Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Conclusion: Year 2 data from this head-to-head study show that the improvements in PROs, including productivity and independence, with both SC abatacept plus MTX and adalimumab plus MTX observed at Year 1 are maintained up to Year 2, with similar onset and durability of response. Reference: 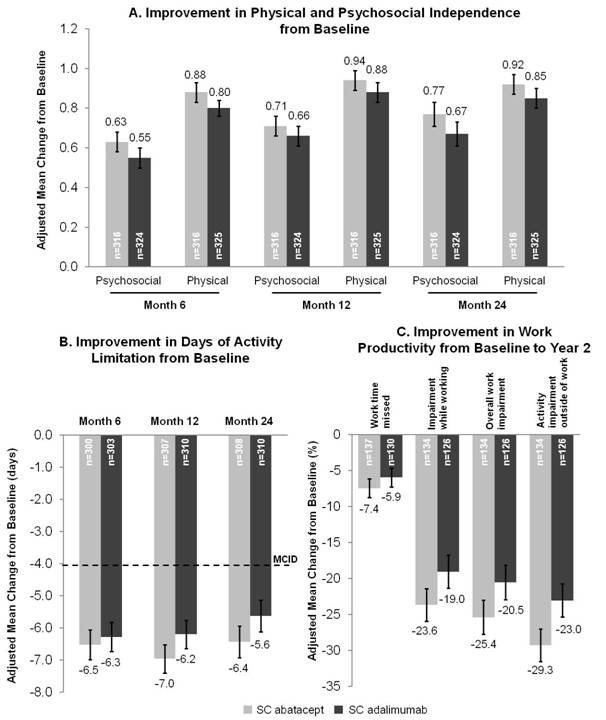
Disclosure:
R. Fleischmann,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbvie,
5,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbvie,
2;
M. Weinblatt,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
2,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche/Genentech, UCB, Janseen,
5;
M. Schiff,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Abbvie,
5;
D. Khanna,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
5;
M. Maldonado,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
3,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
1;
A. Nadkarni,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
1,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
3;
D. Furst,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Actelion, Amgen, Gilead, GSK, NIH, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, UCB,
2,
Bristol-Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Actelion, Amgen, Janssen, Gilead, GSK, NIH, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, UCB,
5,
AbbVie, Actelion, UCB,
8.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/2-year-results-from-the-ample-abatacept-versus-adalimumab-comparison-in-biologic-naive-ra-patients-with-background-methotrexate-trial-changes-in-patient-reported-outcomes-in-response-to-subcutaneou/
