Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Therapeutic goal of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is to achieve disease remission. However, several remission criteria have not always equated to the complete absence of true inflammation. Power Doppler Ultrasonography (PDUS) has been demonstrated to detect subclinical synovitis. The aim of this study was to elucidate the achievement rates of imaging remission and examine characteristics associated with achievement status among RA patients in clinical remission.
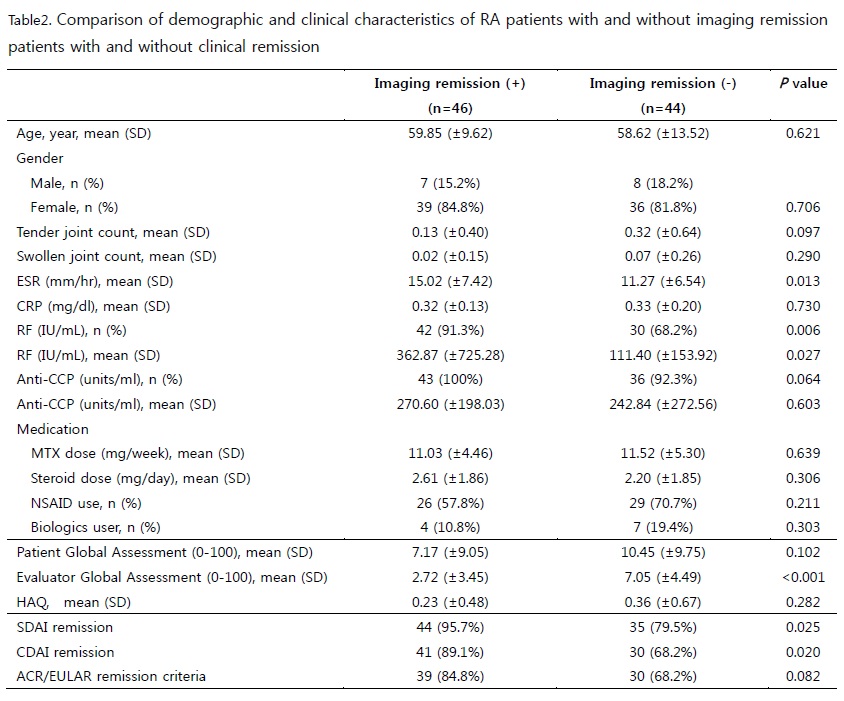
Methods: This study was conducted in 90 RA patients who attained clinical remission, defined by DAS28-ESR remission criteria. PDUS was performed in 16 joints and 2 tendons, including both first to third metacarpophalangeal, second and third proximal interphalangeal, radiocarpal (RC), second and third metatarsophalangeal joints and extensor carpi ulnaris tendons and graded on the basis of a dichotomous assessment (presence/absence). The clinical and laboratory data of patients with imaging remission were compared with only clinical remission.
Results: Rate of imaging remission was 51.1% in patients with clinical remission. Forty four patients (48.9%) were PDUS positive. PD was detected most frequently in right RC joint (n=38, 42.4%). In addition, eleven patients have arthralgia on not evaluation joint, PDUS positivity was 91%. PDUS positive patients had higher evaluator global assessment score (p<0.001), and all clinical disease activity score. Rheumatoid factor was correlated with imaging remission with positivity and level. Overall, Patients could not reach imaging remission tend to more tender and swollen joint count, higher patient global assessment score, higher health assessment questionnaire (HAQ) score. They use more nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Conclusion: Only 51.1% of the patients with RA in clinical remission had PDUS defined imaging remission. Patients who were in imaging remission have lower disease activity, lower pain score and less frequent use of NSAIDs, compared to patients with only clinical remission. 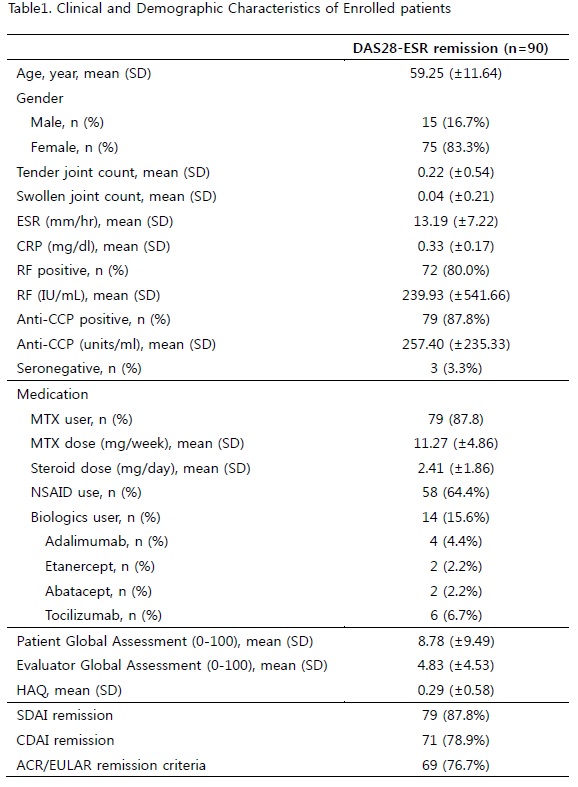
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choi JY, Song R, Hong SJ, Yang HI, Lee SH, Lee YA. Achievement of Imaging Remission Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Clinical Remission and Their Characteristics [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-imaging-remission-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-clinical-remission-and-their-characteristics/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/achievement-of-imaging-remission-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-clinical-remission-and-their-characteristics/