Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients are at increased risk for developing osteoporosis as compared to the general population, even after controlling for glucocorticoid use[1]. Identification and treatment of osteoporosis are important quality measures for prevention of fragility fractures. The National Osteoporosis Foundation recommends bone mineral density (BMD) testing with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) starting at age 50 in patients with significant osteoporosis risk factors, including a history of RA[2]. We used the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) Model for Improvement to implement and assess osteoporosis screening among rheumatoid arthritis patients seen in our academic rheumatology clinic.
Methods: Performance on DEXA screening was calculated as the proportion of RA patients ≥ 50 years old who had ever received a DEXA since 2012. The proportion of patients with an active DEXA order or completion was also measured. Our multidisciplinary quality improvement team utilized a medical assistant led intervention of pending orders for DEXA in patients meeting the following qualification criteria: age ≥ 50 years, RA diagnosis, no prior DEXA or existing order for DEXA, and at least 2 visits in the rheumatology clinic including one within 6 months. We generated two automated electronic health record reports, one to identify BMD screening candidates and one to measure uptake of orders and DEXA completion. Control charts were used to examine performance of these measures over time.
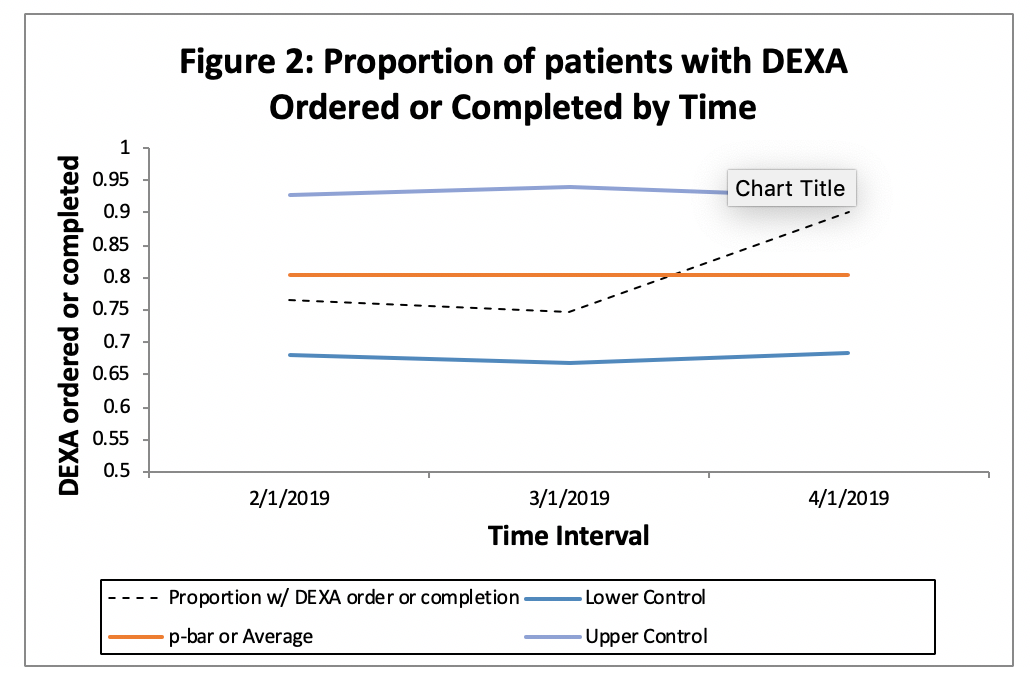
Results: Our clinic provides care for over 500 patients with RA who are ≥ 50 years old. Prior to the intervention, our baseline osteoporosis screening rate was 70% and the proportion of patients with an active DEXA order and/or completion was 76.5%. After our first Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle intervention, our DEXA screening rate increased to 77.3% and the rate of DEXA ordered and/or completed increased to 90% (Figure 1).
Conclusion: Using an interprofessional quality improvement team we were able to improve performance on DEXA ordering and screening, an important measure of health care quality for patients with RA. We plan to pursue future PDSA cycles in order to achieve a target DEXA screening rate of ≥ 85%.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
French S, Ng J, Young D, Evans M, Schmelzinger T, Schmajuk G, Yazdany J, Gross A. A Medical Assistant Driven Quality Improvement Intervention Increases Rates of DEXA Screening Among RA Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-medical-assistant-driven-quality-improvement-intervention-increases-rates-of-dexa-screening-among-ra-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-medical-assistant-driven-quality-improvement-intervention-increases-rates-of-dexa-screening-among-ra-patients/