Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disease that burdens ~3% of North Americans. ~24% of psoriatic patients develop psoriasis arthritis (PsA), an inflammatory disease which is often progressive and in its extreme form, PsA mutilans, causes permanent joint damage and functional disability. PsA is highly heritable; ~40% of patients with PsA have at least one close relative with psoriasis or PsA. Characterizing heritable and de novo genomic variations and cellular processes behind extreme cases of PsA is a promising approach for understanding molecular mechanisms behind PsA and identifying patients at high-risk of PsA mutilans early.
Methods: We conducted Whole Exome Sequences (WES) of 7 trios with PsA mutilans trios (probands with PsA satisfying CASPAR criteria and with arthritis mutilans and their parents), using NovSeq 6000 (Illumina) at depth 100X. We developed a bioinformatics pipeline to identify genes and pathways involved in PsA mutilans with three modules: 1) characterization of genetic variants using WES of PsA mutilans trios; 2) their integration using network-based methods to highlight pathways relevant to identified variants; 3) network analysis to identify genes and pathways to cellular mechanisms involved in PsA mutilans.
We used three available algorithms for detection of genomic variations. To discover systems level dependencies among genes and proteins to perform cellular tasks we integrated these variations with physical protein interaction networks. Next, we applied a graph-mining technique to detect network modules and several novel genes involved in PsA mutilans. Finally, we performed pathway enrichment analysis and characterized several statistically significant pathways involved in PsA mutilans.
Results: We found a subnetwork of 44 proteins [Figure 1A-B] having physical interactions with protein products of the genes identified by three variation detection methods [Table 1] suggesting implication of these 44 genes in triggered pathways in PsA mutilans. Pathway enrichment analysis highlighted WNT, NOTCH, NOTCH1, Adherens, Autophagy, and Apoptosis, suggesting their disruption in PsA mutilans [Figure 1C]. These pathways have been previously studied in psoriasis, PsA, and autoimmunity supporting relevance of identified genes and pathways to PsA mutilans. NTRK1 has the highest rank in the identified subnetwork. NTRK1, its interaction with NGF, and its mutations have previously been linked to autoimmune diseases, inflammatory arthritis, and psoriasis, and some groups are working on developing novel NGF/NTRK1-targeted therapies for these diseases. EED is another highly ranked gene in our list. Mutations in EED have been reported in several cases of over-growth disorders such as Cohen-Gibson and Weaver Syndromes. Its interaction with EZH2 (present in the list- not shown in Figure 1) has been reported to be important in psoriasis. EED mediates repression of gene activity through histone modifications.
Conclusion: Detecting heritable and de novo genomic variations by WES of PsA mutilans trios and application of network analysis has identified novel genes and pathways associated with PsA mutilans.
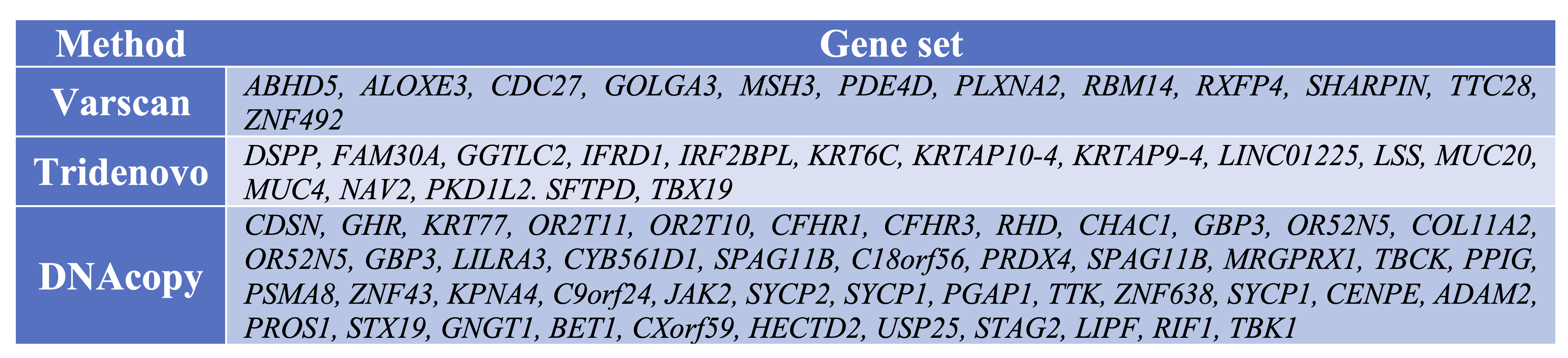 Table 1 List of genes with variants based on different methods.
Table 1 List of genes with variants based on different methods.
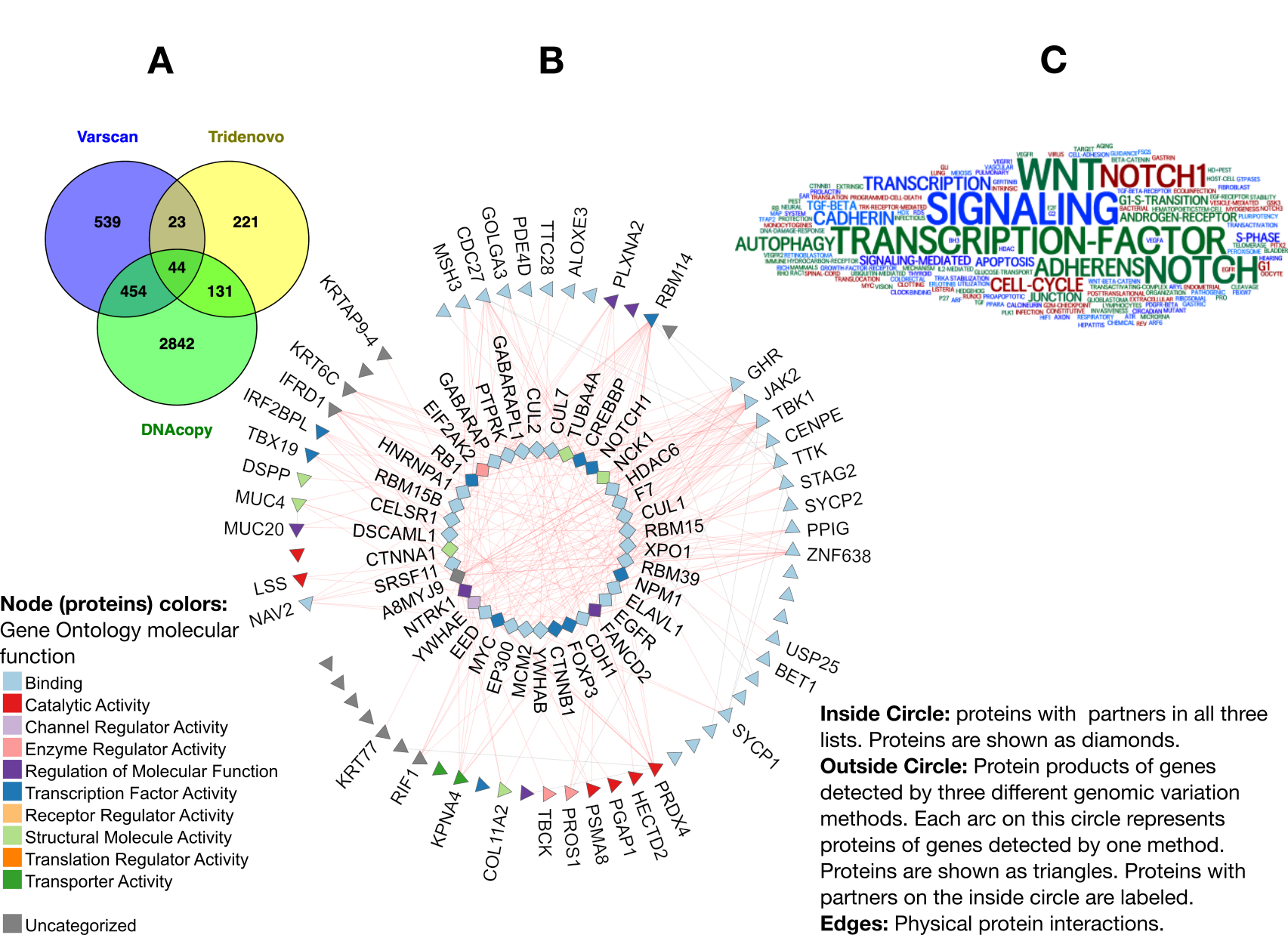 Figure 1 A. Venn diagram summarizing overlapping protein partners of genes detected through different methods (listed in Table 1). B. Protein interaction network of genes in the three lists. For details see legend. C. Results of pathways and term enrichment analysis of the 44 genes in the center of Venn diagram (ordered on the central circle in the network).
Figure 1 A. Venn diagram summarizing overlapping protein partners of genes detected through different methods (listed in Table 1). B. Protein interaction network of genes in the three lists. For details see legend. C. Results of pathways and term enrichment analysis of the 44 genes in the center of Venn diagram (ordered on the central circle in the network).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rahmati S, Li Q, Gladman D, Rahman P, Chandran V. An Integrative Approach to Identify Heritable and De Novo Genomic Variations in Psoriatic Arthritis Mutilans and Understand Its Systems Biology [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-integrative-approach-to-identify-heritable-and-de-novo-genomic-variations-in-psoriatic-arthritis-mutilans-and-understand-its-systems-biology/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-integrative-approach-to-identify-heritable-and-de-novo-genomic-variations-in-psoriatic-arthritis-mutilans-and-understand-its-systems-biology/
