Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Spondyloarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis – Clinical Aspects and Treatment Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Structural damage in the spine is an important determinant of the functional status and spinal mobility in axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). Already present syndesmophytes, elevated C-reactive protein, cigarette smoking, and to a lesser extent male sex are routine clinical parameters predicting radiographic spinal progression in axSpA. In the last years, several biomarkers with a predictive value for radiographic spinal progression were identified. It is, however, not known, if biomarkers have a meaningful added value over clinical parameters in prediction of radiographic spinal progression in axSpA.
The objective of the study was to examine whether adding biomarkers to the routine clinical parameters would improve prediction of radiographic spinal progression in axSpA.
Methods:
Altogether 120 patients with radiographic axSpA who completed a 2-year clinical and radiographic follow-up in the ENRADAS trial were included. Structural damage in the spine was assessed on spinal radiographs at baseline and year 2 according to the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS). Radiographic spinal progression was defined as a worsening of the mSASSS by ≥2 points after 2 years. Clinical predictors of radiographic spinal progression at baseline included syndesmophytes, elevated (>5mg/L) CRP, cigarette smoking, and sex. Serum biomarkers measured at baseline included: matrix metalloproteinase-3, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), calprotectin, leptin, high molecular weight adiponectin (HMW-APN), ostoprotegerin, sclerostin, N-terminal telopeptide, procollagen type II N-terminal propeptide, and serum amyloid A (SAA).
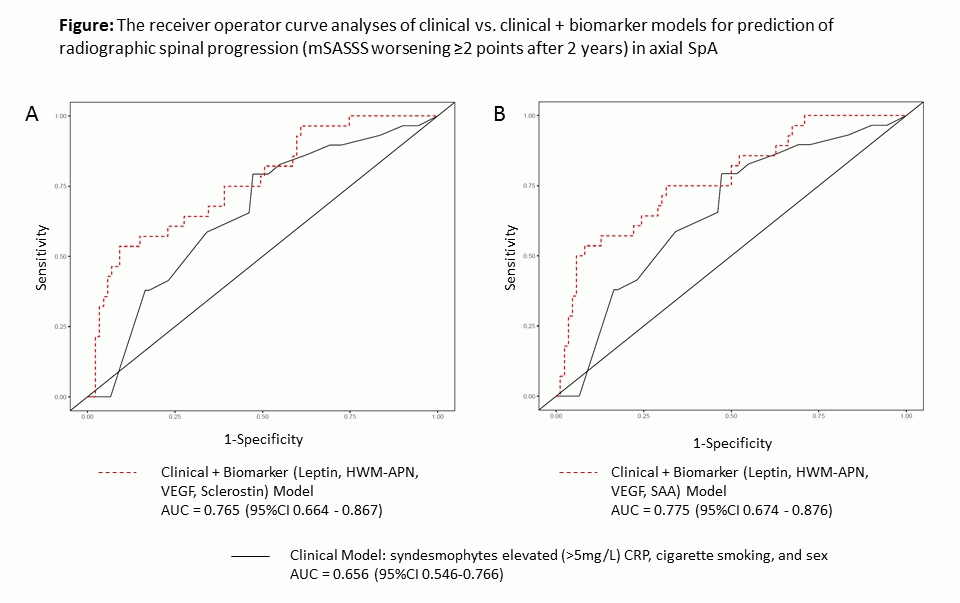
Results: Repeated cross-validation analysis revealed two biomarker combinations: (1) Leptin + HWM-APN + VEGF + Sclerostin and (2) Leptin + HWM-APN + VEGF+ SAA with added predictive value compared to the clinical model (syndesmophytes, smoking, elevated CRP, and sex). Adding these biomarker combinations to the clinical model resulted in improvement of the predictive value reflected by the Area Under the Curve (AUC): AUCClinical+Biomarkers(1)=0.765 (95%CI 0.664-0.867) and AUCClinical+Biomarkers(2)=0.775 (95%CI 0.674-0.876) vs. AUCClinical=0.656 (95%CI 0.546-0.766) – figure. The average prediction error (APE) of the Clinical+Biomarker(1) and Clinical + Biomarker(2) models were 0.227 and 0.229, respectively as compared to the APE for the pure clinical model (0.248). These findings were supported by the results of stability analyses.
Conclusion:
Biomarkers are able to improve prediction of radiographic spinal progression in axSpA if used in addition to the clinical parameters, but the added value seems to be rather small.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tietz L, Le L, Hartl A, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J, Mansmann U, Poddubnyy D. Added Value of Biomarkers Compared to Routine Clinical Parameters for the Prediction of Radiographic Spinal Progression in Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/added-value-of-biomarkers-compared-to-routine-clinical-parameters-for-the-prediction-of-radiographic-spinal-progression-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/added-value-of-biomarkers-compared-to-routine-clinical-parameters-for-the-prediction-of-radiographic-spinal-progression-in-axial-spondyloarthritis/