Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Most of the prognostic indicators are derived from right cardiac catheterization or biomarkers in patients with CTD-PAH. It is not clear whether the non-invasive parameters measured by chest CT are related to the clinical outcome of patients with CTD-PAH. Therefore, we want to explore whether the size of pulmonary artery measured on chest CT is related to the long-term prognosis of patients with CTD-PAH in Chinese population.
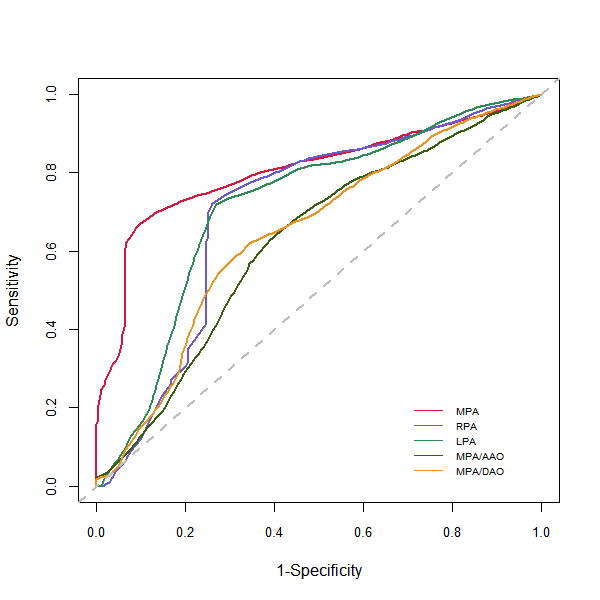
Methods: We retrospectively investigated 140 CTD-PAH patients diagnosed by echocardiography during Jan 2009 and May 2018 at the first affiliated hospital of Nanjing Medical University. The size of pulmonary trunk and its branches was maesured. by two professional radiologists. The primary endpoint was all-cause death. The ability of chest multi-slice CT parameters to predict all cause mortality was tested by time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the corresponding cut-off value were defined by difference maximization method.
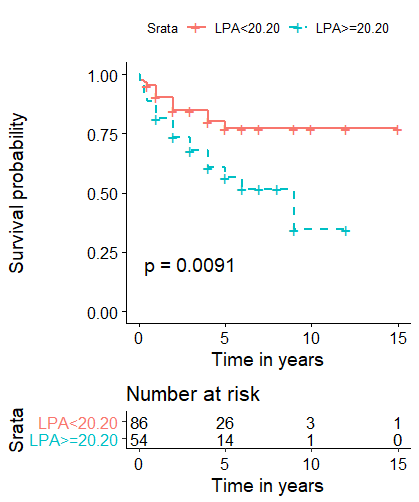
Results: During the observational period of 3.44 ± 0.23 years, 36 patients were died and the longest survival time was 15 years. The time dependent ROC curve suggested that Main pulmonary artery diameter (MPAd), right pulmonary artery diamete (PRAd) and Left pulmonary artery diameter (LPAd) may have the ability to predict mortality in patients with CTD-PAH , the corresponding cut-off values were 37.70 mm for MPAd, 20.46 mm for RPAd and 20.20 mm for LPAd. Patients with MPAd ≥ 37.70 mm (p=0.00012) and LPAd ≥ 20.20 mm (p=0.0091) exhibited poorer long-term outcome. MPAd ≥ 37.70 mm (HR: 2.74; 95% CI: 1.37-5.48 p=0.004) and WHO functional class III-IV (HR: 3.32; 95% CI: 1.42-7.75 p=0.006) was the independent risk factor of poor outcome for patients with CTD-PAH.
Conclusion: Main pulmonary arterial ≥ 37.70 mm measured by chest multi-slice CT was an independent risk factor of the poor long-term prognosis in Chinese CTD-PAH patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
li x, sun x, zhu y, wang Q, zhang m. A New Risk Factor for Predicting the Long-term Outcome of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Connective Tissue Disease: Pulmonary Artery Size Measured by Chest Computed Tomography [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-risk-factor-for-predicting-the-long-term-outcome-of-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-associated-with-connective-tissue-disease-pulmonary-artery-size-measured-by-chest-computed-tomography/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-new-risk-factor-for-predicting-the-long-term-outcome-of-pulmonary-arterial-hypertension-associated-with-connective-tissue-disease-pulmonary-artery-size-measured-by-chest-computed-tomography/