Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Patient Reported Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Health-related quality of life is impacted in patients (pts) with psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Patient-reported outcomes (PROs) are an important means of measuring treatment improvements in PsA pts receiving systemic therapies such as methotrexate (MTX) and tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. PROs reported in the SEAM PsA randomized, controlled trial (RCT)* included SF-36 physical and mental component (PCS, MCS) scores and Health Assessment Questionnaire -Disability Index (HAQ-DI). Results showed significant differences in the SF-36 PCS mean change from baseline (BL) at week 24 in the etanercept (ETN)-containing arms compared to MTX-monotherapy (mono); similar improvements were seen across treatment groups in MCS and HAQ-DI.* Here we report results from analyses of all PROs measured in this RCT.
Methods: Pts with active PsA (N = 851) were randomized to receive 48 weeks of: MTX 20 mg weekly (N = 284), ETN 50 mg weekly (N = 284), or ETN 50 mg plus MTX 20 mg weekly (Combo; N = 283). PROs included: Patient global assessment of disease activity (PtGA); Patient global assessment of joint pain (PtGAJP); HAQ-DI; and SF-36 PCS, MCS, and 8 domains. Analyses included: least squares mean (LSM) changes from BL to week 24 comparing the ETN-containing arms to MTX mono; the proportion of pts reporting improvements ≥ minimal clinically important differences (MCID) at week 24, and the proportion of pts reporting scores ≥ age and gender matched normative values (A/G norms) at 24 weeks in HAQ-DI and SF-36 PCS, MCS, and 8 domains. Tests were not adjusted for multiplicity; P-values are nominal.
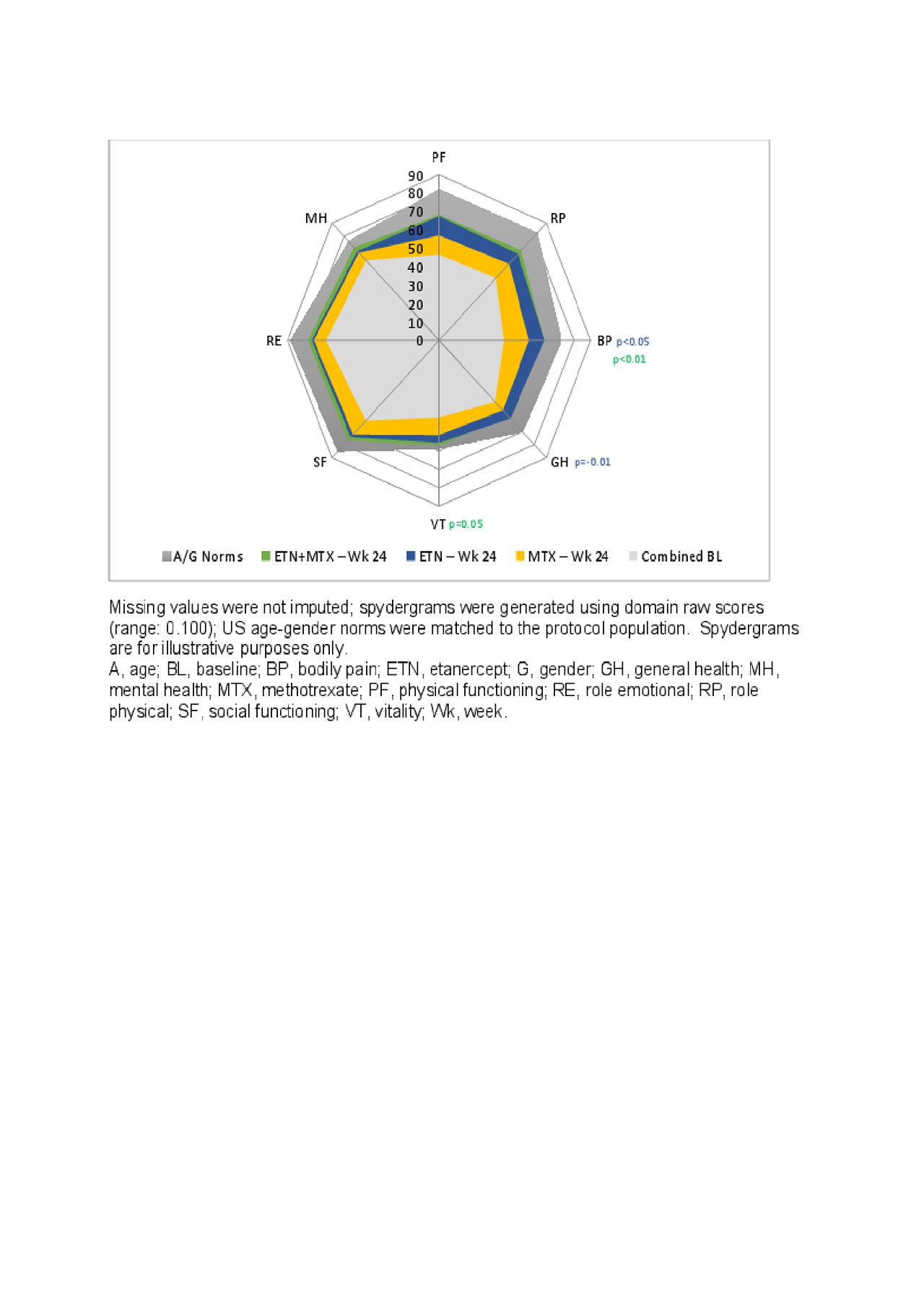
Results: PRO BL values were generally balanced across treatment arms. The largest LSM changes from baseline at week 24 were evident in PtGA, PtGAJP, and SF-36 PCS, with significant differences in both ETN-arms compared to MTX mono (Table 1). Compared to MTX mono, significantly larger differences were reported with ETN mono in the SF-36 Bodily Pain (BP) and General Health (GH) domains and with Combo in the SF-36 BP and Vitality (VT) domains (Figure 1).
Compared to MTX mono at week 24, significantly more pts reported improvements ≥ MCID with ETN mono in PtGA and with Combo in PtGAJP (Figure 2A).
Significantly higher proportions of pts in both the ETN mono and Combo arms reported scores ≥ A/G norms at week 24 compared to MTX mono in HAQ-DI; SF-36 PCS; and SF-36 physical function (PF), role physical (RP), BP, and GH domains. In addition to these, significantly higher proportion of patients receiving Combo reported scores ≥ A/G norms in SF-36 VT and mental health (MH) domains compared to MTX mono (Figure 2B). Continued improvements across PROs were reported through week 48.
Conclusion: In this RCT, significant and clinically meaningful improvements in PROs were reported with ETN mono and Combo compared to MTX mono. In general, pts in ETN-containing arms had greater improvements from BL in several PROs at week 24 compared to MTX mono, with higher percentages reporting improvements ≥ MCID and/or scores ≥ A/G norms.
*Mease et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Feb 12. doi: 10.1002/art.40851 [Epub ahead of print].
Linda Rice at Amgen Inc assisted in writing this abstract.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Mease P, Maksabedian E, Stolshek B, Liu L, Collier D, Kricorian G, Merola J. An Examination of Patient-Reported Outcomes Data from a Randomized Trial Examining Etanercept and Methotrexate as Monotherapy or in Combination in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-examination-of-patient-reported-outcomes-data-from-a-randomized-trial-examining-etanercept-and-methotrexate-as-monotherapy-or-in-combination-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-examination-of-patient-reported-outcomes-data-from-a-randomized-trial-examining-etanercept-and-methotrexate-as-monotherapy-or-in-combination-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis/