Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) negatively impacts patients’ physical health and functional ability, which can contribute to reduced work productivity.1,2 We examined the association between achieving stringent disease control criteria and improvements in work productivity in patients with PsA to 1 year, using data from two phase 3 trials.
Methods: This post hoc analysis used data from two phase 3 studies of subcutaneous bimekizumab 160 mg every 4 weeks: BE OPTIMAL (NCT03895203; biologic DMARD [bDMARD]-naïve) and BE COMPLETE (NCT03896581; TNF inhibitor inadequate response/intolerance [TNFi‑IR]). Both studies were double-blind and placebo-controlled to Week 16. Patients who completed Week 52 of BE OPTIMAL or Week 16 of BE COMPLETE could enter the BE VITAL open-label extension (NCT04009499). Data are reported for patients randomized to BKZ at baseline.
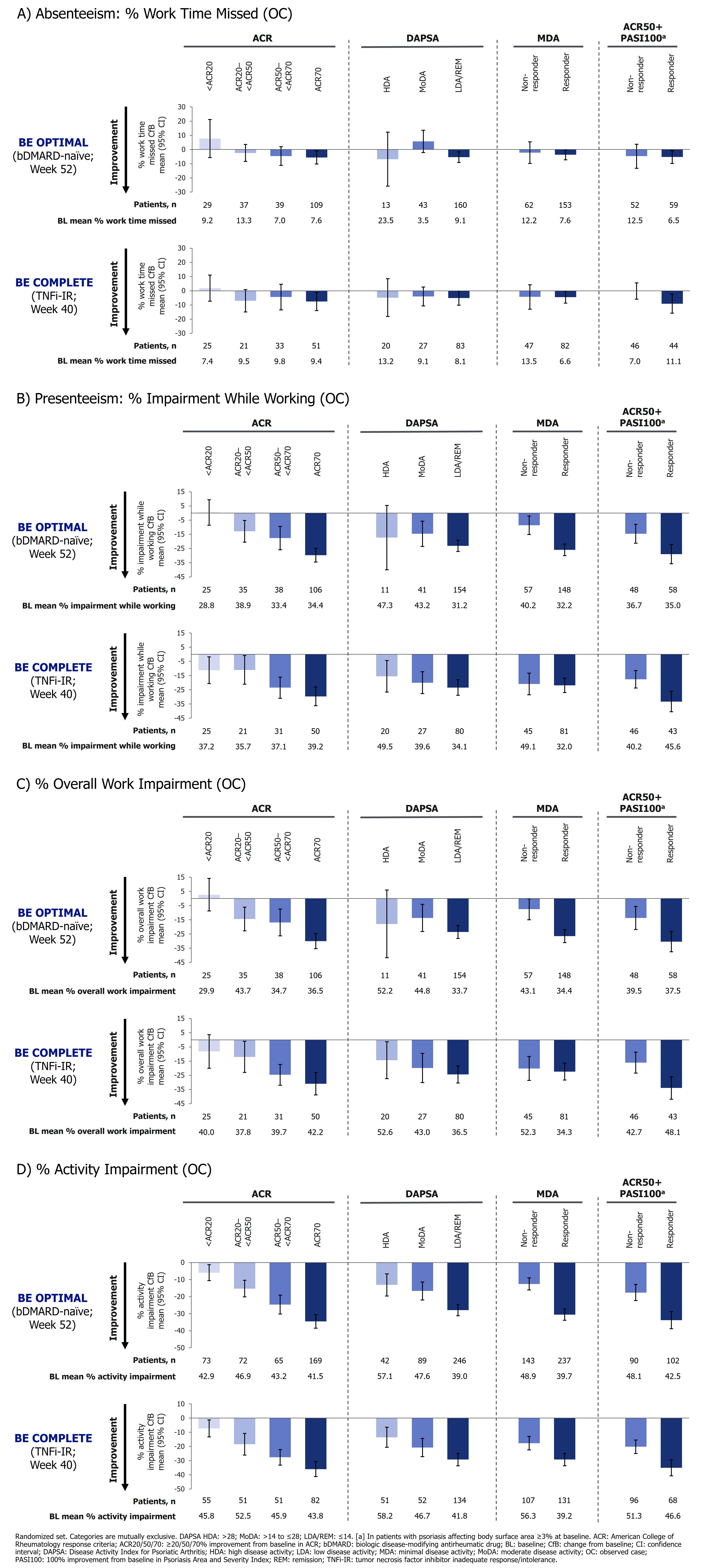
Clinical endpoints used to assess disease control included ACR response criteria, Disease Activity Index for PsA (DAPSA), minimal disease activity (MDA), and the composite endpoint ACR ≥50% improvement from baseline and Psoriasis Area and Severity Index 100% improvement from baseline (ACR50+PASI100). Work Productivity and Activity Impairment (WPAI) was assessed to Week 52 in BE OPTIMAL and to Week 40 in BE COMPLETE. Work productivity dimensions reported include work time missed (absenteeism), impairment while working (presenteeism), overall work impairment, and activity impairment.
We assessed associations between achievement of disease control criteria (mutually exclusive categories) and percentage improvements from baseline in each WPAI dimension score, at Week 52 of BE OPTIMAL and Week 40 of BE COMPLETE (observed case).
Results: 388/431 (90.0%) and 246/267 (92.1%) BKZ-randomized patients completed Week 52 of BE OPTIMAL and Week 40 of BE COMPLETE, respectively. Baseline mean percentage WPAI scores were similar for bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR patients: absenteeism 7.7 and 9.7; presenteeism 34.8 and 38.0; overall work impairment 37.0 and 40.7; activity impairment 43.2 and 46.5.
At Week 52/40, patients achieving more stringent disease control criteria, assessed using ACR, DAPSA, MDA, and ACR50+PASI100 responses, generally demonstrated greater improvements in work productivity, particularly in the WPAI domains of presenteeism, overall work impairment, and activity impairment (Figure). Similar improvements were observed in bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR patients, though improvements in work productivity in MDA responders vs non-responders were more pronounced in bDMARD-naïve patients compared with TNFi-IR patients.
Improvements in work time missed (absenteeism) were smaller than other WPAI domains; thus, trends were less pronounced when assessing the association of absenteeism by disease control criteria response groups (Figure 1A).
Conclusion: Achievement of increasingly stringent disease control criteria and lower disease activity was associated with greater improvements in work productivity up to 1 year in patients with PsA. Similar improvements were observed in bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR patients.
References: 1. Gudu T. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2018;14:405–17; 2. Husni ME. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;47:351–60.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tillett W, Gladman D, Gossec L, Eells J, Healy P, Ink B, Lyris N, Walsh J. Achieving Stringent Disease Control Criteria Was Associated with Greater Work Productivity Improvements in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies of Bimekizumab [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achieving-stringent-disease-control-criteria-was-associated-with-greater-work-productivity-improvements-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies-of-bimekizumab/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achieving-stringent-disease-control-criteria-was-associated-with-greater-work-productivity-improvements-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-studies-of-bimekizumab/