combination of anifrolumab and JAKi developed systemic viral infections (Enterovirus n=1, Human Herpesvirus-6 =1 complicated with encephalopathy), and two patients had a long course of rhinovirus and parainfluenza infections that were resolved after tapering down the dose of JAKi and supportive therapy. Evaluation of cytokines and biomarkers is ongoing.
Conclusion: Anifrolumab effectively suppressed the IFN-1 signature/score in all patients, including in SAVI pts; this was associated with improved serum CRP and ESR in the context of tapering doses of baricitinib and corticosteroids. BK viral titers dropped. Long-term follow-up to assess treatment efficacy in controlling inflammatory organ manifestations and progression of organ damage is critical in determining the impact of IFN-I blockade on the diseases manifestations of the autoinflammatory interferonopathies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alehashemi S, Baumgardner A, Shakoory B, Almeida de Jesus A, Park S, Uss K, Robles M, Palmblad K, Horne A, Brodin P, Akoghlanian S, Abraham R, Mustillo P, Barillas-Arias L, Heras A, Wampler Muskardin T, Lawrence M, Mannem H, Nolan B, Canna S, Reinhardt A, Binstadt B, Goldbach-Mansky R. Anifrolumab Normalizes the Type I Interferon Signature in a Cohort of Patients with Type I Interferonopathies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anifrolumab-normalizes-the-type-i-interferon-signature-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-type-i-interferonopathies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anifrolumab-normalizes-the-type-i-interferon-signature-in-a-cohort-of-patients-with-type-i-interferonopathies/