Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Spondylarthropathies and Psoriatic Arthritis - Clinical Aspects and Treatment: Treatment of AS
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic
arthritis (PsA) is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease associated
with psoriasis which includes peripheral arthritis, enthesitis, dactylitis, and
spondylitis manifestations. Ixekizumab, under investigation for PsA treatment,
is an IgG4 monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity and specificity to
the proinflammatory cytokine IL‑17A.
Methods: In a phase 3
trial, 417 biologic disease-modifying
antirheumatic drug (bDMARD)-naive patients with
active PsA were randomized to up to 24 weeks of placebo (N=106); adalimumab
40 mg (N=101) once every 2 weeks (Q2W; active control); or ixekizumab
80 mg Q2W (N=103) or Q4W (N=107) following 160 mg initial dose at Week 0.
Endpoints included American College of Rheumatology 20 response (ACR20) at Week
24 (primary), ACR50, ACR70, a 75/90/100% improvement in Psoriasis Area and
Severity Index (PASI 75/PASI 90/PASI 100), Disease Activity Score (28 joint
count) based on C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP), Leeds Dactylitis Index (LDI-B)
and Enthesitis Index (LEI), Health Assessment Questionnaire – Disability Index
(HAQ-DI), and Van der Heijde modified Total Sharp (mTSS) score at 12 and 24 weeks. Efficacy
variables were evaluated using the intent-to-treat population. Continuous data
were evaluated using mixed-effects model for repeated measures. Categorical
data were compared using a logistic regression model with missing values
imputed by non-responder imputation, which treats inadequate responders as
non-responders.
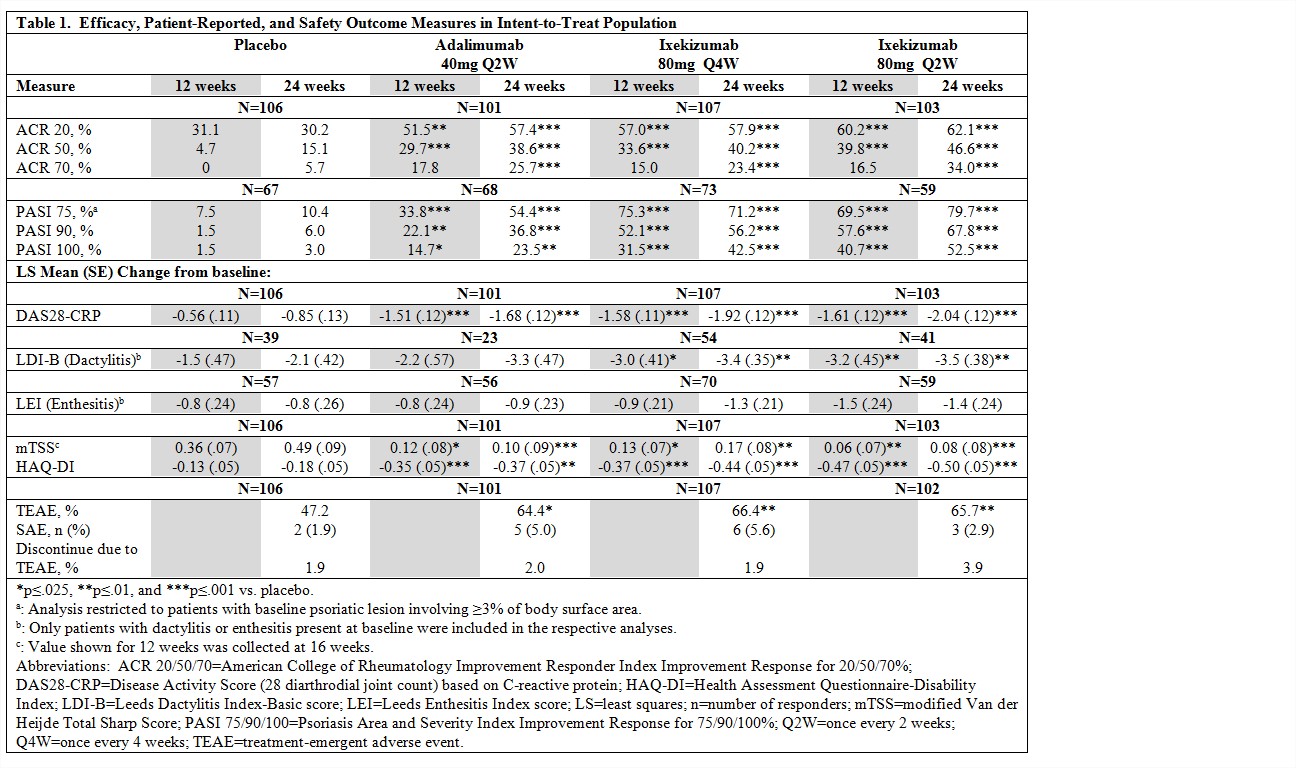
Results: A total of 382
patients completed 24 weeks of the study. A significantly greater percentage of
patients treated with ixekizumab 80 mg Q2W or Q4W achieved ACR 20, ACR50, ACR70
and PASI 75/90/100 responses than with placebo at 12 and 24 weeks (p<.01)
(Table 1). Both ixekizumab groups experienced significantly greater reductions
than placebo for measures of dactylitis (LDI-B) at 12 and 24 weeks but not for
enthesitis (LEI). Disease activity (DAS28-CRP) and functional disability
(HAQ-DI) improved and inhibition of radiographic progression of joint
structural damage (mTSS) was demonstrated with both ixekizumab doses compared
to placebo (p<.025). Efficacy results with adalimumab versus placebo were
significant on most measures, thus validating the study design. At 24 weeks, the
incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE) was greater (p<.05)
and the rate of serious adverse events was higher (p>.27) with ixekizumab
and adalimumab compared to placebo. Discontinuation due to a TEAE was similar
across groups. No deaths occurred.
Conclusion: In bDMARD-naive
patients with active PsA, ixekizumab showed significant, clinically meaningful
improvements of disease activity and physical function, reduction in
dactylitis, greater skin clearance of plaque psoriasis, and inhibition of
structural progression. Ixekizumab was well tolerated with no unexpected safety
findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease PJ, van der Heijde D, Ritchlin CT, Cuchacovich R, Shuler CL, Lee CH, Samanta S, Lin CY, Gladman DD, Vangerow H. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Active- and Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Study of Efficacy and Safety of Ixekizumab, Adalimumab, and Placebo Therapy in Patients Naïve to Biologic Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-double-blind-active-and-placebo-controlled-phase-3-study-of-efficacy-and-safety-of-ixekizumab-adalimumab-and-placebo-therapy-in-patients-naive-to-biologic-disease-modifying-anti/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomized-double-blind-active-and-placebo-controlled-phase-3-study-of-efficacy-and-safety-of-ixekizumab-adalimumab-and-placebo-therapy-in-patients-naive-to-biologic-disease-modifying-anti/