Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
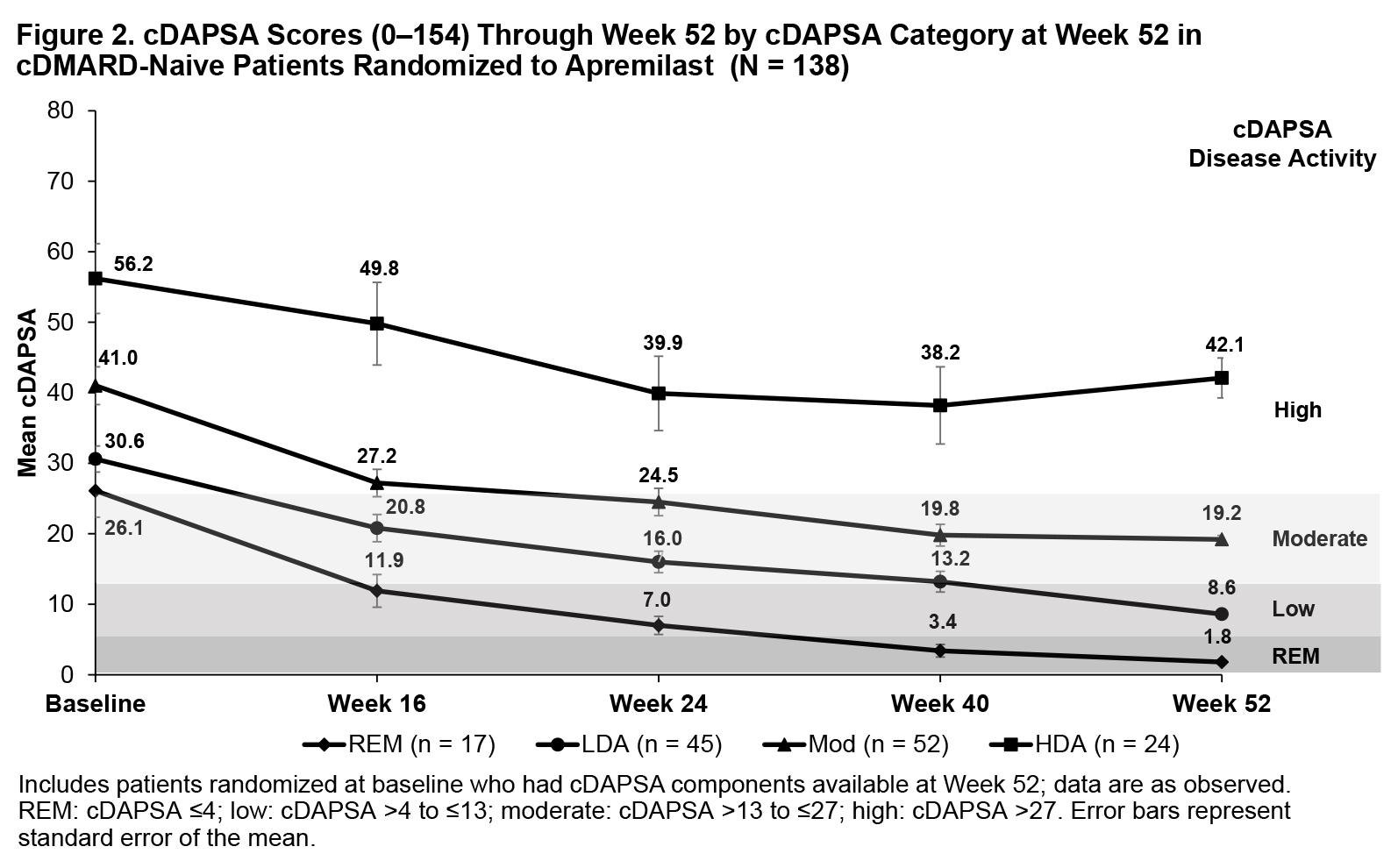
Background/Purpose: Phase III PALACE 4 (NCT01307423) assessed the efficacy of apremilast (APR) in DMARD-naive patients with PsA. The Routine Assessment of Patient Index Data 3 (RAPID3 [0-30]) evaluates disease activity derived from patients’ self-reported measures, including HAQ-DI or multidimensional HAQ, Pain visual analog scale (VAS), and Patient’s Assessment of Disease Activity (PtGA) VAS. The Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA [0-154]) includes objective and subjective physician assessments (ie, swollen and tender joints counts [SJC and TJC]) and the Patient’s Assessment of Pain and PtGA VAS scores. Among patients receiving APR in the DMARD-naive PALACE 4 trial, we examined trajectories for improving RAPID3 scores for those achieving RAPID3 near remission (REM) or low severity, cDAPSA scores among those achieving cDAPSA REM or low disease activity (LDA), and PsA manifestations not measured by either outcome by Wk 52.
Methods: DMARD-naive patients in PALACE 4 who were randomized to receive APR 30 mg BID at baseline with available scores on RAPID3 and/or cDAPSA components at Wk 52 were included and grouped according to RAPID3 categories at Wk 52 using RA cutoffs (near REM: ≤3; low severity: >3-≤6; moderate severity: >6-≤12; and high severity: >12-30) and cDAPSA categories at Wk 52 (REM: ≤4; LDA: >4-≤13; moderate disease activity: >13-≤27; high disease activity: >27). Mean RAPID3 and cDAPSA scores were assessed from baseline through Wk 52. Other measures of PsA disease activity were reported longitudinally by RAPID3 and cDAPSA categories at Wk 52.
Results: The RAPID3 analysis included 139 APR patients; the cDAPSA analysis included 138 APR patients. Achievement of near REM or low severity (RAPID3) or REM or LDA (cDAPSA) by Wk 52 with APR were associated with improvements over time in mean RAPID3 (Figure 1) and cDAPSA (Figure 2) trajectories, with observable improvement at Wk 16. Patients achieving RAPID3 or cDAPSA treatment targets at Wk 52 had mild or resolved articular involvement at Wk 52. Achievement of treatment targets was also associated with improvements in extra-articular disease activity at Wk 52, although not all manifestations were as well controlled in patients achieving RAPID3 treatment targets (Table). In the RAPID3 and cDAPSA analyses, improvements in SJC and TJC were observed for patients with REM or low severity (RAPID3) or REM or LDA (cDAPSA) at Wk 52. In the RAPID3 analysis, mean TJC was higher than expected at Wk 52 in patients achieving low severity. The Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score was the only measure for which a pattern of greater improvement for the near RAPID3 REM/cDAPSA REM group vs the RAPID3 low severity/cDAPSA LDA group was not observed; it was numerically lower in cDAPSA REM vs LDA and numerically higher in RAPID3 REM vs low severity.
Conclusion: DMARD-naive patients achieving RAPID3 and cDAPSA targets with APR showed early and sustained improvements to Wk 52 with continued treatment. Achievement of treatment targets was associated with improvements in other domains not captured directly by RAPID3 or cDAPSA (eg, dactylitis, enthesitis). As shown in a prior analysis, RAPID3 LDA was associated with higher residual TJC than what would be expected from this categorization.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Kavanaugh A, Ogdie A, Wells A, Bergman M, Gladman D, Richter S, Brunori M, Teng L, Guerette B, Smolen J. Achievement of RAPID3 and cDAPSA Treatment Targets Is Associated with Control of Articular and Extra-Articular Manifestations of Active Psoriatic Arthritis in DMARD-Naive Patients Treated with Apremilast [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-rapid3-and-cdapsa-treatment-targets-is-associated-with-control-of-articular-and-extra-articular-manifestations-of-active-psoriatic-arthritis-in-dmard-naive-patients-treated-with-apremil/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-rapid3-and-cdapsa-treatment-targets-is-associated-with-control-of-articular-and-extra-articular-manifestations-of-active-psoriatic-arthritis-in-dmard-naive-patients-treated-with-apremil/