Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) is a multi-organ system disease manifested by fibrosis, vascular damage and dysregulation of the immune system. The leading causes of death are interstitial lung disease (ILD) and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). ILD is present in up to 80% of patients with SSc and clinically significant ILD affects approximately 25% of patients with SSc. Our objective was to evaluate the presence of pulmonary hypertension (PH) in a cohort of patients with early onset SSc-associated ILD (SSc-ILD).
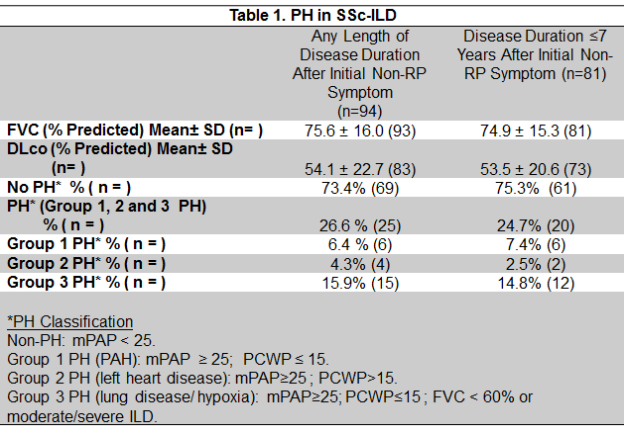
Methods: Subjects with a diagnosis of SSc based on 2013 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and ILD based on high-resolution computed tomography were included in our prospective observational cohort. Subjects with disease duration of ≤ 7 years, based on inclusion criteria for ongoing controlled trials in SSc-ILD, were also identified. Subjects with PH were identified based on right heart catheterization (RHC) and were classified into PH groups 1, 2, and 3 (Table 1).
Results: Ninety-four subjects with SSc-ILD were included in this analysis. Seventy-seven percent of patients were female, the mean age was approximately 52 years old, the mean disease duration was 2.8 years after initial non-Raynaud’s Phenomenon (RP) symptom, approximately 61% had diffuse cutaneous SSc, ANA was positive in 91%, anti-Scl-70 antibody was positive in 28%, and anti-centromere antibody was positive in 8% of subjects. Of those 94 subjects, 25 subjects had a diagnosis of PH based on RHC and 20 of those subjects had early onset SSc (Table 1).
Conclusion: In a large SSc-ILD cohort, with many subjects of earlier disease duration, a significant proportion of patients have co-existing PH. These are novel findings that should be entertained when designing trials for SSc-ILD and should be validated in other cohorts of SSc-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Young A, Fisher C, Namas R, Wilhalme H, Khanna D. A Large Proportion of Patients in an Early Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease Cohort Have Coexisting Pulmonary Hypertension [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-large-proportion-of-patients-in-an-early-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-cohort-have-coexisting-pulmonary-hypertension/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-large-proportion-of-patients-in-an-early-systemic-sclerosis-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-cohort-have-coexisting-pulmonary-hypertension/