Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Olokizumab is a novel IL-6 inhibitor that selectively blocks the final assembly of the IL-6 signaling complex (gp80+gp130+IL-6). We report the safety, PK, and PD results from a pilot single-dose study in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: This was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of RA patients who: were diagnosed by the 1987 ACR criteria; had >6 months’ disease duration; were treated with methotrexate 5–25 mg/week for at least 3 months prior to screening; had an elevated baseline high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP; median 3.37, range 0.6–27.2 mg/L) with a reasonable spread that allowed robust characterization of the PD effect. At baseline, the mean DAS28 (CRP) was 3.07 (olokizumab) and 2.87 (placebo). Patients were randomized (3:1) to a single dose of olokizumab, either iv (0.1 or 1.0 mg/kg) or sc (1.0 or 3.0 mg/kg), or placebo. Primary objectives of the study included evaluating the PK/PD relationship between olokizumab and CRP, and the safety and tolerability of olokizumab over 12 weeks post dose.
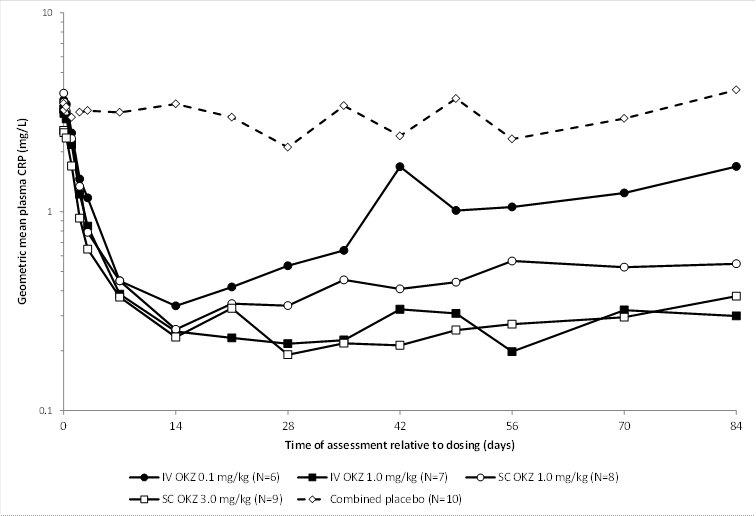
Results: Of 40 randomized patients, 38 completed the 12-week follow-up. Dose-dependent and sustained suppression of plasma CRP followed all doses of olokizumab until the end of the study (except for the 0.1 mg/kg iv group). IL-6 levels were markedly reduced after olokizumab exposure, remaining suppressed for the duration of the study. Commonly reported AEs in olokizumab recipients included headache, infection, decreased white blood cells (WBC), and abnormal liver function tests (LFT), with no dose relationship to severity, grade, or frequency of reported events. Laboratory abnormalities included: reductions in WBC and elevated LFT, cholesterol, and triglycerides. Two serious AEs were reported: 1 for placebo (grade 2 Bowen’s disease) and 1 for olokizumab 1.0 mg/kg sc (worsening of RA). Two patients withdrew: 1 placebo (worsening of RA) and 1 olokizumab 1.0 mg/kg sc (protocol deviation). Dose-related reductions in complement C3 and C4 were seen. The terminal elimination t½ of olokizumab in plasma was consistent regardless of route of administration or dose, with an overall median of 31 days. For the 1.0 and 3.0 mg/kg sc dose groups, the mean Cmax was 6.29 and 19.1 μg/mL, achieved within a median tmax of 13 and 7 days, respectively. Bioavailability determined from PK/PD modeling, pooling data from the first-in-human study1 and this study, was 76%. Non-compartmental analysis, based solely on data from this study, yielded a bioavailability of 66%.
Conclusion: In RA patients, single doses of ≤3mg/kg sc olokizumab demonstrated prolonged suppression of CRP, a marker of inflammation, although CRP in the 0.1 mg/kg iv group showed some recovery after 28 days; all doses were well tolerated. These results provided the rationale for a further study to investigate the clinical efficacy of olokizumab in RA.
Reference: 1. Ann Rheum Dis 2011;70(Suppl3):471
Disclosure:
R. Fleischmann,
Genentech Inc, Roche, Abbott, Amgen, UCB, Pfizer, BMS, Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Lexicon, MSD, Novartis, BiogenIdec, Astellas, Astra-Zeneca, Jansen,
5,
Roche, Abbott, Amgen, UCB, Pfizer, BMS, Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Lexicon, Novartis, Astellas, Astra-Zeneca, Jansen, HGS,
2;
A. J. Kivitz,
Genentech and Biogen IDEC Inc.,
5,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
8,
Takeda,
8,
Forest Laboratories,
8,
Pfizer Inc,
8;
F. Wagner,
None;
J. A. Feinstein,
None;
U. Fuhr,
None;
J. Rech,
None;
J. Sidhu,
None;
P. L. Hill,
Employed by UCB,
3;
R. Oliver,
Employed by UCB,
3;
K. Kretsos,
Employed by UCB,
3.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-pilot-study-investigating-the-tolerability-and-pharmacodynamic-effect-of-single-intravenoussubcutaneous-doses-of-olokizumab-an-anti-interleukin-6-monoclonal-antibody-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-a/