Session Information
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects: Novel Biomarkers and Other Measurements of Disease Activity
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose : In the CAnadian Methotrexate and Etanercept Outcome Study (CAMEO) continued therapy with etanercept (ETN) and methotrexate (MTX) led to better outcomes at month 24 than the withdrawal of MTX in MTX inadequate responders (MTX-IR) with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Patients had to tolerate MTX at a dose of ≥ 15 mg/wk or 10 mg/wk if intolerant. Similar disease activity was observed in both treatment arms at 12 months in the subgroup of patients who achieved low disease activity (disease activity score [DAS28] < 3.2) at 6 months of combination therapy, whereas if not in low DAS28 combination therapy was more effective. Recent evidence suggests that polymorphisms in genes related to metabolism and cellular transport pathways of MTX and to the biological targets of ETN may help predict clinical response in RA. This pre-defined CAMEO sub-study explored pharmacogenetic markers as novel predictors of treatment outcome in patients failing MTX prior to starting ETN.
Methods: All patients were treated with ETN+MTX for 6 months, followed by randomization to either ETN+MTX or ETN alone for an additional 18 months. After consent, DNA extraction and genotyping was performed using TaqMan Genotyping Assays. Fifteen genetic variants in 12 genes related to MTX and 4 variants in 3 genes related to TNF were analyzed. The contribution of genetic variants to therapeutic response (improvement in DAS28 [ΔDAS28] from baseline to months 6, 12, 18 and 24; total Sharp score [TSS] at 12 and 24 months) was assessed using mixed models with adjustments for age and sex.
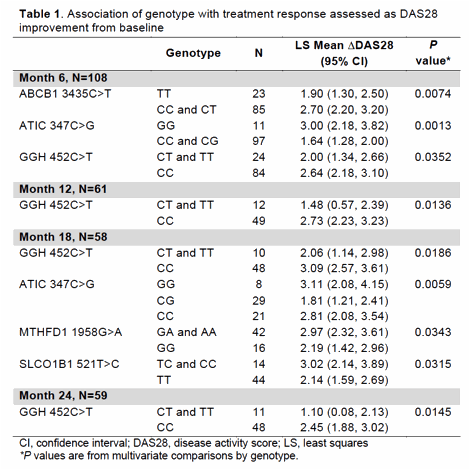
Results: Assessments were performed in 111 patients (mean age 55.2 years, 73% female, 98% Caucasians). Univariate analyses did not suggest an association of genetic variants related to response to ETN (p > 0.25). Patients receiving ETN+MTX after randomization (N=64) were included for multivariate analyses at 12, 18 and 24 months. Patients expressing the ATIC 347GG, GGH 452CC, MTHFD1 1958A, ABCB1 3435C, or SLCO1B1 521C alleles were more likely to have an improvement with combined therapy as reflected by a significantly higher ΔDAS28 from baseline to follow-up (Table 1). At 12 and 24 months, patients having the ATIC 347GG and ABCB1 3435CC alleles showed moderately higher TSS (Table 2). Radiographic assessments also indicated that ABCC2 1249A carriers appear to be less responsive compared with GG carriers.
Conclusion: Genetic polymorphisms in drug transporters and metabolic enzymes related to MTX pathways were associated with clinical response after combined treatment in MTX-IR patients. No association between response to ETN and TNF gene variants was observed.
Disclosure:
U. I. Schwarz,
None;
J. E. Pope,
Abbott/AbbVie, Amgen, Actelion, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Glaxo-Smith Kline, Hoffmann-LaRoche, Janssen, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, UCB,
2,
Abbott/AbbVie, Amgen, Actelion, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Glaxo-Smith Kline, Hoffmann-LaRoche, Janssen, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, UCB,
5;
E. Keystone,
Abbott/AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Centocor, F. Hoffmann-LaRoche, Genzyme, Merck, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, UCB, Genentech, Janssen,
2,
Abbott/AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, F. Hoffmann-LaRoche, Merck, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, UCB, Janssen,
5;
B. Haraoui,
Abbott/AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Pfizer, Roche, UCB,
2,
Abbott/AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, UCB,
5;
C. Thorne,
Amgen, Pfizer, Abbott/AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Centocor, Merck, Roche, UCB,
2,
Amgen, Pfizer, Abbott/AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Centocor, Merck, Roche, UCB,
5;
Y. H. Choi,
None;
M. Poulin-Costello,
Amgen Inc.,
1,
Amgen Inc.,
3;
N. Bayan,
Amgen Canada Inc.,
1,
Amgen Canada Inc.,
3;
R. B. Kim,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-pharmacogenetic-markers-with-treatment-response-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/