Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ARHP)
Background/Purpose
Biologic anti-TNFs in India have improved the patient management. Significant proportions of patients lose response over time or do not respond. Possible explanations are suboptimal trough anti-TNFa concentrations or antibodies to anti-TNFs1.
Anti-infliximab antibodies are found in 12%-44% of patients2 vis-à-vis anti-etanercept antibodies (0%-18%). Anti-etanercept antibodies are without apparent effect on effectiveness or adverse events2. Clinicians should have access to immunogenicity testing facility in India.
The aim of this project was to set up and standardize an independent laboratory to test immunogenicity of anti-TNF biologics (infliximab and etanercept) with the help of pharmaceutical partnership.
<>Methods:
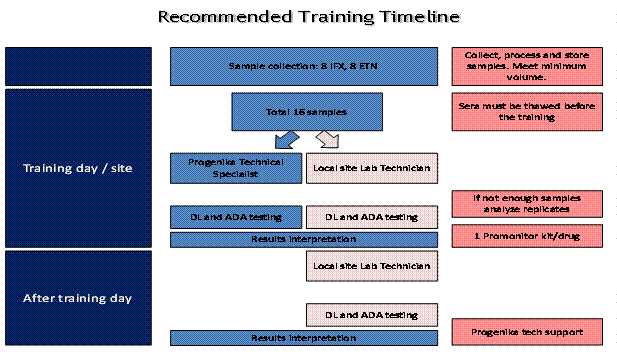
Three rheumatologists piloted this project approved by independent ethics committee and carried out in compliance with ICH/GCP guidelines. Pfizer supplied the immunogenicity kits to the independent laboratory (SRL labs). After informed consent, blood (5 mL) was collected before infusion of infliximab (n=8) or injection of etanercept (n=8). Following all precautions, the blood samples were transported to the laboratory. Promonitor® was the ELISA test used for testing of biological levels and anti-TNFa antibodies in patients samples. Laboratory staff was trained by Progenika specialist from Spain (Table I)
Table I
DL – Drug level; ADA – Anti-drug antibody
<>Results:
Mean age of 16 patients was 42.06 ± 12.89 years. Table II represents the assay cut points and Table III lists the drug and antibody concentrations for patients.
Table II
|
|
Cut-point
|
Interpretation
|
|
Infliximab
|
0.035 ug/mL |
1) < 0.035 ug/mL – Negative 2) 0.035-1.5 ug/mL – Low positive 3) > 1.5 ug/mL – Positive |
|
Anti-Infliximab antibodies
|
2 AU/mL |
1) > 2 AU/mL – Positive 2) ≤ 2 AU/mL – Negative
|
|
Etanercept
|
0.035 ug/mL |
1) < 0.035 ug/mL – Negative 2) > 0.035 ug/mL – Positive |
|
Anti-Etanercept antibodies
|
142 AU/mL |
1) < 142 AU/mL – Negative 2) > 142 AU/mL – Positive |
Table III
|
|
Drug level
|
Interpretation
|
|
Infliximab
|
< 0.035 ug/mL (n=4) 0.8217 ug/mL (n=1) Range 2.706 to 8.079 ug/mL (n=3)
|
Negative Low positive Positive
|
|
Anti-Infliximab antibodies
|
>2 AU/mL (n=1; 12.5%) |
Positive |
|
Etanercept
|
4.20 ± 3.23 ug/mL (n=8) (Range 2.000 – 9.712 ug/mL)
|
All patients positive
|
|
Anti-Etanercept antibodies
|
< 142 AU/mL (n=8)
|
Negative for all patients |
While 4 patients tested negative for infliximab, one patient tested low positive and 3 patients were positive. Anti-infliximab antibody was detected in 1/8 patient (12.5%) and the blood level of infliximab was negligible. When anti-TNFa are used, thereapeutic drug monitoring is of help for optimal clinical outcomes. It might be more cost effective to adjust anti-TNFα dosages according to serum drug concentrations1, 3,4
Conclusion:
This study met its objective of setting up and standardizing an independent laboratory for immunogenicity testing of anti-TNF biologics in India.
References:
1) Radstake TR, Svenson M, Eijsbouts AM, et al. Formation of antibodies against infliximab and adalimumab strongly correlates with functional drug levels and clinical responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2009;68: 1739 – 45.
2) Emi Aikawa N, de Carvalho JF, Artur Almeida Silva C, et al. Immunogenicity of Anti-TNF-alpha agents in autoimmune diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2010; 38(2-3): 82-9.
3) Mulleman D, Chu Miow Lin D, Ducourau E, et al. Trough infliximab concentrations predict efficacy and sustained control of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ther Drug Monit 2010; 32: 232–6.
4) Méric JC, Mulleman D, Ducourau E, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of infliximab in spondyloarthritis: an observational open-label study. Ther Drug Monit 2011; 33: 411–6.
Disclosure:
C. Ghia,
Medical Advisor,
3;
S. Akerkar,
Advisory Board Member,
5;
S. Sabnis,
None;
R. R. Uppuluri,
Speaker, consultant, and advisory board member ,
5;
G. Rambhad,
Associate Director Medical Services,
3.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analytical-and-clinical-evaluation-of-an-immunoassay-for-estimating-immunogenicity-of-infliximab-and-etanercept-in-indian-population/