Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is associated with increased cardiovascular (CV) risk. The mechanisms of CV disease in RA remain poorly understood. Observational data suggest that earlier treatment of RA produces better responses. This RCT (ACTRN12611000972921) evaluated whether adalimumab (ADA) improves CV risk biomarkers in patients ACPA-positive RA and to explore the contribution of known risk factors.Methods:
60 (30 early, 30 established) patients with moderate-highly active ACPA-positive RA were enrolled in a RCT of humira versus placebo (1:1). Patients underwent assessments of Reactive Hyperaemic Index (RHI), carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) and disease activity twice before receiving treatment and then at weeks 1,4,12 and 24. Intention-to-treat analysis compared changes in each treatment arm by t test. Secondary analysis by random effects GLS regression modelling evaluated effects upon RHI and PWV adjusting for clustering within individuals.Results:
There were no significant differences between in treatment arms for RHI. While preliminary analysis suggested that positive shared epitope (SE) status was associated with poorer endothelial function (p 0.02) rather than for inflammation (CRP p0.379) or treatment (p 0.487) this was not significant after adjustment for clustering. A large 0.65m/sec reduction in PWV was seen prior to treatment in both groups. At weeks 4 and 12 PWV was significantly lower in the ADA arm. This trend was seen more consistently in patients with recent onset (<12 months) disease. Secondary analysis found that the most significant effects upon PWV were age (p 0.000), mean arterial pressure (p0.000) and CRP (p0.004).Conclusion:
Treatment with ADA may improve aortic stiffness and treatment may be more effective in early disease. However the greater effects are from blood pressure and ageing. While PWV is clearly influenced by CRP RHI may be influenced more by SE status. Further work is needed evaluating ACPA-negative and SE-negative subjective and pre-clinical RA.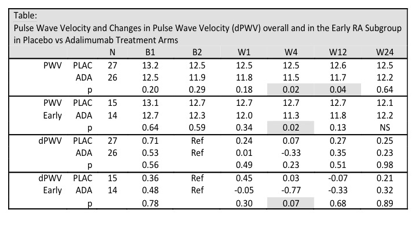
Disclosure: S. Oakley, Abbvie, 2,Abbvie, 5,Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P., 5,Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P., 8,UCB, 5,Abbvie, 9,Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P., 9,UCB, 9,Pfizer Inc, 9; G. Major, Abbvie, 2; D. Mathers, Abbvi, 2; J. van der Kallen, Abbvie, 2; M. Collins, Abbvie, 2; M. Toh, Abbvie, 2; S. Ratnarajah, Abbvie, 2; T. de Malmanche, None; N. Esmaili, None.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Oakley S, Major G, Mathers D, van der Kallen J, Collins M, Toh M, Ratnarajah S, de Malmanche T, Esmaili N. A Randomised Controlled Trial Evaluating the Effect of Adalimumab upon Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Risk in ACPA-Positive Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomised-controlled-trial-evaluating-the-effect-of-adalimumab-upon-biomarkers-of-cardiovascular-risk-in-acpa-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-randomised-controlled-trial-evaluating-the-effect-of-adalimumab-upon-biomarkers-of-cardiovascular-risk-in-acpa-positive-rheumatoid-arthritis/
