Background/Purpose: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is characterized by thrombosis and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). Tissue factor (TF), the major initiator of the extrinsic coagulation system, is induced on monocytes by aPL in vitro. Phosphatidylserine-dependent antiprothrombin antibody (aPS/PT) recognized the phophatidylserin/prothrombin (PS/PT) complex, and is highly associated with APS. We have previously reported that 231D, a mouse monoclonal aPS/PT, induced TF expression on monocytes. However, the cell surface receptor for the binding of PS/PT complex leading to the activation of cell signaling pathways and TF expression is unknown.To investigate the membrane protein involved in the binding of Prothrombin (PT) and aPS/PT to cell surface and the induction of TF expression on monocytes.
Methods: 1) Unknown PT binding membrane protein on monocyte was screened by a proteomics technique using immunoaffinity chromatography and mass spectrometric analysis. FLAG-tagged human PT (FLAG-PT) was constructed and the expression vector encoding FLAG-PT was transfected into HEK293T cells. The expression of full length FLAG-PT in the culture supernatant was evaluated by immunoblotting. RAW 264.7 cells with FLAG-PT were incubated and applied for affinity chromatography with anti-FLAG antibody-conjugated Sepharose beads. The purified fraction was subjected to SDS-PAGE and detected with Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. Immunopurified proteins were analyzed by an online-nano LC-MS/MS. Obtained MS/MS data were searched against nrNCBI database MASCOT algorithm. 2) The binding between PT and Ribophorin II (RPN2) was analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with purified His-tagged human RPN2 (His-RPN2). 3) RPN2 expression on cell surface of CD14 positive cells and RAW 264.7 cells was analyzed by flowcytometoric analysis. 4) To elucidate the role of RPN2 in TF mRNA expression, RAW 264.7 cells treated with RPN2 small interfering RNA (siRNA) expression and TF mRNA was determined by real-time PCR.
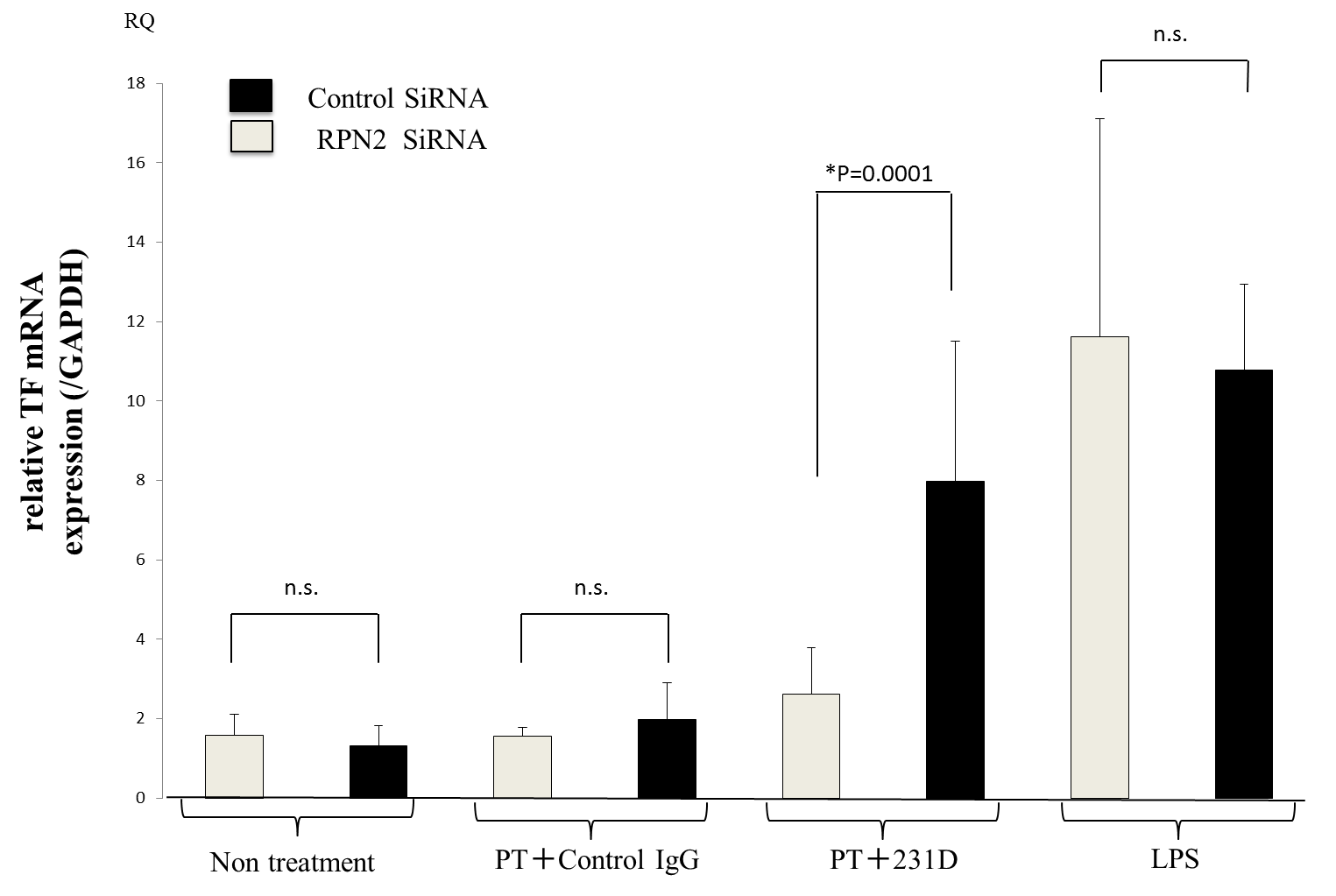
Results: 1) Amoung many proteins confirmed in the spectrometry, RPN2 a part of an N-oligosaccharyl transferase complex was identified as the candidate molecule to be the membrane protein involved in the PT binding to cell surface. 2) The binding between PT and His-RPN2 was confirmed by ELISA. 3) Flowcytometoric analysis showed the expression of RPN2 on monocyte cell surface. 4) Treated cells with RPN2 siRNA showed significantly reduction of the TF expression mediated by PT and 231D (Fig).
Conclusion: RPN2 was detected as a major PT binding molecule by proteomics analysis. RPN2 may be involved in the pathophysiology of thrombosis in patients with APS.
Fig. RAW264.7 cells transfected with RPN2-siRNA were incubated with monoclonal aPS/PT (231D). TF mRNA was quantitated by Real Time PCR.
Disclosure:
Y. Fujieda,
None;
O. Amengual,
None;
Y. Kanetsuka,
None;
T. Odani,
None;
K. Otomo,
None;
K. Oku,
None;
T. Bohgaki,
None;
T. Horita,
None;
S. Yasuda,
None;
K. Kuroki,
None;
K. Maenaka,
None;
M. Matsumoto,
None;
S. Hatakeyama,
None;
T. Atsumi,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ribophorin-ii-is-involved-in-the-tissue-factor-expression-mediated-by-phosphatidylserine-dependent-antiprothrombin-antibody-on-monocytes/