Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD) is a severe extraarticular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) has a poor prognosis. Effectives treatments in RA such as anti-TNF have been implicated in the exacerbation of ILD.
Our objective was see the efficacy of Abatacept in ILD associated with RA.
Methods: Retrospective multicenter study of RA patients with ILD treated with ABA atleast for 3 doses. The ILD was diagnosed by HRCT. We have analyzed the following variables: a) 1-point change the Modified Medical Research Council (MMRC); b) FVC improvement or decline ≥10%; improvement or decrline ≥10% in DLCO c) radiological improvement in HRCT scan, d) changes in DAS28 score. e) prednisone dose. Values were compared with baseline.
Results: We studied 263 patients (150 women /113 men) with ILD associated to RA. The patients were smokers or exsmoker in a 53%. APCC was positive in 88.6%. The follow-up mean was 22.66±19.66 months. The mean age was 64.64 ± 10 years. The median to progression of ILD was 12 [3-41.25] months. The mean DLCO at onset was 65,68±18.33 and the FVC at onset was 85.88±21.77 111 patients were treated in monotherapy.
The most frequent pattern was UIP 41,6% 32,7% NSIP 24,7% “others” thats include mixed patterns BONO or BO.
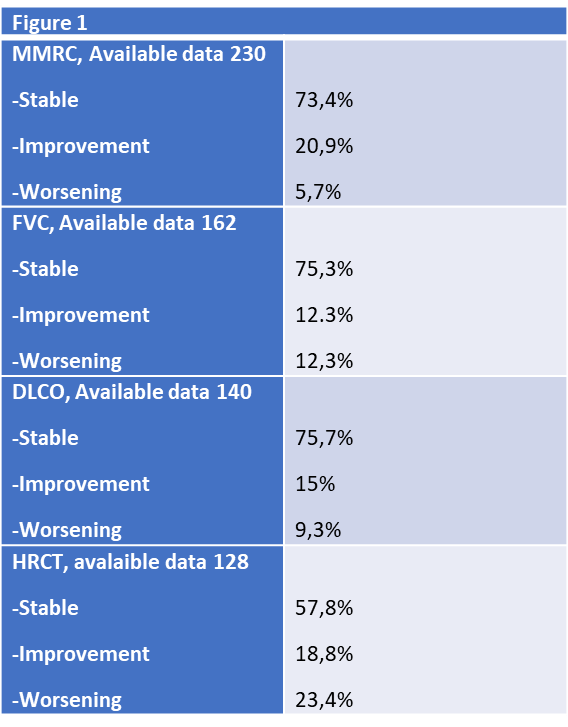
The Figure1 expresses the evolution of the avalible data.
DAS28 also improved from 4.501±1.486 to 3.107±1.333 and we also appreciate a decrease in the dose of prednisone from the initial mean 7.5 [5-10] to the final mean 5mg [5-7.5]. The global mean of FVC at the end of follow up was 85.3±20.69 the global mean of DLCO at the end of follow up was 65.35±19.88 both similar to the onset mean.
Conclusion: Abatacept could be a relatively safe and effective treatment for patients with interstitial lung involvement associated with rheumatoid arthritis. However, should be verified in prospective and randomized studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fernández-Díaz C, Melero R, Loricera J, Castañeda S, Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Casafont-Solé I, carrasco-Cubero C, Juan-Mas A, Almodovar-Gonzalez R, Rodriguez-Garcia S, Castellanos R, Maiz-Alonso O, Aguilera-Cros C, Cabezas-rodriguéz I, Cervantes E, Moreno M, Arboleya L, Montagut C, Carreira P, Ojeda-Garcia C, Bonilla G, Perez-Sandoval T, Vela P, Andreu J, Romero-Yuste S, Urruticoechea-Arana A, Salgado-Pérez E, Hidalgo C, Narváez J, Raya E, Moreno-Ramos M, Morales-Garrido P, Pérez-alba L, Fernández-López C, Villa I, Álvarez-Rivas N, Blanco-Madrigal J, Jimenez-Aberasturi J, Perez-Linaza A, Del-val-del-amo N, Fernández S, García-valle A, Peralta-Ginés C, Garcia-Aparicio A, Exposito-pérez L, Mena-Vazquez N, López-Sánchez R, Garcia-magallon B, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Abatacept in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Interstitial Lung Disease: A Retrospective Multicenter Study of 263 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-interstitial-lung-disease-a-retrospective-multicenter-study-of-263-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-with-interstitial-lung-disease-a-retrospective-multicenter-study-of-263-patients/