Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: RA patients experience stiffness which impacts their daily lives. Although this patient reported symptom was dropped from the RA classification criteria there is growing interest in understanding more about stiffness in RA.(1) Stiffness is described in temporal terms (morning, evening) and patients report difficulty distinguishing stiffness from pain and swelling.(1) The CAPRA-2 (C2) study previously demonstrated significant relative reductions in patient reported morning stiffness duration and severity with 5 mg daily DR prednisone as compared to placebo in RA patients receiving non-biologic DMARDs.(2) We report the 12 week relative change of reoccurrence of joint stiffness and pain during the day collected by patient diary to further characterize these symptoms. Previously a strong correlation between morning stiffness severity and morning pain was reported for C2.(3)
Methods: RA patients with moderate disease on non-biologic DMARDs previously randomized (2:1) to receive DR-prednisone or placebo were evaluated at baseline (BL), 2, 6, and 12 weeks for relative changes in patient reported outcomes listed in Table 1. Data on relative change from baseline to 12 weeks were analyzed for the modified-intent-to-treat population under observed-case and last observation carried forward (LOCF) conditions. Significance (least square means) and 95% confidence intervals were established based on the mean relative percent change from BL. Point biserial correlation of daily reoccurrence of joint stiffness (Y or N) and pain (100mm VAS) for all patients was performed.
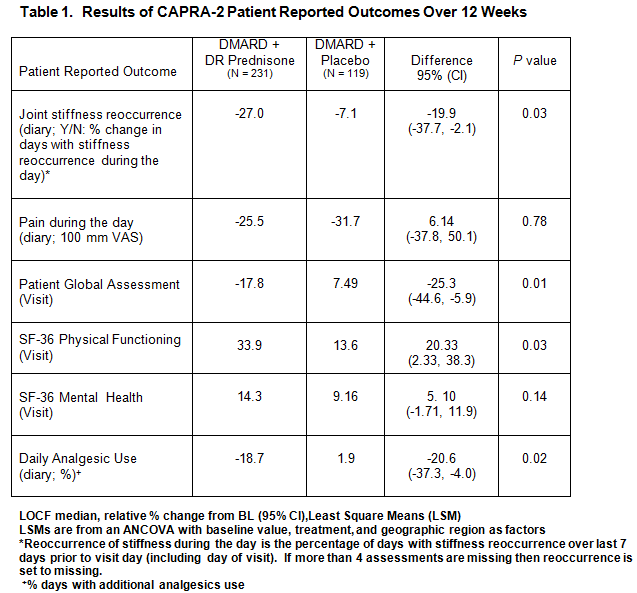
Results: 350 moderate RA patients mean age 57, 58% female, mean duration of RA 8 years, 94% naïve to prednisone. 231 received 5 mg DR prednisone and 119 received placebo, all on stable DMARDs. There was a statistically significant reduction in reoccurrence of joint stiffness during the day over the 12 weeks; pain decreased for all patients with no difference in treatment groups (Table 1). Patient global assessment, SF-36 physical function and analgesic use showed significance between treatment groups. There was moderate correlation of reoccurrence of joint stiffness and pain (r = 0.47).
Conclusion: Adding DR prednisone to the treatment of RA patients on non-biologic DMARDs produced statistically significant reduction in reoccurrence of joint stiffness during the day, improvements in patient global assessment and SF-36 physical function and a decrease in analgesic use over 12 weeks. Correlation was shown regardless of treatment between reoccurrence of joint stiffness and pain during the day further supporting the strong patient relationship of symptoms of stiffness and pain reported previously.(3)
References:
(1) Orbai, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73(2):S261-262.
(2) Buttgereit, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2013;72:204–210.
(3) Buttgereit, et al. Arthritis Rheum2012;64(10):S544-545.
Disclosure:
R. Alten,
Horizon Pharma, Inc,
5;
A. Y. Grahn,
Horizon Pharma, Inc,
3;
P. Rice,
Horizon Pharma, Inc,
5;
R. Holt,
Horizon Pharma, Inc,
5;
F. Buttgereit,
Horizon Pharma, Inc,
5.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-of-patient-reported-symptoms-of-stiffness-and-pain-during-the-day-from-adding-low-dose-delayed-release-dr-prednisone-to-stable-dmard-therapy-over-12-weeks-in-patients-with-moderate-rheumato/