Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The Centers for Disease Control and American College of Rheumatology guidelines recommend pneumococcal vaccination for all immunosuppressed patients, specifically those taking disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) or biologic agents. Despite these guidelines, the rates of pneumococcal vaccination are very low in RA patients. The aim of this study was to improve the rate of administration and documentation of pneumococcal vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients taking DMARDs and biologic agents at rheumatology outpatient clinics.
Methods: An automated electronic medical record (EMR)-based best practice alert (BPA) intervention was designed to be used by clinical staff and to provide user-friendly interface to remind, document and order pneumococcal vaccine for eligible patients. EMR determined the eligibility of the patients at the time of rooming by medical assistant (MA) or nurse, and the BPA appeared for eligible patients. MA confirmed eligibility, documented prior vaccination or patient refusals and ordered the vaccine using the BPA if the patient agreed. Physicians reviewed and verified orders, and the patient either received the vaccination or a written prescription based on clinic/patient preferences. If the patient was unsure, the BPA was passed on to the physician for further discussion. The process continues at each visit until patient is vaccinated or documentation occurs. The study was designed as a pre- and post-intervention comparison. Clinical staff and physicians were educated on the guidelines and intervention. Patient education about vaccination was performed during clinic visit, and educational material was also provided. Eligibility for pneumococcal vaccine was all RA patients on immunosuppressant medications (DMARDs or biologics) who have not completed pneumococcal vaccination. Vaccination and documentation rates for the pre-intervention period (July 2012-June 2013) were compared with post-intervention period rates (2/17/2014 – 5/17/2014) using chi square test.
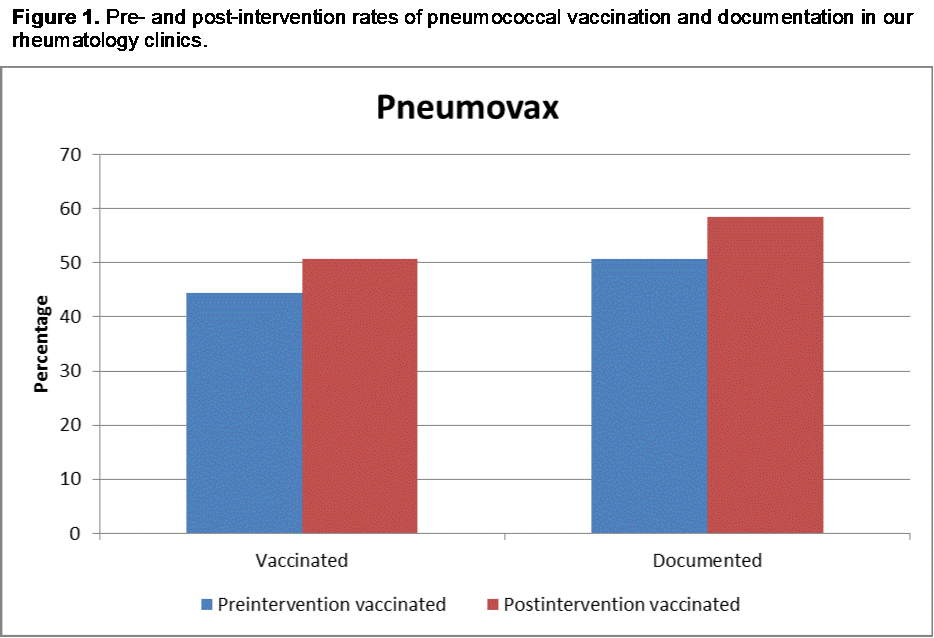
Results: 3285 and 1949 patients were analyzed for baseline and intervention data, respectively. Demographic characteristics were similar in both groups. Vaccination and documentation rates increased significantly from 44.4% and 51.4% in pre-intervention phase to 50.8 % and 58.4%, respectively within 3 months of intervention phase (p<0.0001). Approximately 3% of patients refused vaccination, and for 4% of patients, physicians noted deferral during both study phases.
Conclusion: Pneumonia vaccination administration rates in immunosuppressed patients with RA are low. Implementation of an automated EMR and clinical staff-based BPA intervention significantly improved vaccination rates without the need for considerable physician input. The project is ongoing and will become standard of practice in our rheumatology clinics.
Disclosure:
H. Sheth,
None;
L. W. Moreland,
Pfizer Inc,
9;
H. J. Peterson,
None;
R. Aggarwal,
Questcor,
2,
Pfizer Inc,
2,
NIEHS-NIH,
2,
Questcor,
5,
aTyr Pharma,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/electronic-medical-record-based-best-practice-alert-used-by-clinical-staff-improved-pneumococcal-vaccination-and-documentation-among-immunosuppressed-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/