Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CR6086 is a potent and selective antagonist of the prostaglandin EP4 receptor. EP4 receptors have a role in T-cell differentiation and expansion, and thus in the altered immune response in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. EP4 receptors are then a rational target for novel DMARDs/immunomodulators with added anti-inflammatory properties. Indeed, when oral CR6086 was tested in a series of widely accepted models of arthritis in rodents, it was at least as effective as biological DMARDs in all parameters examined, including edema, clinical arthritis score, and histology. The present first-in-human study evaluated the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of CR6086 in single ascending doses.
Methods: Oral doses of CR6086 ranging from 5 to 300 mg were administered to healthy men in a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled fashion. Each of the nine cohorts comprised 6 volunteers on active and 2 on placebo. Food interaction was assessed at 150 mg.
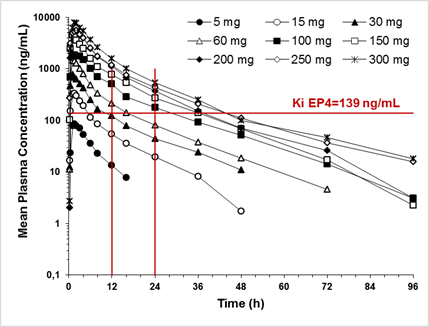
Results: CR6086 was well tolerated up to 300 mg, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached.The few observed adverse events where mild or moderate in severity, all resolved spontaneously, and their incidence was not dose-related. The pharmacokinetics of CR6086 were dose-independent, with mean peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) ranging from 90 to 8151 ng/mL and occurring between 1 and 1.75 h after administration. The extent of bioavailability (AUC) ranged from 602 to 68200 ng.h/mL and a high fat meal did not affect CR6086 bioavailability. Plasma protein binding was around 95% (unbound fraction; fu = 0.0564) and CR6086 did not invert into its antipode. CR6086 elimination half-life averaged 13 h and urinary excretion of the unchanged drug was a minor elimination route. Mean peak plasma concentrations of CR6086 (Figure) were above the Ki for the human EP4 receptor (adjusted for plasma protein binding) already at a dose of 15 mg. From the 100 mg dose, the plasma concentrations of CR6086 were higher than the adjusted Ki for a 24-hour period. A comparison with the exposure in rodents indicated that from the single dose of 30 mg, the exposure is pharmacologically relevant in humans.
Conclusion: CR6086 was safe up to the maximum tested dose of 300 mg. The compound is characterized by dose-independent pharmacokinetics producing therapeutically relevant concentrations at well tolerated doses in support for further clinical development as a novel DMARD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Persiani S, Manzotti C, Vitalini C, Giacovelli G, Girolami F, D'Amato M, Caselli G, Rovati LC. a First-in-Human Study of CR6086, a New Potent EP4 Prostanoid Receptor Antagonist, Demonstrates Good Safety and Tolerability at Therapeutically Relevant Exposures [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-first-in-human-study-of-cr6086-a-new-potent-ep4-prostanoid-receptor-antagonist-demonstrates-good-safety-and-tolerability-at-therapeutically-relevant-exposures/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-first-in-human-study-of-cr6086-a-new-potent-ep4-prostanoid-receptor-antagonist-demonstrates-good-safety-and-tolerability-at-therapeutically-relevant-exposures/