Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: T-614 is a small molecular drug that has multiple immunomodulatory effects and has been used for treating rheumatoid arthritis. Previous work has revealed this agent may have inhibitory effects on B cells. Since excessive B cell activation is a characteristic of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), here we investigated efficacy of T-614 on lupus-like disease and its potential mechanism in MRL/lpr mouse, a classic lupus model.
Methods: Female MRL/lpr mice were randomly given T-614 (30mg/kg‧d), vehicle solution or cyclophosphamide (CTX, 20mg/kg‧w) as controls before their disease onset. 24-hour-urine and blood samples were collected regularly. Kidney and spleen samples of each mouse were collected at the end point of observation. Urine protein concentrations were measured by bicinchoninic acid protein assay, serum C3 and immunoglobulin were detected by ELISA, anti double strand DNA (dsDNA) antibody titers were quantified by radioimmunoassay and serum alanine transaminase (ALT), creatinine and blood cell counts were analyzed by auto analyzer. Expressions of B cell related cytokines by splenic cells were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction, CD20+ B cell invasions in kidney were detected by immunohistochemistry, immune complex deposition in kidney was determined by immunofluorescence, and kidney injury was blindly scored by a renal pathologist.
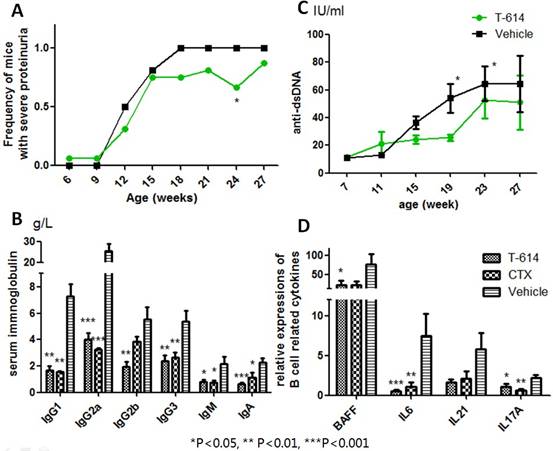
Results: T-614 ameliorated lupus-like disease activity in MRL/lpr mice. Mice in T-614 group had lower frequancy of severe proteinuria (over 20mg/24h, Figure A), lower serum creatinine (15.53 ±0.5845 vs 19.19 ±0.9184 µmol/L, P=0.025) and higher levels of serum C3 (2.027 ±0.1807 vs 1.296 ±0.0866 g/L, P=0.026) than vehicle controls. Kineys from T-614 treated mice had less lymphocyte invasions, creasants, casts in tubula and vasculitis changes than those from controls. Glomerular injury scores showed statistically significant difference (median: 1.46, QR 1.35-3.745 vs median: 3.37, QR 2.17-4.0, P=0.0381) between these two groups. Immunofluorescence also showed less immune complex depositions in kidneys from T-614 group. For B cells, T-614 remarkably reduced serum immunoglobulin (Figure B), anti-dsDNA antibody titers (Figure C) and B cell related cytokine (Figure D) expressions in splenic cells. Notably, effects of T-614 on immunoglobulin and B cell cytokines were comparable to CTX. Furthermore, mice from T-614 group had less CD20+ B cell invasions in their kidneys than vehicle group (mdian: 1.0, QR 0.875-2.0 vs mdian: 2.0,QR 2.0-3.0, P=0.0157). Lastly, overt adverse effects, including infection, elevated serum ALT or abnormal peripheral blood cell counts, were not observed.
Conclusion: T-614 can ameliorate lupus-like disease in MRL/lpr mice mostlikely through B cell suppression without overt toxity. Our results suggest that T-614 has potential for the therapy of SLE.
Disclosure:
Q. Yan,
None;
F. Du,
None;
C. Bao,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-novel-small-molecular-anti-rheumatic-drug-t-614-ameliorates-lupus-like-disease-in-mrllpr-mice-by-suppressing-b-cell-functions/