Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: A treat-to-target approach in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) was recommended by EULAR and GRAPPA to achieve remission (REM) or low disease activity (LDA), by regular disease activity assessment and therapeutic adjustment.1,2 Disease activity index for psoriatic arthritis (DAPSA) or the minimal disease activity (MDA) are considered for defining REM/LDA in secukinumab (SEC) treated patients (pts) with PsA.3 Very low disease activity (VLDA) is a more stringent measure compared to MDA in defining REM/LDA.4 Currently, limited reports are available on pts with PsA achieving sustained REM in clinical trials or real-world evidence, using these stringent criteria. Here, we report an exploratory analysis on sustained REM/LDA in pts with PsA treated with SEC and its impact on health-related quality of life (QoL) and physical function, in the FUTURE 5 study (NCT02404350).
Methods: FUTURE 5 is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled 2-year phase 3 trial in pts with active PsA. The study design has been previously reported.5 Pts randomized to SEC 150 mg could be escalated to 300 mg from Week (Wk) 52 to 104, based on investigators’ judgement. The pts were categorized as either achieving REM/LDA once only or sustained REM/LDA, which was defined as pts who achieved REM/LDA between Wk 24-52 and maintained the same response at least 2 of the next 6 visits (visit every 8 wks). Of pts who achieved REM/LDA (VLDA, DAPSA REM, MDA, DAPSA LDA+REM) between Wk 24 and 52, the relationship between REM/LDA, sustained REM/LDA and physical function (health assessment questionnaire disability index [HAQ-DI]), QoL (short form-36 physical component score [SF-36 PCS]) were assessed. To assure that sustainability of responses were uniformly assessed for all pts at the same time period, only pts who completed the 2-year study with no missing REM/LDA assessment at Wks 24 and 104 were evaluated.
Results: In total, 996 pts were randomized to one of 4 treatment groups: SEC 300 mg loading dose (LD; N=222), SEC 150 mg LD (N=220), SEC 150 mg no loading dose (NL; N=222), and placebo (N=332). The baseline clinical characteristics were comparable across treatment groups. A total of 48-62% and 19-36% of all SEC-treated groups, respectively achieved sustained LDA (DAPSA LDA+REM or MDA) and sustained REM (DAPSA REM or VLDA) in at least three visits (Table 1). Higher improvements in QoL (SF-36 PCS) (Table 2) and physical function (HAQ-DI) were observed from baseline to Wk 104 in pts who had achieved sustained REM or LDA when compared with pts who had not achieved this or who had achieved this only once.
Conclusion: The majority of pts treated with SEC were able to achieve sustained REM/LDA. Sustained LDA/REM was associated with higher improvement of QoL and physical function compared to pts who achieved this response at only one visit.
References:
- Gossec L, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:700–712.
- Ogdie A, et al. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(1):i37‐i46.
- Coates LC, et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. (ahead of print)
- Coates LC, et al. J Rheumatol. 2018;46(1):38-42.
- van der Heijde D, et al. Rheumatology. 2020;59(6):1325‐1334.
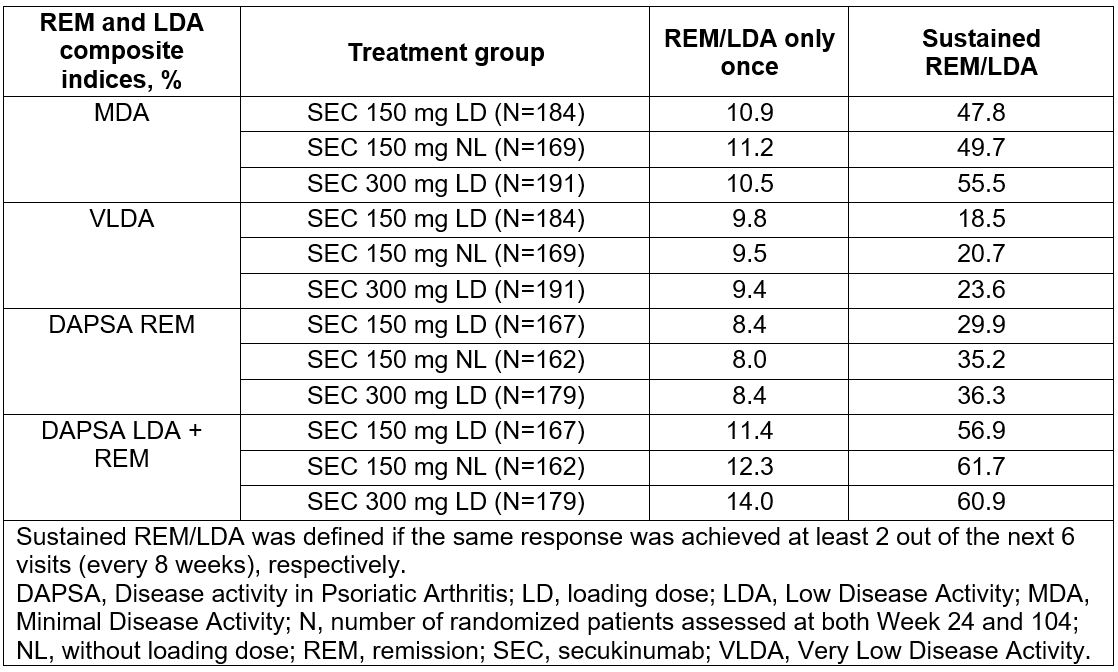 Table 1: Proportion of patients achieving remission or low disease activity
Table 1: Proportion of patients achieving remission or low disease activity
 Table 2: Summary of change from baseline in SF36-PCS at Week 104 by REM/LDA and sustained REM/LDA status
Table 2: Summary of change from baseline in SF36-PCS at Week 104 by REM/LDA and sustained REM/LDA status
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates L, Mease P, Gladman D, Navarra S, Bao W, Gaillez C. Achievement of Sustained Remission and Low Disease Activity with Secukinumab Improves Quality of Life and Physical Function in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from a Randomized Phase 3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-sustained-remission-and-low-disease-activity-with-secukinumab-improves-quality-of-life-and-physical-function-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-randomized-phase-3-stud/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-sustained-remission-and-low-disease-activity-with-secukinumab-improves-quality-of-life-and-physical-function-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-randomized-phase-3-stud/
