Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 13, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients (pts) with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA), conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs), preferably methotrexate (MTX), are recommended as first line therapy.1,2 For pts who remain in moderate to high disease activity (HDA), despite csDMARDs, TNF inhibitors are a potential treatment option.1 The purpose of this analysis was to evaluate clinical, functional, and radiographic outcomes following the addition of adalimumab (ADA) to a subgroup of MTX insufficient responders (IR) who experienced rapid radiographic progression (RRP) and/or remained in HDA.
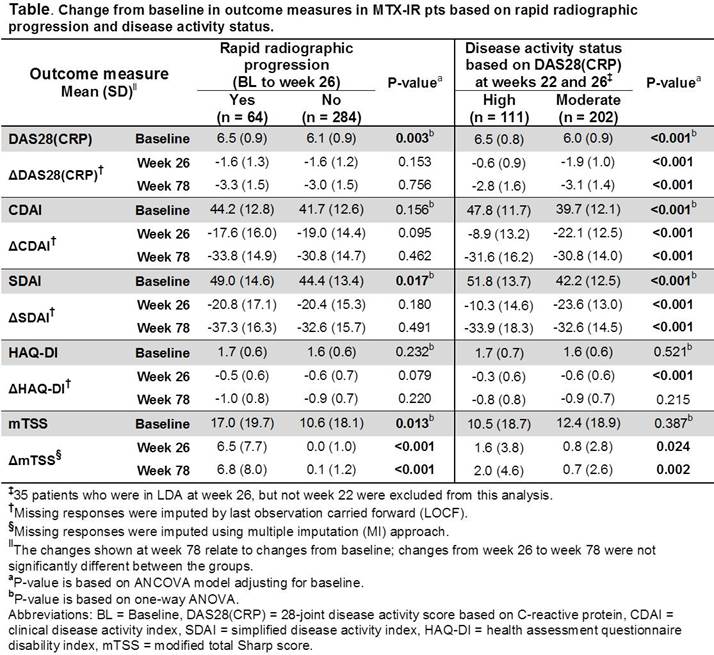
Methods: OPTIMA3 was a 78-week (wk) randomized, double-blind, double-period trial comparing safety and efficacy of ADA+MTX with placebo (PBO)+MTX in early RA pts. This post hoc analysis included pts who received PBO+MTX for 26 wks (Period 1) and did not achieve stable low disease activity [LDA, DAS28(CRP) <3.2] at wks 22 and 26. These MTX-IR pts received open-label (OL) ADA+MTX for a subsequent 52 wks (Period 2) and were categorized at wk 26 by 1) whether they experienced RRP [change from baseline (BL) in modified total Sharp score (mTSS) >1.5] and 2) disease activity [HDA = DAS28(CRP) ≥5.1 or moderate (MDA) = 3.2≤ DAS28(CRP) <5.1]. For each subgroup, BL values and changes from BL in DAS28(CRP), CDAI, SDAI, HAQ-DI, and mTSS were analyzed.
Results: At wk 26, 348 (75.7%) PBO+MTX pts did not achieve stable LDA and received OL ADA+MTX for up to 52 wks. Among these MTX-IR pts, 64 (18.5%) experienced RRP during Period 1; 111 (31.9%) and 202 (58.0%) were in HDA or MDA, respectively. Pts experiencing RRP had significantly higher mean BL DAS28(CRP), SDAI, and mTSS compared with non-RRP pts (Table). Following ADA addition, mean DAS28(CRP) and SDAI decreased in RRP pts to levels that were comparable with those observed in non-RRP pts; while mean mTSS did not progress further in both groups. MTX-IR pts who remained in HDA, versus those in MDA, had significantly higher mean BL disease activity scores and less clinical and functional improvements at wk 26, indicating that high BL activity may be a predictor of poor response to initial MTX therapy (Table). Importantly, regardless of wk 26 disease activity status, the addition of ADA resulted in a decrease in mean disease activity and HAQ-DI; among pts starting Period 2 in MDA, but not HDA, mean disease activity scores fell below the LDA threshold after 52 wks of OL ADA+MTX therapy.
Conclusion: The addition of ADA in early RA pts with a poor response to initial MTX therapy led to a reduction in disease activity and prevention of further radiographic progression. Nearly 20% of pts accumulated radiographic damage during the 26 wks of MTX exposure; the identification of unique characteristics within these pts may allow for a differential therapeutic approach to preserve structural integrity. References:
- Singh JA, et al., Arthritis Care Res, 2016; 68(1):1-25.
- Smolen JS, et al., Ann Rheum Dis, 2014; 73(3):492-509.
- Smolen JS, et al., Lancet, 2014; 383:321-32.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smolen JS, van Vollenhoven RF, Wolfe BA, Chen S, Suboticki JL, Kavanaugh A. Adalimumab (HUMIRA) Halts Radiographic Progression and Reduces Disease Activity in Patients with a Poor Initial Response to Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adalimumab-humira-halts-radiographic-progression-and-reduces-disease-activity-in-patients-with-a-poor-initial-response-to-methotrexate/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/adalimumab-humira-halts-radiographic-progression-and-reduces-disease-activity-in-patients-with-a-poor-initial-response-to-methotrexate/