Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: SB4, SB2, and SB5 are biosimilars of etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab. Phase III randomized, double-blind studies were conducted to compare efficacy and safety between biosimilars and reference products.
The objective of this study is to assess and compare 1-year outcomes among 6-month responders and non-responders.
Methods: Patients who had 6-month data from each phase III study were pooled and categorized, based on their disease status at 6 months (week 24 for etanercept and adalimumab and week 30 for infliximab) and 1 year (week 52 for etanercept and adalimumab and week 54 for infliximab).
Responders included patients who achieved an ACR20 response or low disease activity (including remission) by DAS28, SDAI, or CDAI at 6 months. Those who did not or dropped out were considered non-responders.
The primary outcome was the proportion of responders who maintained responses from 6 months to 1 year or non-responders at 6 months who achieved responses at 1 year.
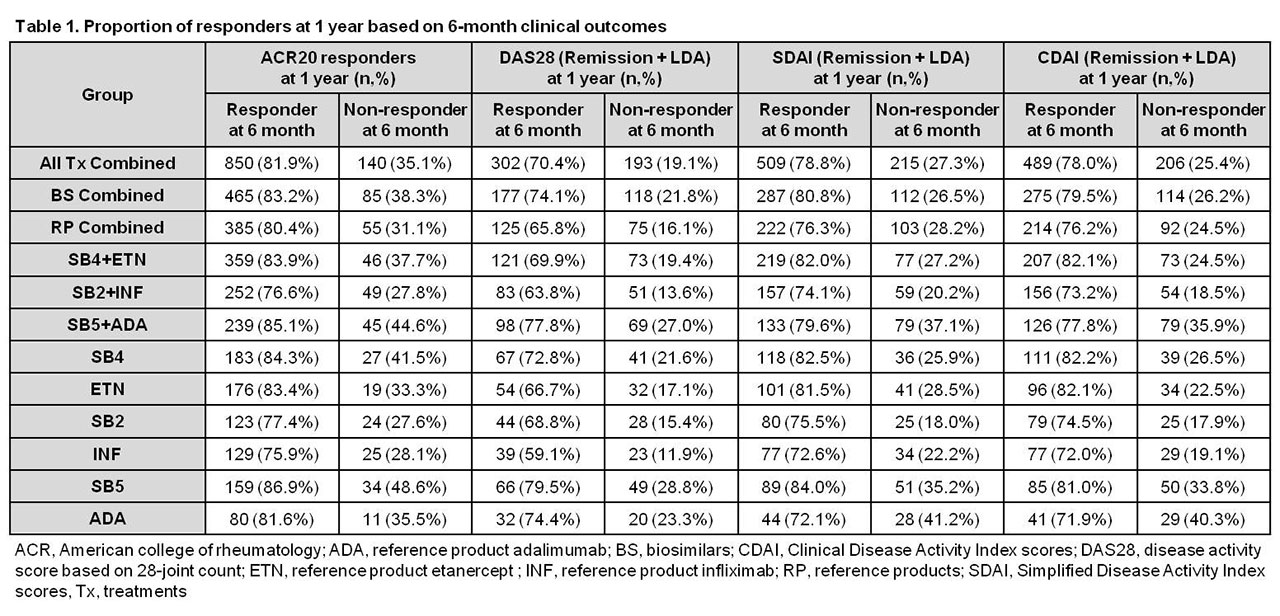
Results: Data from 1,437 patients were included in the analysis. For all treatments combined, 81.9% of ACR20 responders, 70.4%, 78.8%, and 78.0% of responders with DAS28, SDAI, and CDAI low disease activity (LDA) at 6 months maintained their responses at 1 year, and 35.1%, 19.1%, 27.3%, and 25.4% of 6-month non-responders achieved responses at 1 year, respectively. The proportions of patients maintaining or achieving an ACR20 response or DAS28, SDAI, and CDAI LDA at 1 year were similar across different treatment groups (Table 1).
Conclusion: A pooled analysis of TNF inhibitor biosimilars and reference products showed that about 20-30% of responders lost their response, while about 20-30% gained it. Thus, the overall stability of disease fluctuation in our 1-year phase III studies is a consequence of a similar success and failure rate. The validity of these data can be seen by the similarities in these outcomes between different types of TNF-inhibitors and similarity between biosimilars and respective reference products.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Smolen J, Weinblatt M, Emery P, Choe J, Kay J, Lee J, Myung G, Seo H, Ghil J. A Pooled Analysis of 1-year Clinical Outcomes Among 6-month Responders and Non-responders from Three Randomized Controlled Studies of TNF Inhibitor Biosimilars in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-pooled-analysis-of-1-year-clinical-outcomes-among-6-month-responders-and-non-responders-from-three-randomized-controlled-studies-of-tnf-inhibitor-biosimilars-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-pooled-analysis-of-1-year-clinical-outcomes-among-6-month-responders-and-non-responders-from-three-randomized-controlled-studies-of-tnf-inhibitor-biosimilars-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/