Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis-Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy I: Biologics
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose:
In autoimmune
diseases reduced numbers and functional impairment of regulatory T cells
(Tregs) have been observed (1). Tregalizumab (BT-061) is a humanized, anti-CD4
mAb, inducing selective Treg activation in vitro. Previous trials suggested efficacy
in RA at doses ≥25 mg subcutaneously (SC). In a population PK/PD
analysis, down-modulation of CD4 expression was identified as a biomarker to
monitor CD4 target engagement in humans.
Methods:
This two-part, Phase 2b randomized controlled
trial (RCT) included subjects with active RA for ≥6 months despite MTX
(≥15mg/wk), with ≥6/28 TJC, ≥6/28 SJC and elevated CRP or ESR.
Subjects were randomized to receive 25 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg, or PBO once-weekly SC
injection + MTX over 24 wks. Primary endpoint was ACR20 at wk 12. At wk 12 (end
of Main part I), non-responders were re-randomized to active treatment or
higher doses. Subjects responding at wk 24 (end of Main part II) could extend
treatment for an additional 24 wks. A data safety monitoring board (DSMB) was
established for safety evaluation throughout the study.
Results:
Of 321 subjects enrolled from Europe, USA,
Canada, Russia and Mexico, 37 (11.5%) withdrew at ≤ wk 12. Demographics and
baseline disease characteristics were well balanced across groups: mean SJC and
TJC 16 and 24, respectively; CRP 11.7 mg/L, DAS (ESR) 6.58 and HAQ-DI 1.56.
ACR20 responders at wk 12 (42.3%/47%/44.3% vs. 35.2% in 25 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg groups
and PBO, respectively), ACR20 responders at wk 24 and secondary endpoints did
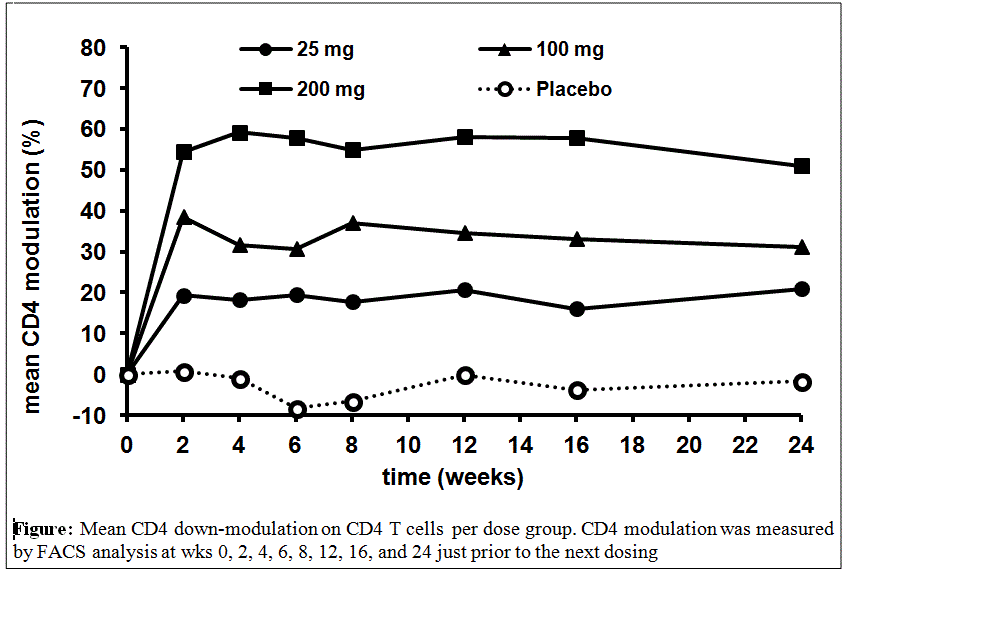
not differ significantly between tregalizumab groups and PBO. However, dose
dependent modulation of CD4 expression on T cells occurred rapidly with BT-061 treatment,
as predicted from previous analyses.
Through wk 12, TEAE (39.4%
and 37.5%) and serious TEAEs rates (2.1% and 1.3%) were similar between BT-061
and PBO. For responder at wk 24, TEAEs (48.3% and 52.3%) were similar between BT-061
and PBO. Serious TEAEs were only reported in BT-061 treated subjects (2%). Three
deaths occurred considered unrelated to treatment (car accident, acute coronary
syndrome, death of unknown cause in a war area). There was no difference in
infections between tregalizumab and PBO. One serious infection (peritonitis)
occurred at wk 22 in the 25 mg dose group. Apart from acute coronary syndrome
with fatal outcome, no further MACE events, Tuberculosis, opportunistic
infections nor malignancies were reported.
Figure
Conclusion:
No tested doses of
tregalizumab demonstrated significant efficacy improving signs and symptoms of
active RA based on ACR20 responses at wk 12 and 24 despite dose dependent down-modulation
of CD4 expression. Tregalizumab was generally well tolerated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Vollenhoven RF, Keystone EC, Strand V, Pacheco-Tena C, Vencovsky J, Behrens F, Zipp D, Rharbaoui F, Wolter R, Tiemann RD, Knierim L, Schmeidl R, Zhou X, Aigner S, Daelken B, Wartenberg-Demand A. A Phase 2b Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Subcutaneously Administered Tregalizumab in Subjects with Active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Despite Treatment with Methotrexate (MTX) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2b-study-evaluating-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-subcutaneously-administered-tregalizumab-in-subjects-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-despite-treatment-with-methotrexate-mtx/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-phase-2b-study-evaluating-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-subcutaneously-administered-tregalizumab-in-subjects-with-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-despite-treatment-with-methotrexate-mtx/