Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Treatments II: Potential Harms & Adverse Events (1998–2002)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: Low dose methotrexate (LD-MTX), a cornerstone in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, is associated with a moderately increased risk of anemia and leukopenia, but the risk of myelosuppression during LD-MTX use of up to 20mg/week remains incompletely described. We examined the hematologic outcomes among patients taking LD-MTX versus placebo in a large randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Methods: We pre-specified secondary analyses of a double-blind placebo-controlled RCT that included adults with known cardiovascular disease plus diabetes or metabolic syndrome in the US and Canada. Subjects with rheumatic disease were excluded. Subjects were randomly allocated to LD-MTX (20mg/week maximum) or placebo, and all subjects received folic acid 1mg daily for six days/week. Laboratory monitoring was performed every 1-2 months. Abnormal cell count definitions were pre-specified according to the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE v.5.0). We assessed the frequency of blindly adjudicated hematologic adverse events (AEs) and laboratory abnormalities.
Results: 2,391 subjects were randomized to LD-MTX (mean dosage 14.9 mg/week) and 2,395 to placebo. Simultaneous two-line cytopenias were infrequent in both the LD-MTX arm (n=92, 3.9%) and the placebo arm (n=70, 2.9%) during follow-up. Pancytopenia was rare but numerically more common among patients randomized to LD-MTX (n=13, 0.5%) versus placebo (n=6, 0.3%). We examined the cases of LD-MTX-associated pancytopenia in detail (see Table 1). Pancytopenia developed as soon as 4 months and as late as 3.5 years after beginning LD-MTX, though the latter subject was diagnosed with multiple myeloma a week prior. The median age of subjects who developed pancytopenia was 70.5 years (interquartile range, IQR 69, 75), compared to a median age of 65.6 years (IQR 59.7, 71.8) in the entire LD-MTX arm. The platelet counts in all 13 cases showed only mild reductions.
Figure 1 presents median hemoglobin levels and platelet and leukocyte counts during follow-up. Baseline values represent the end of the active follow-up period immediately before randomization. Between baseline and final study visits, median hemoglobin decreased in both arms: by 0.40g/dL (IQR -0.90, 0.10) in the LD-MTX arm and by 0.10g/dL (IQR -0.60, 0.30) in the placebo arm. White blood cell counts did not change in the LD-MTX arm (median change 0.00k/uL; IQR -0.90, 0.80) and increased by 0.20k/uL in the placebo arm (IQR -0.70, 1,10). The median platelet count did not change in the LD-MTX arm (median change 0.00k/uL; IQR, -18, 16k/uL) but decreased by 9k/uL (IQR -26, 9) in the placebo arm.
Conclusion: Among subjects using LD-MTX, simultaneous two-line cytopenias and pancytopenia were uncommon. The absolute reductions in hemoglobin were small, white blood cell counts did not change between baseline and end of follow-up, and platelet counts decreased in the placebo arm but not in LD-MTX. These findings offer reassurance about the hematologic safety of LD-MTX.
 Hgb, hemoglobin; WBC, white blood cell count; PLT, platelet count; LD-MTX, low dose methotrexate
Hgb, hemoglobin; WBC, white blood cell count; PLT, platelet count; LD-MTX, low dose methotrexate
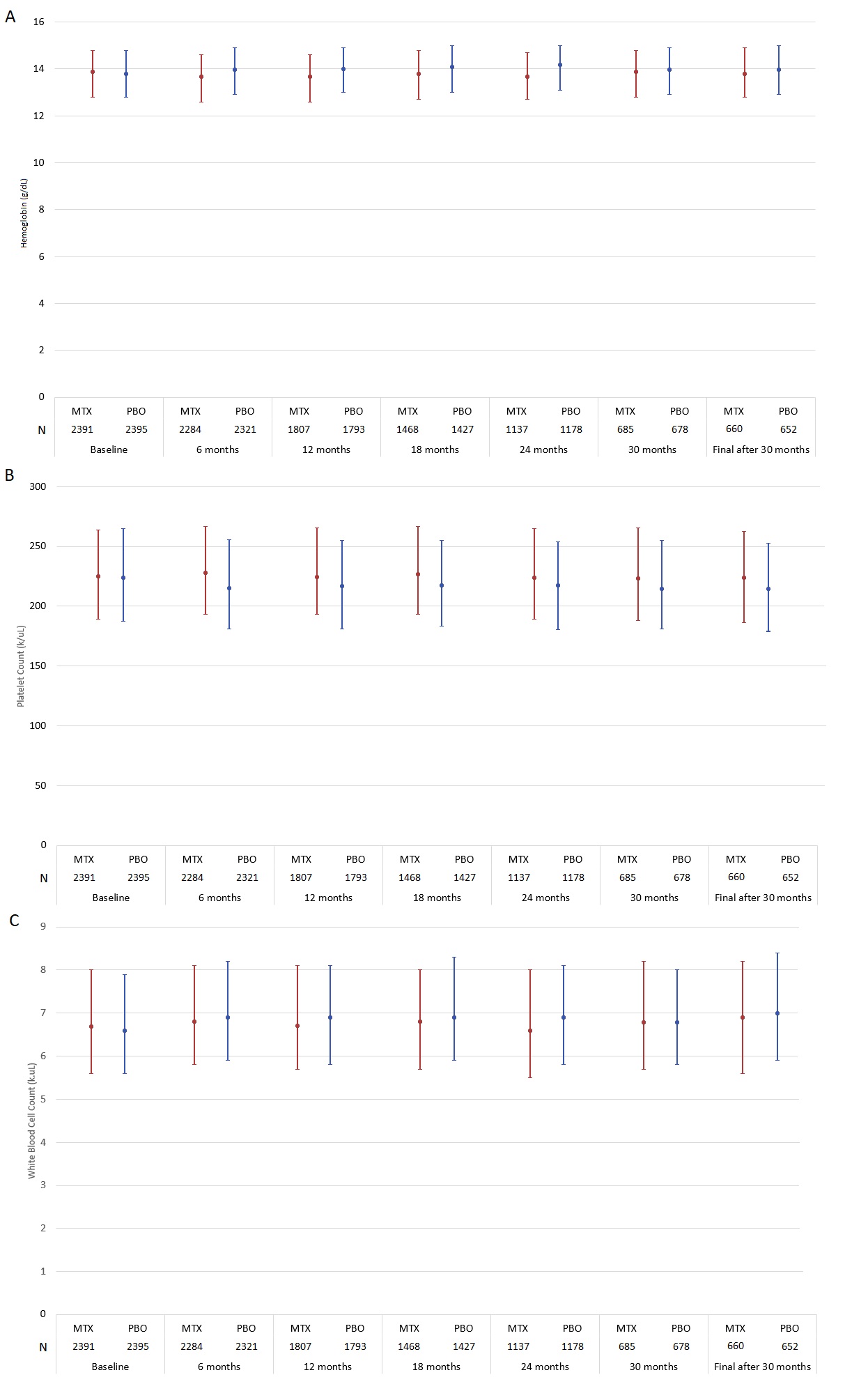 This figure represents the median (filled circle) and interquartile range for (A) hemoglobin, (B) platelet count and (C) white blood cell (WBC) count during the CIRT trial. Compared to baseline, by the end of the study, the median hemoglobin value among patients randomized to LD-MTX decreased by 0.4 g/dL (IQR -0.90, 0.10) and decreased by 0.1 mg/dL (IQR -0.60, 0.30) among those randomized to placebo. The median platelet count did not change in the LD-MTX arm (IQR -18, 16 k/uL) and decreased by 9 k/uL (IQR -26, 9) among those randomized to placebo. The median WBC count did not change in the LD-MTX arm (IQR -0.90, 0.80) and increased by 0.2 k/uL (IQR -0.70, 1.10) in the placebo arm. LD-MTX, low dose methotrexate. PBO, placebo.
This figure represents the median (filled circle) and interquartile range for (A) hemoglobin, (B) platelet count and (C) white blood cell (WBC) count during the CIRT trial. Compared to baseline, by the end of the study, the median hemoglobin value among patients randomized to LD-MTX decreased by 0.4 g/dL (IQR -0.90, 0.10) and decreased by 0.1 mg/dL (IQR -0.60, 0.30) among those randomized to placebo. The median platelet count did not change in the LD-MTX arm (IQR -18, 16 k/uL) and decreased by 9 k/uL (IQR -26, 9) among those randomized to placebo. The median WBC count did not change in the LD-MTX arm (IQR -0.90, 0.80) and increased by 0.2 k/uL (IQR -0.70, 1.10) in the placebo arm. LD-MTX, low dose methotrexate. PBO, placebo.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vanni K, Berliner N, Paynter N, Glynn R, MacFadyen J, Colls J, Lu F, Xu C, Ridker P, Solomon D. Adverse Effects of Low Dose Methotrexate: Adjudicated Hematologic Outcomes in a Large Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adverse-effects-of-low-dose-methotrexate-adjudicated-hematologic-outcomes-in-a-large-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adverse-effects-of-low-dose-methotrexate-adjudicated-hematologic-outcomes-in-a-large-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-trial/
