Session Information
Session Type: ACR Late-breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
SB5
is a biologic agent developed as a biosimilar of the adalimumab reference product (ADL). Equivalence in
pharmacokinetics (PK) between SB5 and ADL in healthy subjects has been
demonstrated1 in a phase I study. This phase III study was a
randomized, double-blind, multicenter study to compare the efficacy, safety,
PK, and immunogenicity of SB5 with ADL in patients with moderate to severe
rheumatoid arthritis (RA) despite methotrexate (MTX) treatment up to 52 weeks.
Results up to 24 weeks are presented in this abstract.
Methods:
Patients
with moderate to severe RA despite MTX treatment were randomly assigned to
receive 40 mg of either SB5 or ADL administered subcutaneously every other week
for 24 weeks. At Week 24, patients in ADL group were randomized again to
receive 40 mg of either SB5 or ADL for additional 28 weeks. Patients in
SB5 group continued to receive SB5. The primary endpoint was the ACR20 response
rate at Week 24. Other secondary efficacy endpoints and safety were measured.
Results:
A
total of 544 patients were randomized to either SB5 (N=271) or ADL (N=273).
Baseline demographic and disease characteristic were comparable between two
treatment groups. The ACR20 response rate at Week 24 in the per-protocol set
(PPS) was 72.5% (174/240) in SB5 and 72.0% (170/236) in ADL. The 95% confidence
interval (CI) of the treatment difference adjusted by region and baseline
C-reactive protein was –7.66% to 8.30%, which was within the pre-defined
equivalence margin of [–15%, 15%]. The ACR20 response rate at Week 24 was shown
to be equivalent in the full analysis set as well (95% CI: -7.03%, 8.56%) when
non-responder analysis was applied. The 95% CI of the estimated difference
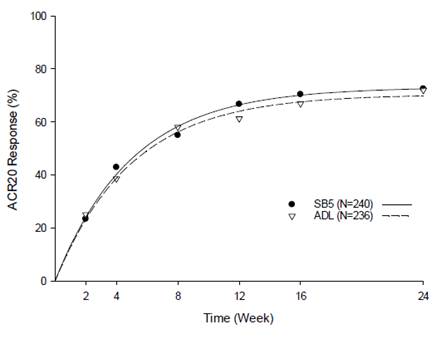
between the time-response curves of SB5 and ADL in the PPS met the pre-defined
equivalence margin (Figure). The ACR50 response rates at Week 24 in the PPS
were 38.3% vs. 39.8% and the ACR70 response rates were 19.2% vs. 20.3% in SB5
and ADL, respectively. The safety profile of SB5 was generally similar to that
of ADL (Table). The overall incidence of anti-drug antibody up to Week 24 was
32.8% in SB5 vs. 31.7% in ADL. The PK profile was also comparable between the
two treatment groups.
Conclusion:
SB5
was shown to be equivalent in terms of clinical efficacy when compared with
ADL. SB5 was well tolerated with similar safety profile, PK, and immunogenicity
to ADL.
Table.
Safety Results
|
Patients with |
SB5 (N=268*) |
ADL (N=273) |
||
|
n |
(%) |
n |
(%) |
|
|
At least 1 TEAE |
96 |
(35.8) |
110 |
(40.3) |
|
At least 1 serious TEAE |
3 |
(1.1) |
7 |
(2.6) |
|
Serious infection |
1 |
(0.3) |
2 |
(0.7) |
|
Tuberculosis |
0 |
(0.0) |
0 |
(0.0) |
|
Injection site reactions** |
8 |
(3.0) |
8 |
(2.9) |
|
Malignancy |
0 |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.7) |
|
Death |
0 |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.7) |
|
TEAE: treatment-emergent adverse event *Three patients withdrew before receiving at least one dose of the study drug. **Numbers are based on high-level group term of administration site reactions. |
||||
Figure. Estimated
Time-response Curves of ACR20 Response Rate up to Week 24 (PPS)
Reference
1.
Shin DH et al. EULAR 2015, FRI0110.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Weinblatt ME, Baranauskaite A, Niebrzydowski J, Dokoupilova E, Zielinska A, Sitek-Ziolkowska K, Jaworski J, Racewicz A, Pileckyte M, Jedrychowicz-Rosiak K, Zhdan V, Cheong SY, Ghil J. A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical Study Comparing SB5, an Adalimumab Biosimilar, with Adalimumab Reference Product (Humira®) in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Despite Methotrexate Therapy (24-week Results) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-iii-randomized-double-blind-clinical-study-comparing-sb5-an-adalimumab-biosimilar-with-adalimumab-reference-product-humira-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-iii-randomized-double-blind-clinical-study-comparing-sb5-an-adalimumab-biosimilar-with-adalimumab-reference-product-humira-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis/