Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Osteoporosis, characterized by low bone mineral density (BMD) and micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue, increases bone fragility and susceptibility to fractures. Denosumab, a fully human immunoglobulin G2 monoclonal antibody to receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand, inhibits osteoclast differentiation, activity, and survival, decreasing bone resorption in cortical and trabecular bone. This abstract reports the results of the randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel-arm, Phase 3 study comparing efficacy, safety, and pharmacodynamics (PD) of Bmab-1000 (proposed biosimilar denosumab) and US-licensed Prolia in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.
Methods: A total of 479 patients (mean age, 66.6 years) were randomized 1:1 to receive either 60 mg Bmab-1000 (n=238) or 60 mg Prolia (n=241) subcutaneously. Randomization was stratified by geographical region (US, Europe), prior bisphosphonate treatment (Yes, No), and age (< 65, ≥65 years). This study comprised two periods: Period 1, a double-blind, active-controlled period (Week 0-52 predose; two study treatment doses on Day 1 and Week 26), and Period 2, a transition (switching) period (Week 52-78, including third dose at Week 52). Patients completing Period 1 were rerandomized before study drug administration at Week 52: patients receiving Prolia were randomized 1:1 to 60 mg Bmab-1000 or 60 mg Prolia, while those receiving Bmab-1000 had no change in treatment. Period 1 evaluated therapeutic and PD equivalence between Bmab-1000 and Prolia based on lumbar spine BMD at Week 52 (after two doses) and area under the effect curve (AUEC) of serum C-terminal telopeptide of Type 1 collagen (sCTX) at Week 26 week, respectively. Period 2 is ongoing. Secondary analyses included additional efficacy, PD, safety and tolerability, immunogenicity, and pharmacokinetics (PK) parameters. Immunogenicity and PK results will be presented separately.
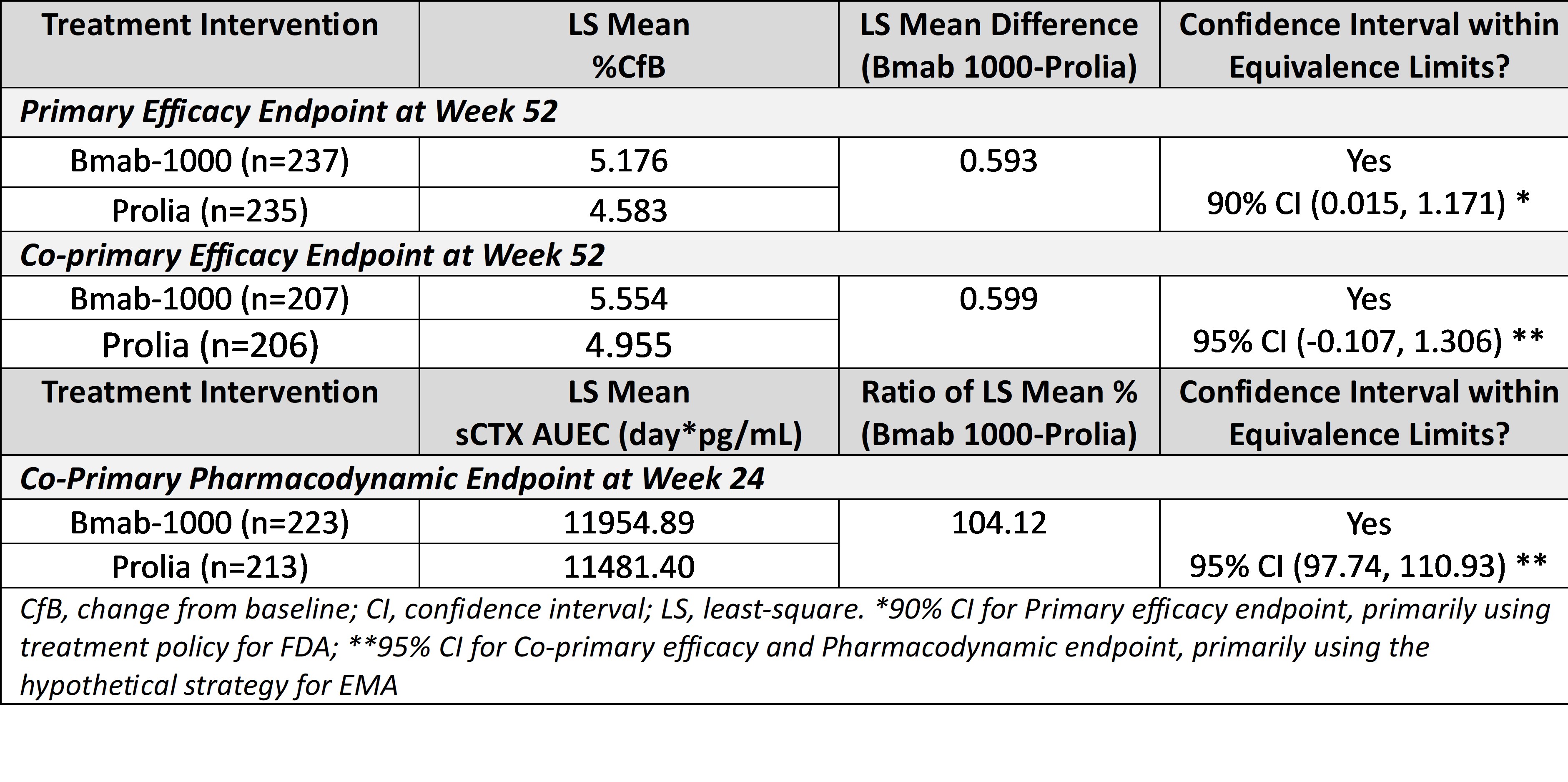
Results: For the primary and co-primary efficacy endpoints (90% confidence intervals [CI], FDA; 95% CI, EMA, respectively), therapeutic equivalence was demonstrated in terms of efficacy as the CIs for the difference in least square (LS) means in % change from baseline (%CfB) in lumbar spine BMD at Week 52 between Bmab-1000 and Prolia were entirely contained within the predefined margins (Table). For the co-primary PD analysis, the sCTX AUEC up to 26 weeks was comparable to that observed following a single dose of Prolia, with a geometric LS mean ratio (Bmab-1000/Prolia) of 104.12% and the 95% CI around the geometric LS mean ratio (97.74%, 110.93%) being contained entirely within the predefined acceptance limits (Table). The secondary efficacy and PD analyses supported the primary analyses. Bmab-1000 was safe and well tolerated compared with Prolia. The proportion of patients reporting treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs; 59.2%, Bmab1000; 63.3%, Prolia) and study drug-related TEAEs (8.0%, Bmab1000; 11.3%, Prolia) was similar for both groups.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated equivalent efficacy (%CfB in lumbar spine BMD) and PD (sCTX, AUEC) between Bmab-1000 and Prolia®, with similar safety and tolerability profiles.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strzelecka A, Kania G, Singh P, Kumar K, Thakur B, Marwah A, Basu S, Chaudhari N, Deodhar S, Holz E, Athalye S, L S. A Randomized, Double-blind, Multicenter, Parallel-arm Phase 3 Study to Compare the Efficacy, Pharmacodynamics, Safety, and Immunogenicity Between Bmab-1000 and Prolia in Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-double-blind-multicenter-parallel-arm-phase-3-study-to-compare-the-efficacy-pharmacodynamics-safety-and-immunogenicity-between-bmab-1000-and-prolia-in-postmenopausal-women-with-oste/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-double-blind-multicenter-parallel-arm-phase-3-study-to-compare-the-efficacy-pharmacodynamics-safety-and-immunogenicity-between-bmab-1000-and-prolia-in-postmenopausal-women-with-oste/