Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Treatment goals in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are moving toward attainment of absolute therapeutic thresholds rather than relative improvement. Minimal disease activity (MDA), a composite endpoint of up to 7 individual measures, has been recommended as an appropriate aim in PsA.
Methods: Data were analyzed from an integrated database of 2 double-blind, phase III SPIRIT trials investigating the efficacy and safety of ixekizumab (IXE), a high-affinity monoclonal antibody selectively targeting interleukin-17A, for patients with active PsA. The integrated database consisted of patients who were biologic DMARD naive (SPIRIT-P1, NCT01695239) or who had an inadequate response or were intolerant to TNF inhibitors (SPIRIT-P2; NCT02349295). Patients were randomized to placebo (n = 224) or 80 mg IXE every 4 weeks (IXEQ4W, n = 229) or every 2 weeks (IXEQ2W, n = 226) after a 160 mg starting dose. Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) and productivity were evaluated using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36; higher scores indicate better functioning), European Quality of Life 5 Dimension 5 Level Health Questionnaire (EQ-5D-5L; higher values indicate better health utility), EQ-5D visual analog scale (EQ-5D VAS; 0-100 scale; higher scores indicate better health), and Work Productivity and Activity Impairment–Specific Health Problem (WPAI-SHP; higher scores indicate higher impairment). MDA was achieved if 5 of 7 criteria were met: tender joint count ≤1; swollen joint count ≤1; Psoriasis Area and Severity Index total score ≤1 or body surface area ≤3%; patient’s assessment of pain VAS ≤15; patient’s global assessment of disease activity VAS ≤20; Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index ≤0.5; and tender entheseal points ≤1 (assessed by the Leeds Enthesitis Index).
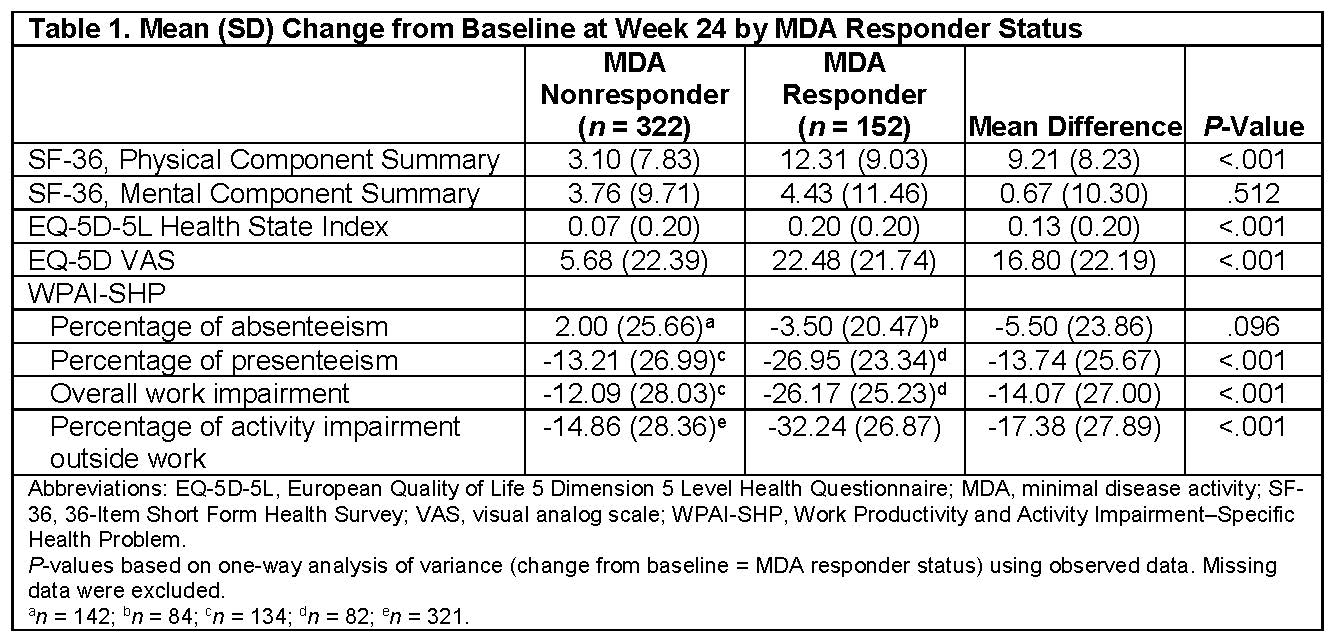
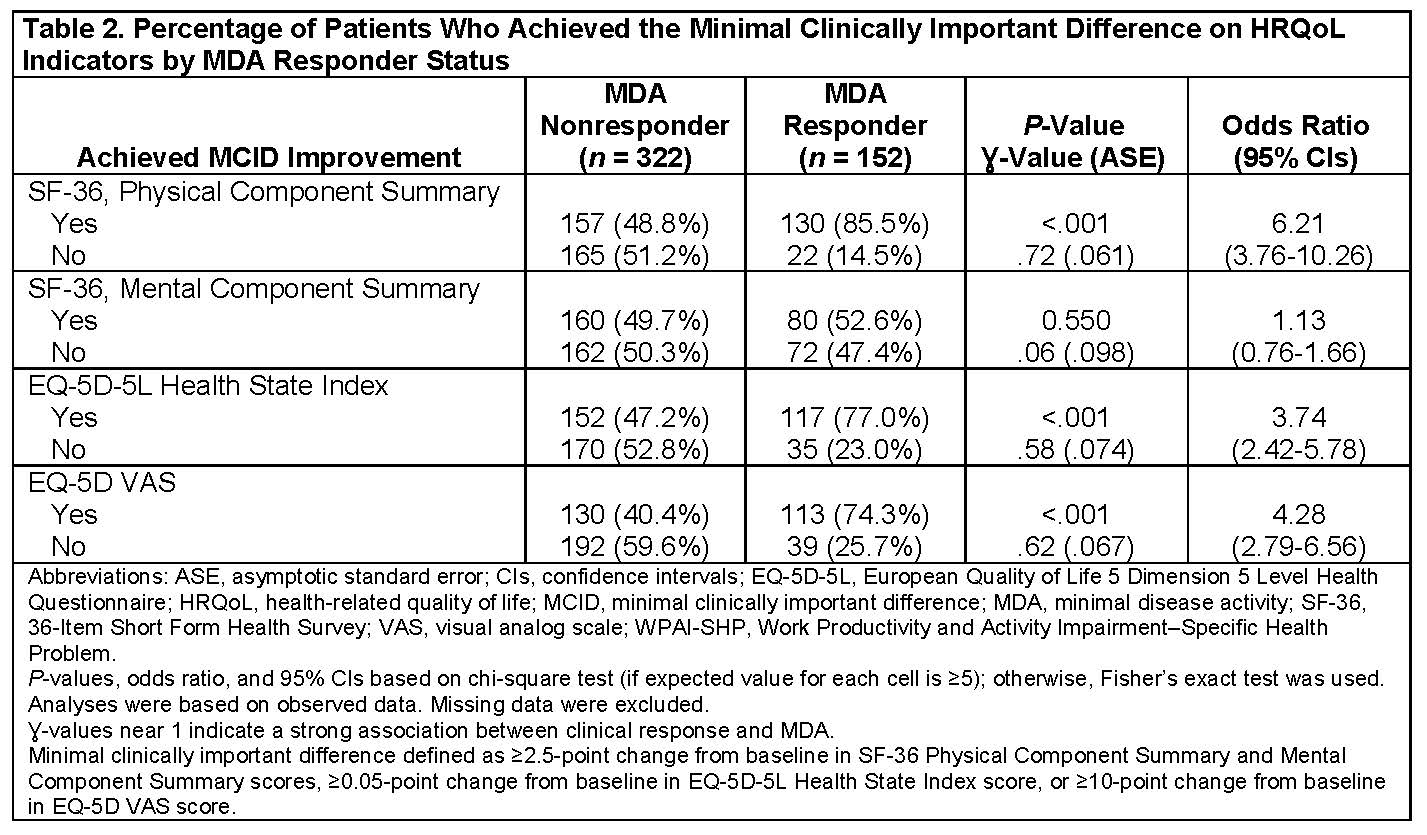
Results: At Week 24, 474 of 679 patients had nonmissing MDA and HRQoL data. At Week 24, MDA responders had significantly improved SF-36 Physical Component Scores (PCS), EQ-5D-5L index values, and EQ-5D VAS scores but similar SF-36 Mental Component Scores (MCS) relative to MDA nonresponders (Table 1). MDA responders also had a significantly improved percentage of presenteeism, overall work impairment, and percentage of activity impairment on the WPAI-SHP relative to MDA nonresponders at Week 24 (Table 1). MDA responders were more likely to achieve the minimal clinically important difference on the SF-36 PCS, EQ-5D-5L index score, and EQ-5D VAS score but not the SF-36 MCS (Table 2).
Conclusion: Achievement of MDA is associated with improvement of patient-reported HRQoL and productivity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Coates LC, Orbai AM, Birt J, Kerr L, Benichou O, Helliwell PS. Achievement of Minimal Disease Activity Is Associated with Improvements in Health-Related Quality of Life and Productivity in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-minimal-disease-activity-is-associated-with-improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life-and-productivity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-minimal-disease-activity-is-associated-with-improvements-in-health-related-quality-of-life-and-productivity-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/