Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is an antimalarial agent used commonly to treat selected autoimmune rheumatic diseases because of its therapeutic benefits, low cost, and favorable safety profile. While minor side effects may occur, the most feared toxicity is retinal thinning with irreversible loss of vision. The February 2011 American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) Revised Recommendations on Screening for Hydroxychloroquine Retinopathy advise a three-component baseline evaluation prior to initiation of therapy: 1)retinal exam, 2)Humphrey 10-2 visual-fields, and 3)either multifocal-electroretinogram, spectral-domain optical coherence tomography or fundus autofluorescence.
Methods: In this descriptive study, we utilized Highmark medical and pharmacy claims data to examine adherence to baseline screening recommendations in rheumatic disease patients initiating HCQ. We also explored ophthalmologic screening patterns in patients with ≥1 risk factor for development of retinal toxicity (“high risk” patients) and in rheumatic disease diagnostic subsets.
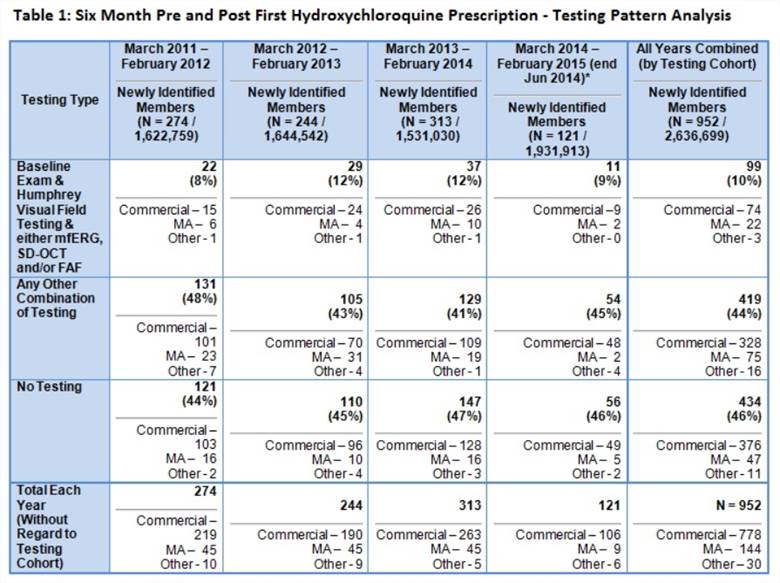
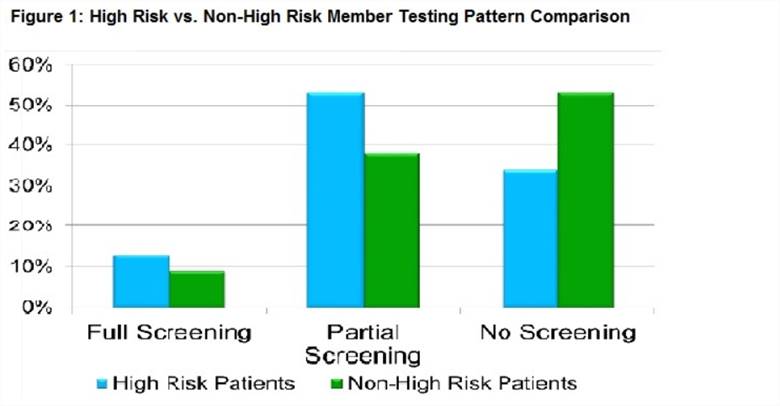
Results: From March 2011 through June 2014, 952 rheumatic disease patients initiated HCQ; 10% received the recommended 3 component ophthalmology screening, 44% completed partial screening, and 46% had no baseline eye evaluation (Table 1). Patients with commercial type insurance are more likely to complete screening than those with other types (Table 1). Of the 367 “high risk” patients, 13% had full screening, 53% had partial screening, and 34% had no baseline evaluation (Figure 1). Adherence patterns did not substantially differ by diagnostic subsets. In multivariable logistic regression analysis, the only predictor of full baseline screening was a history of retinal disease (Table 2).
Conclusion: Adherence rates to AAO recommendations for retinal baseline screening in rheumatic disease patients initiating HCQ are quite low, though somewhat better in those with risk factors for retinal toxicity. Our findings suggest that education of practitioners and patients is warranted to improve adherence to screening guidelines and optimize safe prescribing patterns.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Payne C, Gladowski P, Byers J Jr., Tang A, Wasko MCM. Adherence Patterns to American Academy of Ophthalmology Guidelines for Hydroxychloroquine Baseline Screening: Quality Assurance Assessment Utilizing Highmark Claims Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adherence-patterns-to-american-academy-of-ophthalmology-guidelines-for-hydroxychloroquine-baseline-screening-quality-assurance-assessment-utilizing-highmark-claims-data/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adherence-patterns-to-american-academy-of-ophthalmology-guidelines-for-hydroxychloroquine-baseline-screening-quality-assurance-assessment-utilizing-highmark-claims-data/