Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Depletion of CD4-effector memory T cells and clonally expanded IgG4 memory B cells may explain the therapeutic efficacy of rituximab in IgG4-related disease: Studies using flow cytometry and single-cell sequencing
Background/Purpose:
The clinical effectiveness of rituximab-mediated B cell depletion in chronic inflammatory disorders such as multiple sclerosis and Type I diabetes, which are not believed to be autoantibody-driven conditions, has not been explained satisfactorily. A mechanistic explanation is also lacking for the efficacy of rituximab in IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by fibrosis that might be T cell mediated. Although CD4+ T cells contribute to the activation of B cells during T-B collaboration, activated B cells are required in turn both for the generation of T follicular helper cells and for the induction and maintenance of CD4+ memory T cells. We hypothesize that in IgG4-RD, some as yet unidentified antigens induce T follicular helper cell-mediated B cell activation and the subsequent generation of a Th2 type of CD4+ effector and memory T cell response. The fibrosis that characterizes this disorder may reflect the generation of a B cell-dependent pathogenic Th2 cell response to these uncharacterized antigens.
Methods:
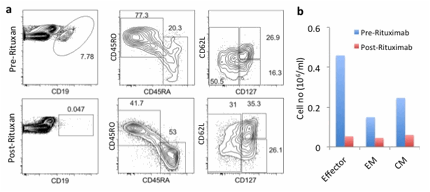
We performed detailed flow cytometry studies on B and T cell populations before and after treatment with rituximab in four patients, accompanied by single cell cloning studies of IgG4 memory B cells.
Results:
We have detected an expansion of circulating IgG4 memory B cells and of CD4+ effector memory T cells in subjects with active IgG4-RD (a, b). Rituximab therapy not only mediates the depletion of all circulating B cells in IgG4-RD, including the expanded IgG4 memory B cells, but also of the CD4+ effector memory T cell population. Single cell cloning of IgG4 memory B cells from subjects with active disease followed by sequencing of matched Ig heavy and light chains reveals the possible expansion of a few IgG4 B cells with common VH and VL usage.
Conclusion:
These results support the notion that B cell depletion with rituximab mediates loss of the disease-promoting effector memory CD4+ T cells in IgG4-RD. These studies offer the possibility that the inciting antigen(s) in IgG4-RD may be identified in due course as a result of the identification of clonally-expanded B cells.
Disclosure:
H. Mattoo,
None;
A. Khosroshahi,
None;
V. Mahajan,
None;
M. Carruthers,
None;
J. Stone,
None;
S. Pillai,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/depletion-of-cd4-effector-memory-t-cells-and-clonally-expanded-igg4-memory-b-cells-may-explain-the-therapeutic-efficacy-of-rituximab-in-igg4-related-disease-studies-using-flow-cytometry-and-single-ce/