Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We compared
clinical features,
longitudinal pulmonary physiology,
and survival among 3 groups
of patients evaluated at our center between February 2008 to August 2014: definite
connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (dCTD-ILD), suggestive
CTD-ILD (sCTD-ILD) and idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Methods : Survival and longitudinal
analyses were used to
compare survival and changes in percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC%) over time.
Results : 56 subjects had sCTD-ILD, 191 had dCTD-ILD (99 scleroderma, 42 rheumatoid arthritis, 26 myositis, 14 Sjšgren’s syndrome) and 62 had
IPF. Compared to IPF (67.9±8.5 years),
those with sCTD-ILD (57.5±10.9 years) or dCTD-ILD (54.6±10.3 years) were younger (p<0.001), more likely to be female
(16% vs. 67% vs. 71%, respectively), and less likely to be nonsmokers (30.6% vs. 67.9%
vs. 52.4%, respectively). Most subjects
with sCTD-ILD or dCTD-ILD had a nonspecific interstitial pneumonia pattern on chest HRCT
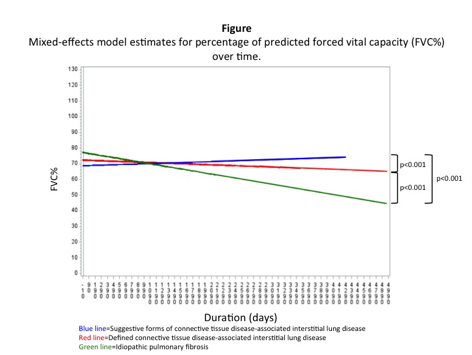
scan (69.2% and 58.1%, respectively). Baseline FVC% was similar between
groups (sCTD-ILD: 68.4±16.0% vs. dCTD-ILD:
71.7±15.4% vs. IPF: 73.1±15.9%; p=0.25). Modeled FVC%
values are displayed in the Figure.
During similar follow-up periods (1561±626 vs.
1733±576 vs. 1692±589 days, respectively;
p=0.16), there were no deaths in the sCTD-ILD group, 37
(19.4%) in CTD-ILD group and 35 (56.5%) in the IPF group (log-rank p<0.001 for each pairwise comparison).
Conclusion: In this retrospective study, we observed
that patients with sCTD-ILD or dCTD-ILD had better FVC% trajectories and survival. The natural history of sCTD-ILD resembled that of dCTD-ILD more than IPF underscoring the
importance of differentiating this
patient population from idiopathic
interstitial pneumonia for purposes of treatment and prognostication.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chartrand S, Peykova L, Swigris JJ, Fischer A. A Comparison of the Clinical Features and Natural History of Autoimmune Interstitial Lung Disease Vs. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-the-clinical-features-and-natural-history-of-autoimmune-interstitial-lung-disease-vs-idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/a-comparison-of-the-clinical-features-and-natural-history-of-autoimmune-interstitial-lung-disease-vs-idiopathic-pulmonary-fibrosis/