Session Information
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Clinical Aspects (ACR): Comorbidities, Treatment Outcomes and Mortality
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Fibromyalgia (FM) occurs commonly in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its effect on treatment response is unknown. In this study we aimed to evaluate if patients with RA and concomitant FM have an impaired response to treatment measured by traditional activity scores.
Methods: Patients from the ESPOIR cohort were analyzed. This prospective cohort included 813 patients with early arthritis not initially receiving disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). We defined FM at baseline using Pollard et al. (Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010;49:924–928) validated criteria of tender joint count at least 7 higher than swollen joint count (72% sensitivity and 98% using ACR 1990 FM criteria as gold standard). Among the 697 patients who met RA classification (either ACR 1987 or ACR/EULAR 2010) criteria, we studied two groups, one with and the other without FM. The following endpoints were compared at 6, 12 and 18 months using a mixed linear regression model: 28-joint Disease Activity Score (DAS28), Simple Disease Activity Index (SDAI), Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) and the Health Assessment Questionnaire. In addition attainment of low disease activity (LDA) (DAS28<3.2) and remission (DAS28<2.6, SDAI<3.3, CDAI<2.8) at these timepoints were analyzed using a log binomial regression.
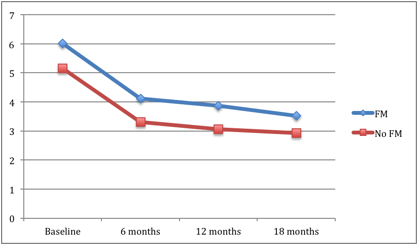
Results: At baseline, patients with FM (n=120) had a higher DAS28, SDAI, CDAI and HAQ than patients with isolated RA (n=548). While they started out higher, DAS28 and other disease activity scores improved to a similar extent as in the isolated RA group. However, scores remained consistently higher among FM patients. (see figure) Achievement of LDA and of remission was significantly less likely in subjects with FM and few would have met treat to target goals.
Conclusion: Patients with FM and RA have a similar response to treatment according to a decrease in indexes of disease activity but may miss the target of remission or low disease activity.
Table 1. Comparison of rheumatoid arthritis activity scores and radiologic scores over follow up according to the presence of fibromyalgia
|
|
FM
|
No FM
|
Difference in scores
|
P value*
|
|
DAS 28 |
3.50 |
3.05 |
0.45 |
<0.0001 |
|
SDAI |
16.09 |
11.54 |
4.55 |
<0.0001 |
|
CDAI |
14.98 |
10.75 |
4.23 |
<0.0001 |
|
HAQ |
0.63 |
0.45 |
0.17 |
0.0002 |
|
SJC |
2.32 |
2.18 |
0.14 |
0.5476 |
|
TJC |
5.64 |
3.27 |
2.37 |
0.0001 |
|
PtGH VAS |
3.82 |
3.01 |
0.81 |
<0.0001 |
|
PhGH VAS |
2.88 |
2.38 |
0.51 |
0.0044 |
|
CRP (mg/l) |
0.75 |
0.84 |
0.09 |
0.4147 |
|
ESR (mm/h) |
13.99 |
15.05 |
1.06 |
0.3602 |
|
SHARP |
7.33 |
7.68 |
0.34 |
0.3125 |
*P values denote the overall significance of a linear regression adjusting for baseline score, gender, age and smoking status. HAQ: Health Assessment Questionnaire; SJC: swollen joint counts, TJC: tender joint counts PtGH: patient global health; PhGH: physician global health; VAS: visual analog scale; RF: rheumatoid factor; CCP: Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies; ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP: C-reactive protein
Figure 1. DAS28 score at different time points grouped by fibromyalgia presence
Disclosure:
J. Durán Santa Cruz,
None;
B. Combe,
None;
J. Niu,
None;
N. Rincheval,
None;
C. Gaujoux-Viala,
None;
D. T. Felson,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fibromyalgia-and-its-effect-on-treatment-response-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/