Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Acupuncture has been widely used for pain relief in adults. Evidence on effects of acupuncture for pediatric chronic musculoskeletal pain is scarce. We have reviewed existing randomized controlled trials, expecting to summarize the high-quality evidence of acupuncture on chronic musculoskeletal pain before advocating it in the pediatric population.
Methods: Methods: We performed a comprehensive search in MEDLINE as well as reference lists until June 2019. Selection criteria included: chronic musculoskeletal pain, randomized controlled trials, sample size ≥20.
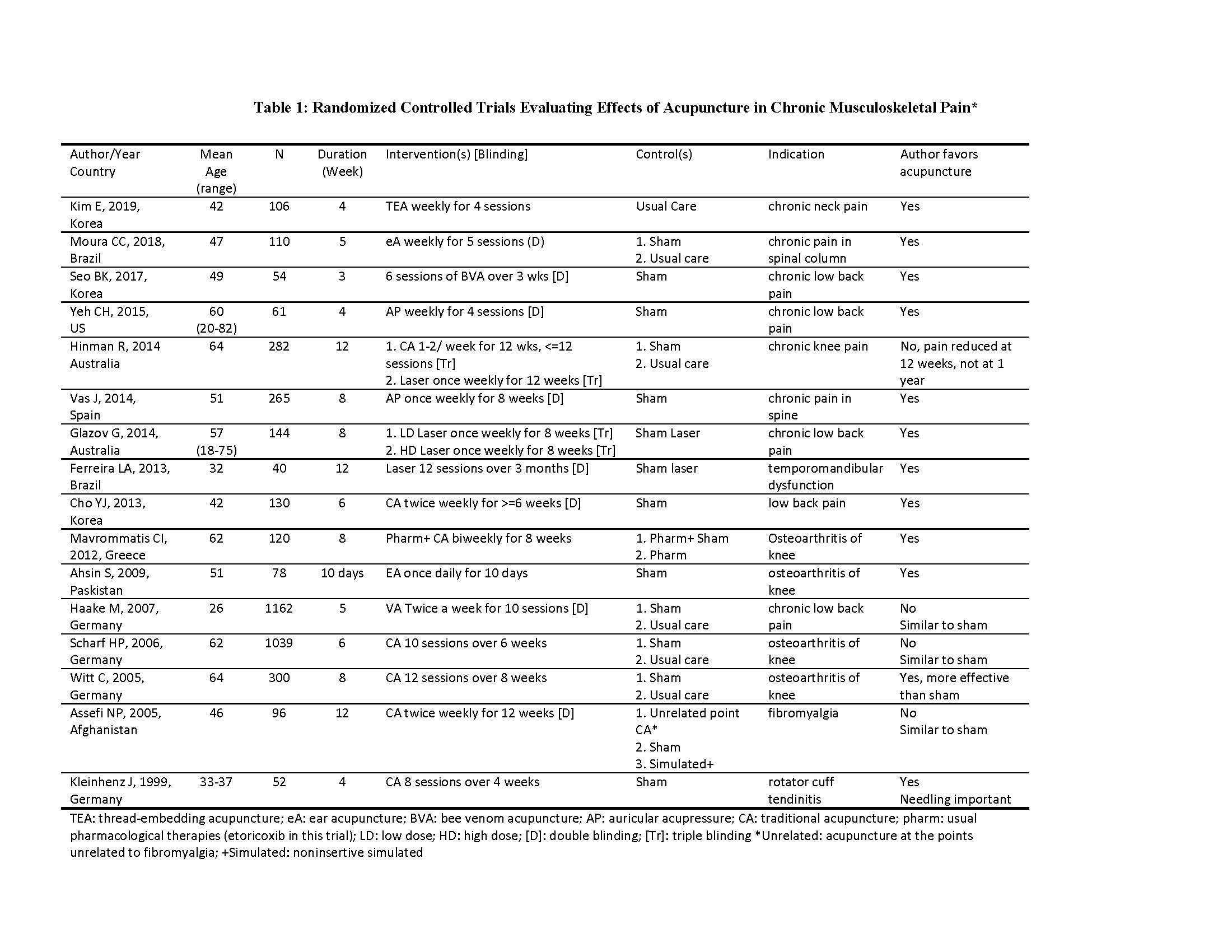
Results: Results: We identified 16 randomized controlled trials with a total of 4039 subjects met the eligibility criteria. All the subjects were age 18 or older, with most of them middle aged. Number of trials included chronic pain in temporomandibular joint (1), neck (1), back or spine (7), knee (5), fibromyalgia (1) and rotator cuff tendinitis (1). Seven trials used traditional Chinese acupuncture, two used auricular acupressure, two used verum or bee venom acupuncture, one used electro-acupuncture, two used laser with acupuncture, and one used thread-embedding acupuncture. Ten of the 16 trials (62.5%) were either double or triple blinded. Mean treatment duration was 6.6 weeks (range from 10 days to 12 weeks). Table 1 summarizes the trials evaluating the effect of acupuncture on pain and the authors’ conclusions whether the acupuncture therapies were favorable. Of the 16 trials, 12 (75%) reported that the acupuncture therapy was effective compared to a variety of control groups; nine of those trials reported better pain reduction of acpunture s than sham/placebo groups. Among those 10 trials with double or triple blinded design, 7 out of 10 trials (70%) suggested acupuncture favorable. However, 4(25%) suggested that acupuncture was not more effective than the controlled/sham groups. One trial did show a pain reduction in acupuncture groups at 12 weeks but effects did not sustain at 1-year follow up.
Conclusion: Conclusion: Our review showed a mixed result in the effect of acupuncture in pain relief for chronic musculoskeletal pain. The majority of the trials suggested that acupuncture maybe effective beyond the placebo effect. To date, there are no high-quality trials in pediatric population. Rigorous and well-controlled randomized trials in pediatric population are warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang Y, Wang C. Acupuncture for Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: A Review of Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/acupuncture-for-chronic-musculoskeletal-pain-a-review-of-randomized-controlled-trials/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/acupuncture-for-chronic-musculoskeletal-pain-a-review-of-randomized-controlled-trials/